The effect of virtual avatar experience on body image discrepancy, body satisfaction and weight regulation intention
Vol.12,No.1(2018)
This experimental study aimed to investigate the effect of having a virtual avatar experience on health outcomes in the context of body image and weight regulation. Ninety-three U.S. non-clinical participants (51 men and 42 women) were recruited, who were 18 years and older and had no history of chronic health problems or mental illnesses. Each experiment consisted of the three data collection phases, including the pre-experiment survey, an experience session of a virtual self-avatar, and the post-experiment survey. For the development of the virtual avatar protocol, this study employed 3D body scanning to create a participant’s virtual body model based on accurate anthropometric data, to simulate a virtual avatar closely matched with the participant’s actual physique. Overall, the data indicated an increase in perceived body image discrepancy and a decrease in body satisfaction after participating in a virtual avatar session, and those who showed higher body dissatisfaction exhibited a stronger intention regulated for weight control. Specifically in gender, the statistical results were generally intensified in the female group, but the male group showed a stronger intention to be involved in exercising after virtual avatar experience. The insights gained from this study suggested future directions for research and program development, and urged that practical applications of the virtual avatar approach must be implemented with caution when it uses clinical samples, because its risk-benefit assessment has not been sufficiently investigated yet.
Virtual avatar; 3D body scanning; body image; weight regulation intention
Juyeon Park
Department of Design and Merchandising, Human Body Dimensioning Laboratory, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, USA & Department of Environmental and Occupational Health, Colorado School of Public health, Fort Collins, USA
Juyeon Park is Associate Professor of Design and Merchandising at Colorado State University and Associate Professor of Environmental and Occupational Health at Colorado School of Public Health. She leads the Human Body Dimensioning Laboratory at CSU. Her research interests include psychosocial and anthropometric perspectives of the human body and development of novel interventions for positive health outcomes using emerging technologies.
Adams, G., Turner, H., & Bucks, R. (2005). The experience of body dissatisfaction in men. Body Image, 2, 271-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2005.05.004
Anschutz, D. J., Engels, R. C., & Becker, E. S. (2008). The bold and the beautiful. Influence of body size of televised media models on body dissatisfaction and actual food intake. Appetite, 51, 530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2008.04.004
Barnett, M. D., Moore, J. M., & Harp, A. R. (2017). Who we are and how we feel: Self-discrepancy theory and specific affective states. Personality and Individual Differences, 111, 232-237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.02.024
Bessenoff, G. R., & Snow, D. (2006). Absorbing society’s influence: Body image self-discrepancy and internalized shame. Sex Role, 54, 727-731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-006-9038-7
Bish, C. L., Blanck, H. M., Serdula, M. K., Marcus, M., Kohl, H. W., & Khan, L. K. (2005). Diet and physical activity behaviors among Americans trying to lose weight: 2000 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Obesity Research, 13, 596–607. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2005.64
Cafri, G., & Thompson, J. K. (2004). Measuring male body image: A review of the current methodology. Psychology of Men and Masculinity, 5, 18-29. https://doi.org/10.1037/1524-9220.5.1.18
Cash, T. F. (2004). Body image: Past, present, and future. Body Image, 1, 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1740-1445(03)00011-1
Cash, T. F., & Deagle, E. A. (1997). The nature and extent of body-image disturbances in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: a meta-analysis. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 22, 107-125. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-108X(199709)22:2<107::AID-EAT1>3.0.CO;2-J
Cash, T. F., & Szymanski, M. L. (1995). The development and validation of the body-image ideals questionnaire. Journal of Personality Assessment, 64, 466-477. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa6403_6
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2017). About Adult BMI. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/index.html
Chang, V. W., & Christakis, N. A. (2003). Self-perception of weight appropriateness in the United States. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 24, 332–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-3797(03)00020-5
Cornelissen, K. K., McCarty, K., Cornelissen, P., & Tovée, M. J. (2017). Body size estimation in women with anorexia nervosa and healthy controls using 3D avatars. Scientific Report, 7, 15773. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15339-z
Delinsky, S. S., & Wilson, G. T. (2006). Mirror exposure for the treatment of body image disturbance. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 39, 108-116. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20207
Dittmar, H. (2009). How do “body perfect” ideals in the media have a negative impact on body image and behaviors?: Factors and processes related to self and identity. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 28, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2009.28.1.1
Fairburn, C. G., Cooper, Z., & Shafran, R. (2003). Cognitive behaviour therapy for eating disorders: A ‘‘transdiagnostic’’ theory and treatment. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 41, 509–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(02)00088-8
Fallon, A. E. (1990). Culture in the mirror: Sociocultural determinants of body image. In T. F. Cash & T. Pruzinsky (Eds.), Body images: Development, deviance, and change (pp. 80-109). New York, NY: Guilford.
Fallon, A. E., & Rozin, P. (1985). Sex differences in perceptions of desirable body shape. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 94, 1045-1056. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.94.1.102
Farrell, C., Lee, M., & Shafran, R. (2005). Assessment of body size estimation: A review. European Eating Disorders Review, 13, 75-88. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.622
Furnham, A., Badmin, N., & Sneade, I. (2002). Body image dissatisfaction: Gender differences in eating attitudes, self-esteem, and reasons for exercise. Journal of Psychology, 136, 581-596. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980209604820
Gardner, R. M., & Brown, D. L. (2014). Body size estimation in anorexia nervosa: A brief review of findings from 2003 through 2013. Psychiatry Research, 219, 407-410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2014.06.029
Garner, D. M., Olmstead, M. P., & Polivy, J. (1983). Development and validation of a multidimensional eating disorder inventory for anorexia nervosa and bulimia. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 2, 15–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-108X(198321)2:2<15::AID-EAT2260020203>3.0.CO;2-6
Higgins, E. T. (1987). Self-discrepancy: A theory relating self and affect. Psychological Review, 94, 319-340. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.94.3.319
Higgins, E. T., Bond, R. N., Klein, R., & Strauman, T. (1986). Self-discrepancies and emotional vulnerability: How magnitude, accessibility, and type of discrepancy influence affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 5-15. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.51.1.5
Higgins, E. T., Klein, R., & Strauman, T. (1985). Self-concept discrepancy theory: A psychological model for distinguishing among different aspects of depression and anxiety. Social Cognition, 3, 51-76. https://doi.org/10.1521/soco.1985.3.1.51
Jarry, J. L., & Kossert, A. L. (2007). Self-esteem threat combined with exposure to thin media images leads to body image compensatory self-enhancement. Body Image, 4, 39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2006.12.003
Kuo, H., Lee, C., & Chiou, W. (2016). The power of the virtual ideal self in weight control: Weight-reduced avatars can enhance the tendency to delay gratification and regulate dietary practices. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 19, 80-85. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2015.0203
Kwan, S., & Graves, J. (2013). Framing fat: Competing constructions in contemporary culture. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
Lynch, M. F., La Guardia, J. G., & Ryan, R. M. (2009). On being yourself in different cultures: Ideal and actual self-concept, autonomy support, and well-being in China, Russia, and the United States. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 4, 290-304. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760902933765
Manzoni, G. M., Cesa, G. L., Bacchetta, M., Castelnuovo, G., Conti, S., Gaggioli, A., . . . Riva, G. (2016). Virtual reality–enhanced cognitive–behavioral therapy for morbid obesity: A randomized controlled study with 1 year follow-up. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, & Social Networking, 19, 134-140. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2015.0208
McGuinness, S., & Taylor, J. E. (2016). Understanding body image dissatisfaction and disordered eating in midlife adults. New Zealand Journal of Psychology, 45(1), 4-12.
Mölbert, S. C., Thaler, A, Mohler, B.J., Streuber, S., Romero, J., Black, M. J., . . . Giel, K. E. (2018). Assessing body image in anorexia nervosa using biometric self-avatars in virtual reality: Attitudinal components rather than visual body size estimation are distorted. Psychological Medicine, 48, 642-653. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291717002008
Olivardia, R., Pope, G. P., Borowiecki, J. J., & Cohane, G. H. (2004). Biceps and body image: The relationship between muscularity and self-esteem, depression, and eating disorder symptoms. Psychology of Men and Maculinity, 5, 112-120. https://doi.org/10.1037/1524-9220.5.2.112
Park, J. (2016). Self-determination and motivation for bariatric surgery: A qualitative study. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 21, 800-805. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2015.1131996
Park, J. (2018). Emotional reactions to the 3D virtual body and future willingness: The effects of self-esteem and social physique anxiety. Virtual Reality, 22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-017-0314-3
Richins, M. L. (1991). Social comparison and the idealized images of advertising. Journal of Consumer Research, 18, 71-83. https://doi.org/10.1086/209242
Riva, G. (2002). Virtual reality for health care: The status of research. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 5, 219-225. https://doi.org/10.1089/109493102760147213
Riva G. (2005). Virtual reality in psychotherapy: Review. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 8, 220-230. https://doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2005.8.220
Rothbaum, B. O., Price, M., Jovanovic, T., Norrholm, S. D., Gerardi, M., Dunlop, B., . . . Ressler, K. J. (2014). A randomized, double-blind evaluation of d-cycloserine or alprazolam combined with virtual reality exposure therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 171, 640–648. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.13121625
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2002). Overview of self-determination theory: An organismic dialectical perspective. In E. L. Deci & R. M. Ryan (Eds.), Handbook of self-determination research (pp. 3-33). Rochester, NY: University of Rochester Press.
Ryan, R. M., Williams, G. C., Patrick, H., & Deci, E. L. (2009). Self-determination theory and physical activity: The dynamics of motivation in development and wellness. Hellenic Journal of Psychology, 6, 107-124.
Schwartz, M. B., & Brownell, K. D. (2004). Obesity and body image. Body Image, 1, 43-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1740-1445(03)00007-X
Serino, S., Pedroli, E., Keizer, A., Triberti, S., Dakanalis, A., Pallavicini, F., . . . Riva, G. (2016). Virtual reality body swapping: A tool for modifying the allocentric memory of the body. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 16, 127-133. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2015.0229
Shafran, R., Lee, M., Payne, E., & Fairburn, C. G. (2007). An experimental analysis of body checking. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45, 113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2006.01.015
Shokouhi-Moqhaddam, S., Khezri-Moghadam, N., Javanmard, Z., Sarmadi-Ansar, H., Aminaee, M., Shokouhi-Moqhaddam, M., & Zivari-Rahman, M. (2013). A Study of the Correlation between Computer Games and Adolescent Behavioral Problems. Addiction & Health, 5, 43-50.
Slade, P. D. (1994). What is body image? Behavior Research and Therapy, 32, 497-502. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(94)90136-8
Slevic, J., & Tiggemann, M. (2011). Media exposure, body dissatisfaction, and disordered eating in middle-aged women. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 35, 617-627. https://doi.org/10.1177/0361684311420249
Stice, E., & Shaw, H. (1994). Adverse effects of the media portrayed thin-ideal on women and linkages to bulimic symptomatology. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 13, 288-308. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.1994.13.3.288
Strauman, T. J., Vookles, J., Berenstein, V., Chaiken, S., & Higgins, E. T. (1991). Self-discrepancies and vulnerability to body dissatisfaction and disordered eating. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61, 946-956.
Stunkard, A. J., Sorensen, T. I., & Schulsinger, F. (1983). Use of the Danish adoption register for the study of obesity and thinness. New York, NY: Raven Press.
Vartanian, L. R. (2012). Self-discrepancy theory and body image. In T. Cash (Ed.), Encyclopedia of body image and human appearance (Vol. 2) (pp. 711-717). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Veale, D., Kinderman, P., Riley, S., & Lambrou, C. (2003). Self-discrepancy in body dysmorphic disorder. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 42, 157-169. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466503321903571
Williamson, D. A., Gleaves, D. H., Watkins, P. C., & Schlundt, D. G. (1993). Validation of self-ideal body size discrepancy as a measure of body dissatisfaction. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 15, 57-68. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964324
Williamson, D. A., White, M. A., York-Crowe, E., & Stewart, T. M. (2004). Cognitive-behavioural theories of eating disorders. Behavior Modification, 28, 711–738. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445503259853
Zamani, E., Kheradmand, A., Cheshmi, M., Abedi, A., & Hedayati, N. (2010). Comparing the social skills of students addicted to computer games with normal students. Addiction & Health, 2, 59–65
Editorial Record:
First submission received:
May 13, 2017
Revisions received:
November 16, 2017
May 5, 2018
July 3, 2018
Accepted for publication:
July 4, 2018
Introduction
Body image is a mental image that we hold of our body (Fallon, 1990). Cash (2004) defined it as “the multifaceted psychological experience of embodiment, especially but not exclusively one’s physical appearance” (p. 1). That is, body image involves not only one’s physical body size and shape, but also encompasses one’s body-related self-perceptions and self-attitudes such as thoughts, beliefs, feelings, and behaviors. Here, it is worth noting that the actual self has a basis in one’s self-perceptions on their body, not the individual’s objective standing on a given attribute. Therefore, it is particularly important to be mindful that people often misperceive the shape and size of their own body (Vartanian, 2012). For example, women and men both tend to overestimate their weight and body size (Fallon & Rozin, 1985; Olivardia, Pope, Borowiecki, & Cohane, 2004). Specifically, men’s body image concerns stem from a perceived lack of muscles, while women are concerned about perceived excess weight (Cafri & Thompson, 2004; Olivardia et al., 2004). Research have shown that when comparing to idealized images of models in media, women tend to experience a higher level of body dissatisfaction (Richins, 1991), resulting in a “negative affective state” expressed with negative emotions and an increase in body image anxiety (Anschutz, Engels, & Becker, 2008; Stice & Shaw, 1994) Likewise, researchers (Jarry & Kossert, 2007) found that being exposed to the thin ideal female body that is portrayed in media engendered healthy women with lower self-esteem. Furthermore, modern society tends to stigmatize people who do not meet the thin ideal, making them internalize the message (Schwartz & Brownell, 2004), and it often forces them to lose weight as a means to redefine their negative social and personal body image to meet the hegemonic standard that is almost unattainable for most people in contemporary Western culture (Kwan & Graves, 2013). Hence, realizing a gap between their self-image and their ideal body likely leads people to experience body image discrepancy, its negative affective state on mental health, and behavioral intention for weight regulation.
Researchers (e.g., Riva, 2002, 2005; Rothbaum et al., 2014) suggested virtual technology as a useful tool in helping patients gain awareness of their need and take action to improve their health condition with a greater sense of personal efficacy, in a safe and controllable virtual environment, which otherwise is challenging to practice in real life. Particularly in the context of body image, Kuo, Lee, and Chiou’s study (2016) experimented with the effect of viewing a weight-reduced avatar on the participant’s impulsive eating behavior, and demonstrated the decrease in temporal discounting and the increase in healthy dietary choices after viewing the ideal future body. Another study (Serino et al., 2016) investigated the feasibility of virtual body swapping as an effective tool for modifying the enduring memory of one’s body image. The study, based on 21 female participants’ experiences of virtual body swapping, revealed evidence that viewing a virtual body with a skinny belly could update one’s stored representation of the body. Additionally, Manzoni and his colleagues (2016) studied the long-term efficacy of a virtually enhanced cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) with 163 female morbidly obese patients, and they found the virtual CBT, when it was combined with a standard behavioral inpatient program, was significantly more effective in improving and maintaining the patients’ weight maintenance at a 1-year follow up, than when only the inpatient program was implemented. However, still unknown is the mechanism of how psychological states related to body image and body satisfaction interplay with behavioral outcomes.
While the aforementioned studies employed virtual avatars created using computer-generated imagery (CGI), recent efforts have made use of three-dimensional (3D) body scanning in developing virtual avatars based on anthropometric body measurements. For example, Cornelissen, McCarty, Cornelissen, and Tovée (2017) assessed body size estimation in women with anorexia nervosa (AN), using virtual avatars based on 3D body scan data. They observed that women with AN who were receiving treatment tended to overestimate their body size in the experiment, which demonstrated consistency of findings in the studies conducted over the last decades (Cash & Deagle, 1997; Farrell, Lee, & Shafran, 2005; Gardner & Brown, 2014). On the other hand, another recent study (Mölbert et al., 2018), adopted 3D body scanning, demonstrated a contradictory result to the previous consensus in literature about body estimation in patients with AN. Interestingly, the study discovered that women with AN and the control group without AN both underestimated their body weight. That is, regardless of whether or not they had AN, all women tended to perceive thinner body avatars as their actual bodies (underestimation). However, those with AN wanted their desired body to be fatter than their actual body, while the controls showed the opposite. The authors speculated about the conflicting outcome of their study in that the underestimation could be explained by the AN patients’ judgements on conceptual representations such as ‘I am thin.’ However, these incongruent research findings must be further clarified and validated with additional research.
Given the need in literature, this study investigated how experiencing a virtual self-avatar affects body image discrepancy (i.e., underestimation or overestimation from the actual body), how it influences body satisfaction, and further how body image discrepancy and/or body satisfaction leverages a behavioral intention for weight regulation. It is imperative to research this topic, as an accurate 3D virtual representation of one’s real body may facilitate a new and powerful experience, beyond traditional mirror body checking or even CGI virtual avatars. To achieve these research goals, the following hypotheses were formulated:
H1: There is a significant difference in body image discrepancy following a virtual avatar experience.
H2: There is a significant difference in body dissatisfaction following a virtual avatar experience.
H3: Body image discrepancy influenced by a virtual body experience is strongly related to behavioral intention for weight regulation.
H4: Body satisfaction influenced by a virtual avatar experience is strongly related to behavioral intention for weight regulation.
Additionally, we adopted gender as a particular predictor variable to gauge the roles of the potential confounding factor in the effects of virtual avatar experience in people’s body image disparity, body satisfaction, and regulated intention for weight control. As discussed earlier, the effects of gender on body image and its associated behavioral parameters are well documented in current literature (e.g., Furnham, Badmin, & Sneade, 2002). However, there is a dearth of information about the influence of the potential confounding factor in the virtual avatar domain. Considering the emerging stage of this research topic, we further explored the data in light of gender to gain additional insights.
The subsequent health outcomes (risks vs. benefits) of the proposed virtual avatar approach with human subjects are unclear. Given the ethical concern, we recruited participants from the non-clinical adult population. Researchers (Fairburn, Cooper, & Shafran, 2003; Shafran, Lee, Payne, & Fairburn, 2007; Williamson, White, York-Crowe, & Stewart, 2004) justified the use of non-clinical participants in their studies, in that, regardless of having body image related complications, overall psychological trends observed in participants were similar, although presumably the degrees of influence could be intensified when studied with the clinical sample. Moreover, we considered the use of the non-clinical population to be reasonable, particularly in view of the prevalence of virtual avatars in the gaming and fashion industries that likely influence people in daily (non-clinical) contexts, thus offering broader impacts of the outcomes uncovered from this study, beyond clinical settings.
Self-Discrepancy Theory and Body Image
The fundamental premise of this study was based on the Self-Discrepancy Theory (SDT). According to the SDT, there are three domains of the self, which include the actual, ideal, and ought self. Higgins (1987) explained that the actual self is one’s representation of attributes that someone (the one or another) believes the one actually possesses; the ideal self is one’s representation of attributes that someone (the one or another) would ideally like the one to possess; and the ought self refers to one’s representation of attributes that someone (the one or another) believes the one should or ought to possess (Higgins, 1987, pp. 320-321). Moreover, Higgins introduced two distinctive standpoints on the self, including one’s own personal standpoint and the standpoint of one’s significant others (i.e., mother, father, best friend, romantic partner, roommate, teacher). The ideal and actual self-concept tends to vary by culture (Lynch, Guardia, & Ryan, 2009).
The SDT further suggests that the greater the divergence of attributes between the two self-state representations, the greater the magnitude of body image disparity, the greater the intensity of emotional discomfort when the disparity is activated (Higgins, 1987). Additionally, Higgins explained that people try to reach a condition whereby their self-concept corresponds with their personally relevant self-guides, which direct and motivate people to reduce the discrepancy from their internalized self-evaluative standards. Previous studies have affirmed that body image discrepancy is associated with negative body image (Cash & Szymanski, 1995; Dittmar, 2009), body dissatisfaction (Strauman, Vookles, Berenstein, Chaiken, & Higgins, 1991; Williamson, Gleaves, Watkins, & Schlundt, 1993), affective emotional states (Barnett, Moore, & Harp, 2017; Bessenoff & Snow, 2006), and disordered mental health (Higgins, Klein, & Strauman, 1985; Veale, Kinderman, Riley, & Lambrou, 2003). Moreover, women who have higher body dissatisfaction are more dispositioned to be involved in weight-loss efforts than their opposite gender counterparts (Bish et al., 2005; Chang & Christakis, 2003). Vartanian (2012), however, argued that describing such body image discrepancy as ‘body dissatisfaction’ is like skipping a step from the perspective of the SDT. He elucidated that body image discrepancy is a cognitive process evoked from a perceived discrepancy between two self-states, and it results in body satisfaction or dissatisfaction. Namely, perceived body image discrepancy is a realization of a discrepancy between the self-state representations, and body (dis)satisfaction is an affective state resulted from the realization. However, what is uncertain is what triggers behavioral modification for healthy weight control, the realization of a discrepancy or evoked emotions from the realization?
Methods
Participants and Procedures
We recruited non-clinical participants who were 18 years and older; both genders; and had no history of chronic health problems or mental illnesses. We adopted convenient sampling and used multiple recruitment methods, including sending recruitment emails through the researcher university’s e-blast system, visiting college classrooms, and posting recruitment flyers to bulletin boards in public areas (e.g., libraries, student center, etc.). Snowball sampling was also allowed via the participants who already participated in the study and were willing to ask their peers about the research participation opportunity. Interested individuals were guided to contact the research lab to schedule their visit. Each experiment consisted of the three phases: a) pre-experiment survey, b) virtual avatar experience, and c) post-experiment survey. Prior to their study participation, participants were asked to review the informed consent form and sign it if they agreed to participate in the study. The research procedures were approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of the participating university.
A sample of 93 participants (N = 93) were recruited for this study. Based on a power analysis using G*Power 3.1.9.2., the desired sample size was 89, based on the parameters for linear multiple regressions (Effective size f2 = .15; Power (1 – β) = 0.95; Critical t(86) = 1.99; two-tailed). Therefore, the sample size of 93 was appropriate. Of the study participants, 51 were men (54.8%) and 42 were women (45.2%). The average age of men was 24.94 (SD = 7.82; range 19-58), and that of women was 25.02 (SD = 9.48; range 19-64). 76.3% of the participants (N = 71) were Caucasians, followed by 6.5% Hispanics (N = 6), 2.2% Asians (N = 2), and 2.2% African Americans (N = 2). The average height and weight of men were 71.06 inches (5 feet 11.06 inches, 180.49 cm, SD = 2.94) and 179.35 pounds (81.35 kg, SD = 29.39), and those of women were 65.38inches (5 feet 5.38 inches, 166.07 cm, SD = 3.46) and 141.27 pounds (64.79 kg, SD = 33.35). The mean Body Mass Indexes (BMIs) were 24.10 (SD = 6.11) and 24.56 (SD = 3.38) for men and women respectively, which categorized both BMIs in the normal or healthy status according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2017). The study participants represented varying university populations such as faculty, staff, students, post-docs, and their family and friends who characterized diverse demographic backgrounds in age, gender, ethnicity, and physical profiles. The demographic and physical profiles of the study participants are detailed in Table 1.
Table 1. Demographic and Physical Profiles.
|
Characteristics: M (SD) |
Male (N = 51) |
Female (N = 42) |
Combined (N = 93) |
|
|
Age |
24.92 (7.86) |
25.02 (9.48) |
24.97 (8.58) |
|
|
Height (inch) |
71.06 (2.94) |
65.38 (3.46) |
68.49 (4.25) |
|
|
Weight (lbs.) |
179.35 (29.39) |
141.27 (33.35) |
162.38 (36.41) |
|
|
BMI (kg/m2) |
24.10 (6.11) |
24.56 (3.38) |
24.30 (5.00) |
|
|
BMI category (%) |
Underweight Healthy weight Overweight Obese |
7 (13.7) 28 (54.9) 16 (31.4) 0 (0.0) |
2 (4.8) 24 (57.1) 16 (38.1) 0 (0.0) |
9 (9.7) 52 (55.9) 32 (34.4) 0 (0.0) |
|
Ethnicity (%) |
Caucasian Hispanic African American Asian |
39 (76.5) 3 (5.9) 1 (2.0) 1 (2.0) |
32 (76.2) 3 (7.1) 1 (2.4) 1 (2.4) |
71 (76.3) 6 (6.5) 2 (2.2) 2 (2.2) |
Pre-experiment survey. The pre-experiment survey was developed based on Stunkard’s Figure Rating Scale (SFRS) (Stunkard, Sorensen, & Schulsinger, 1983). The gender-specific SFRS featured nine body figures, from 1 (thinnest) to 9 (fattest) and a corresponding scale for each gender group (i.e., the female body scale for women and the male scale for men). Participants were then asked to choose body figure numbers (1-9) on the SFRS scale that best represented their actual, ideal, and ought body (pre Part A). The following section (pre Part B) was adopted and modified from the Body Image Ideals Questionnaire (BIQ) (Cash & Szymanski, 1995), which contained 12 items that measured the attributes of one’s body image ideal. Using the modified BIQ scale, the participants were guided to compare the selected ideal and ought self-images with their own perception of the actual self-image, based on the following body characteristics – the height, weight, muscle tone or definition, body proportions, chest size, and overall physical appearance, on a scale ranging from 0 (“very unlike me”) to 3 (“exactly as I am”). Some of the questions in the modified BIQ scale included “My ideal height is …” and “My ought muscle tone or definition is … .” In the last section of the pre-experiment survey (pre Part C), the participants were asked to think of one particular significant other (e.g., mother, father, sister, brother, romantic partner, close friend, relative, society in general) and complete the same BIQ scale as they did in Part B from the significant other’s standpoint.
Virtual avatar experience. This study employed a particular virtual technology – 3D body scanning that creates a virtual body surface model based on accurate anthropometric dimensions of one’s body using non-invasive depth sensors (refer to Figure 1). Upon the completion of the pre-survey, participants were guided to the 3D body scanning room, where a full-body scanner was located ([TC]2, KX-16). Prior to 3D body scanning, their height and weight were measured using a stadiometer (Seca®) and digital weight scale (Tanita®, TBF-310GS), and entered into the 3D scan data file. For body scanning, participants were scanned wearing their own undergarments; women wore their own bra and underpants, and men wore underpants only. The 3D body scan data was then converted into a virtual avatar using the virtual body modeling software (ImageTwin™), integral to the operational system of 3D body scanning. The study participants were allowed to participate in the avatar creation process when their avatar skin and hairstyle were selected from a set of standard textures to match with their actual body. The total time for 3D body scanning and avatar creation per participant was appropriately 10-15 minutes including clothes changing time. After scanning, a researcher showed the participants their 3D surface body model (i.e., avatar) on the computer screen, located adjacent to the scanner, and demonstrated the viewing techniques of the 3D surface model (e.g., zoom-in, zoom-out, and rotation) using a mouse. Once a participant became comfortable with the viewing techniques, the researcher exited the room to allow the participant to freely examine his/her own virtual avatar in an undisrupted, private setting. When they were done examining their virtual avatar, they exited the room. The viewing time varied between seconds and minutes.

Figure 1. Creation of a virtual avatar using 3D body scan data (Left: a raw 3D scan image, Center:
body measurement data, Right: a virtual avatar created based on the measurement data).
Post-experiment survey. After participating in the virtual avatar experience, the participants completed the post-survey that consisted of the three sub-sections. The first section of the post-survey was similar to that of the pre-survey, in that, showing the same SFRS figure scale, the participants rated their perception of the actual self after experiencing their virtual avatar (post Part A), to gauge body image discrepancy pre- vs. post-experiment based on the ratings of the perceived actual self-images The second section (post Part B) contained 10 five-point scale items, modified from the Body Satisfaction Scale (BSS) (Garner, Olmstead, & Polivy, 1983). The modified BSS scale measured the degree of the participants’ satisfaction with their specific body measurement components, including the height, waist, stomach, thighs, buttocks, hips, legs, body proportion, and overall physical appearance. The last set of questions contained three five-point scale items that measured the participants’ regulated intention toward weight management, i.e., whether they are willing to put effort into weight loss, physical exercises, and nutritional diets. The time commitment for the entire experiment, including the two surveys and virtual body checking, was approximately 45 min – one hour per participant.
Data Analysis
Descriptive and inferential statistics were analyzed using IBM SPSS 24.0. To measure internal consistency of the survey scales, reliability tests were performed. The alpha coefficients for pre-experiment survey Part B and Part C were .89 and .94, and those for post-experiment survey Part B and Part C were .87 and .81 respectively. The reliability of SFRS (pre- and post- Part A) was not calculated because it was a single-item scale per question. The results of the reliability tests suggested the survey scales used in this study had high internal consistency, which indicated each scale measured the same construct across the survey items.
Independent samples t-tests and repeated-measures ANOVA, as well as descriptive analyses, were employed to understand the overall trends of body image and body image discrepancy in the domains and standpoints of the self. For hypotheses testing, we used within-subjects, paired samples t-tests to compare between the scores of the actual self-state at the pre- vs. post-experiment; and independent samples tests and one-way ANOVA to compare mean scores in body image discrepancy and body dissatisfaction by gender. Additionally, we performed linear regression analyses to predict the strengths of the relationships between the study variables: i.e., between body image discrepancy (∆ post SFRS actual self – pre SFRS actual self) and weight regulation intention; and between body dissatisfaction and weight regulation intention. Specifically the regression analyses were conducted to infer whether and how the independent variables (body image discrepancy and body dissatisfaction) affect behavioral intention for weight regulation. All results were interpreted at the 95% confidence interval.
Results
Overall Trends of Perceived Body Image and Body Image Discrepancy
Before testing the hypotheses, we overviewed perceived self-images and gaps between the self-images experienced by the study participants. The results were organized in the following two perspectives – the self and the significant others. Viewing the data through the different standpoints particularly helped us gain a comprehensive understanding of perceived self-images and body image discrepancy based on how the participants thought of their own body and how they believed their significant others would think of their body. Although this part of the analyses did not directly contribute to the hypothesis testing, it was important to be sensible, because one’s body image is constructed by their own psychological judgment as well as through social interactions. Namely, the results of this part described the baseline stance of the participants’ body image and body image discrepancy before having an experience of their virtual self-avatar.
Through the lens of the self. As Figure 2 illustrates, on the 9-point SFRS scale being 1 (thinnest) to 9 (fattest), the participants rated their actual self with the highest score (x̄ = 4.34, SD = 1.54), followed by the ought self (x̄ = 3.73, SD = 1.08) and the ideal self (x̄ = 3.68, SD = 1.02). The result of the mean comparison was significant at the 95% confidence level (p = .000). To interpret, on the SFRS scale, the participants scored their actual self the fattest and the ideal self the thinnest (although the difference between the ideal and ought self was marginal). Overall, the male participants rated their self-images at 4.62 (actual, SD = 1.34), 4.17 (ideal, SD = 0.79), and 4.31 (ought, SD = 0.79), while the female participants rated them at 3.98 (actual, SD = 1.68), 3.05 (ideal, SD = 0.93), and 3.05 (ought, SD = 0.98). That is, the male participants generally perceived their self-images in all three domains (actual, ideal and ought) bigger than the female participants, which could be commonly understood, because male bodies are typically larger than female bodies.
Furthermore, to determine gender differences in body image discrepancy within subjects, repeated-measures ANOVA was performed. The test results showed a significant gender difference in the self-state scores at p = < .05 (Wilks’ Lambda = .729, F(2, 88) = 16.377, p = .000). More specifically, the post-hoc tests for the repeated measures ANOVA (Figure 2) revealed that the mean intervals (Δ actual – ideal and Δ actual – ought) of female participants was 0.93 (SD = 1.11), which indicated a statistical significance in body image discrepancy at p < .05 (p = .041).
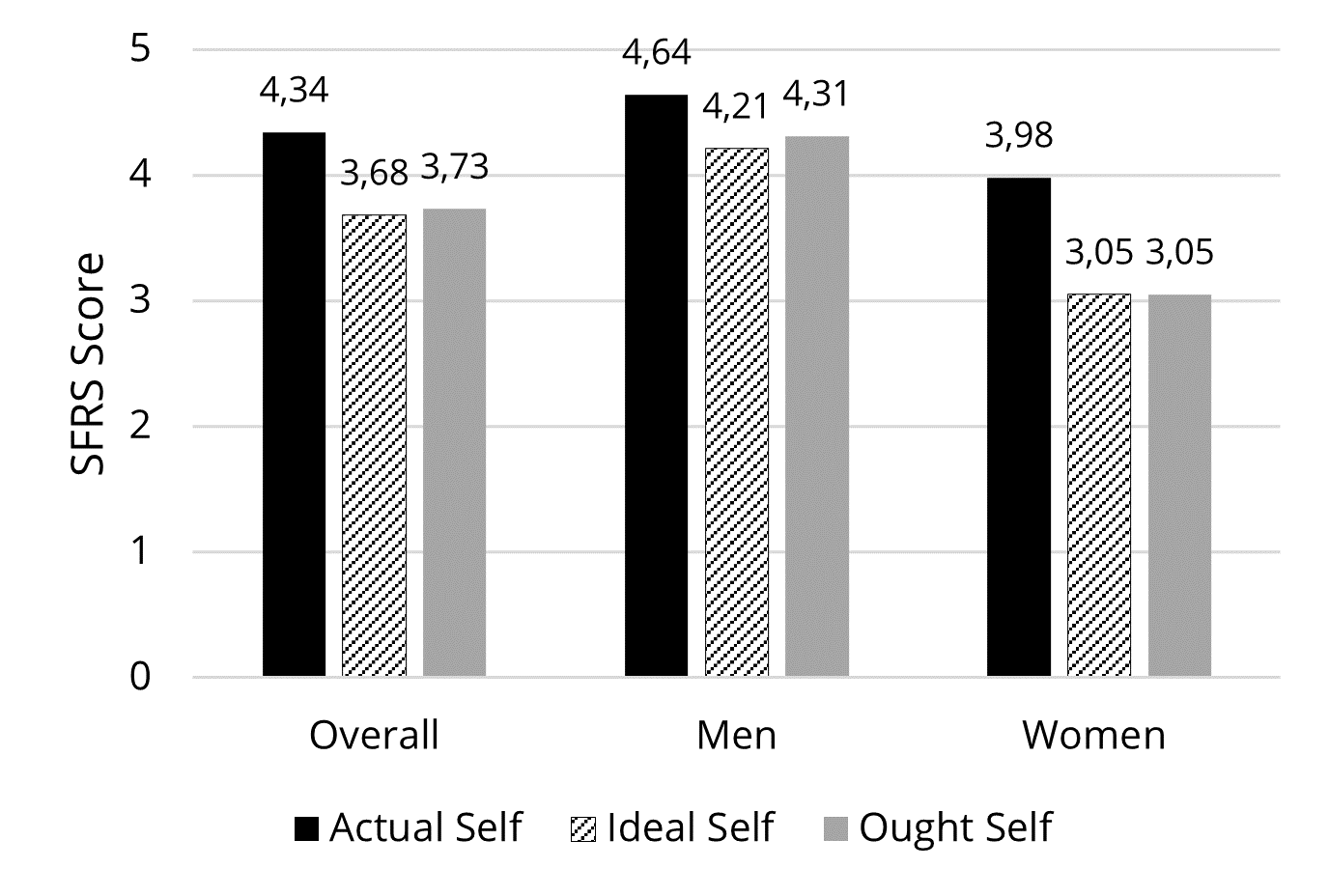
Figure 2. SFRS figure scores of self-images (actual, ideal, and ought)compared
by gender, based on the participants’ own standpoint.
This result can be inferred that the female participants experienced discrepancy between their self-images, especially between their actual self and their ideal self and between their actual self and their ought self, to a statistically meaningful degree. That is, they perceived that their actual body image was noticeably different from what they believed met the cultural beauty ideal or what they felt they ought to look like. However, the male participants’ self-images showed no significant discrepancy in any mean intervals, meaning that the SFRS ratings on their actual, ideal, and ought self image were close enough, so they were within a similar range.
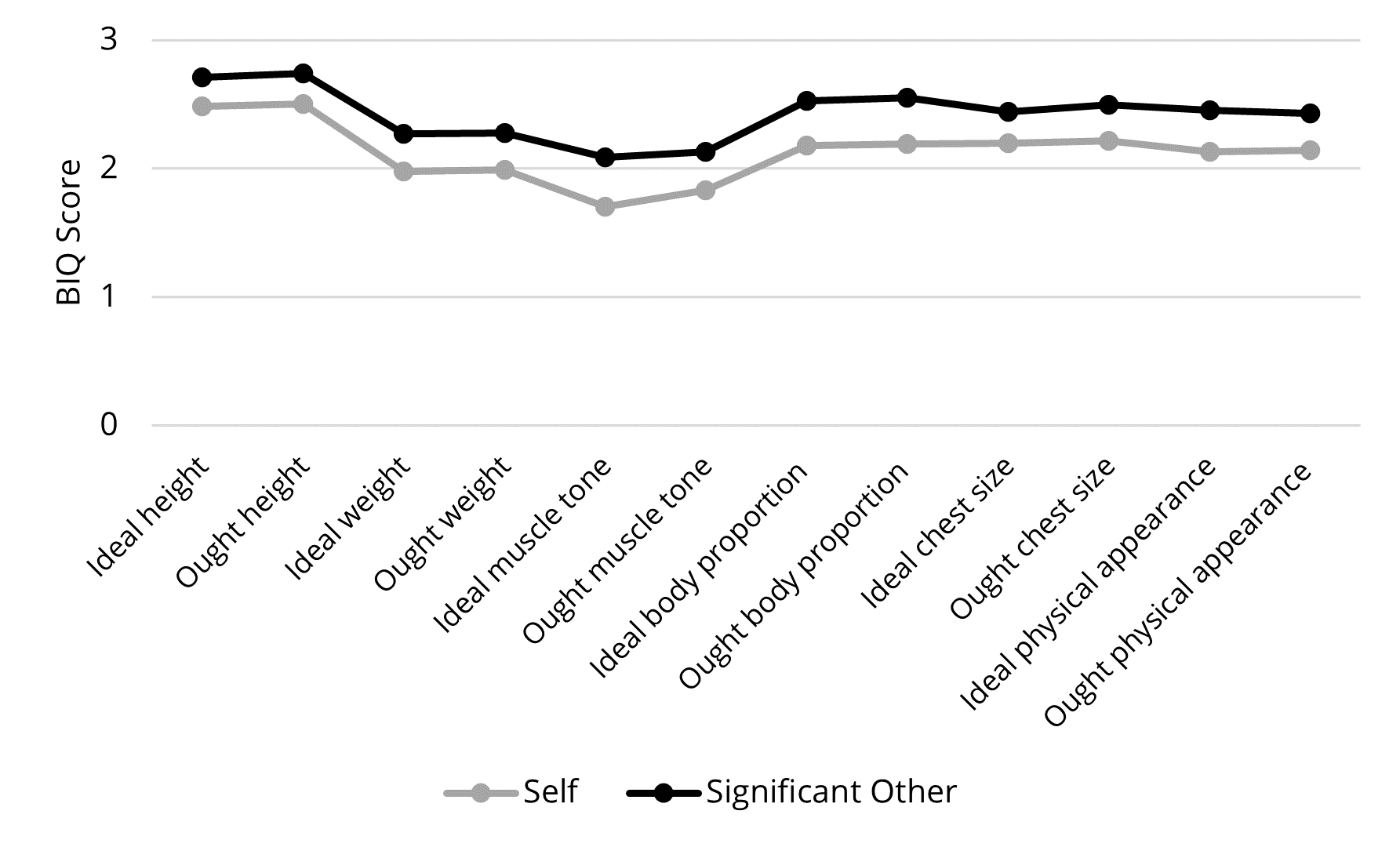
Figure 3. Comparison of BIQ scores by the self and the self-selected significant other.
Through the lens of significant others. On the modified BIQ scale (0 = very unlike me, 3 = exactly as I am), the participants showed the lowest body image discrepancy in their ought height (x̄ = 2.51, SD = 0.69), while they showed the highest body image discrepancy in their ideal muscle tone or definition (x̄ = 1.70, SD = 0.65). These results can be explained that the participants reported, among the scale items listed in Figure 3, their ought height (that the participant believes he or she should or ought to possess) would be the closest to their actual physical body, while their ideal muscle tone or definition (that the participant would ideally like to possess) was the furthest from their perceived actual physical body. The significant other most frequently selected was a romantic partner (49% men, 42.9% women), followed by mother (11.8% men, 26.2% women) and society in general (11.8% men, 16.7% women). Overall, the participants’ body image perceptions based on their significant other’s standpoint showed a similar trend to the perceptions based on their own standpoint. To compare the mean differences between the ratings based on their own and their significant other’s standpoint, paired samples t-tests were performed. The results showed strong mean differences in all items at p < .05. This indicates that the participants believed their significant other possessed more positive approval of their body than they did themselves. However, no statistically significant gender difference was found in this inquiry. That is, both gender groups showed a similar trend with respect to this finding.
The Effect of Virtual Avatar Experience
Body image discrepancy (H1). After experiencing their virtual avatar, the participants rated their actual self again using the same SFRS scale as the one they used for the pre-survey (Figure 4). To evaluate the effect of the virtual avatar experience on perceived body image, paired samples t-tests were performed between the scores on the actual self between the pre-avatar experience and post-avatar experience at the 95% confidence level. Data showed that overall, the scores of the actual self had increased after the virtual avatar experience, as much as 0.51, since the mean at pre-experiment was 4.33 (SD = 1.54) and that at the post experiment was 4.84 (SD = 1.18). The mean increase was statistically significant (t = 5.987, p = .000). These results signified that after experiencing their virtual avatar, the participants rated their actual body image larger than they did before the experience, which supported H1.
Likewise, the statistical trend was valid in each gender group (refer to Figure 4). That is, the actual self-image score increased as much as 0.32 (SD = 0.78) in the male participants and as much as 0.73 (SD = 0.82) in the female participants. The differences in the actual self scores measured at pre-experience and post-experience were statistically significant in both genders (for men, x̄ = -0.323, t = -2.886, p = .006); for women, x̄ = -0.738, t = -5.828, p = .000). Further, the discrepancy in the actual self-image scores, pre- vs. post-virtual avatar experience, was compared by gender. The result of an independent-samples t-test showed a strong gender difference (t = -2.466. df = 88, p = .016). To explain, the female participants perceived their body significantly larger after having an experience of their virtual avatar, than the male participants did.
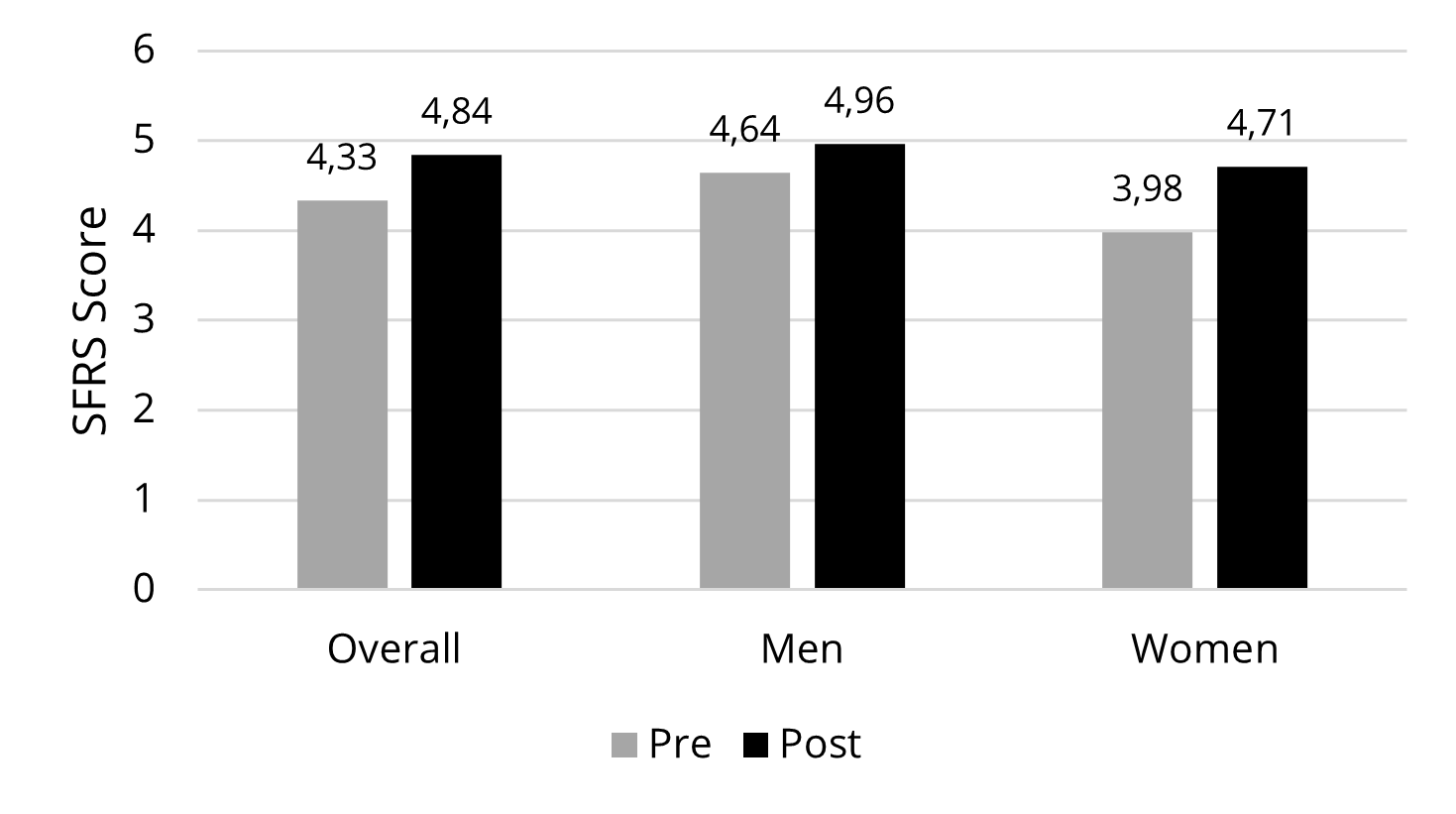
Figure 4. Differences in body image discrepancy pre- vs. post-experiment.
Body dissatisfaction (H2). The BSS scale items were designed to measure comparative evaluations of body satisfaction, in relation to the participants’ presupposition of their body before the virtual avatar experience. Given, the mean scores of the BSS, ranging 2.65 – 3.27 (out of 5), exhibited that the participants had moderately negative body satisfaction after participating in a virtual avatar experience (Table 2). Overall, the participants showed negative evaluations on their height, buttocks, and hips after viewing their virtual avatar. The result leads us to interpret that the participants became more negative about their body, especially on their height, buttocks and hips after having the experience of their virtual avatar, which supported H2.
Significant gender difference was found in all 10 BSS items measured. That is, the results of independent-samples t-tests showed that after viewing their virtual avatar, the female participants became significantly more dissatisfied with their body than the male participants did. In other words, after virtual avatar experience, the female participants thought their height looked shorter than they thought; their body in seven different areas (i.e., weight, waist, stomach, thighs, buttocks, hips and legs) looked bigger than they thought; their body proportions and overall physical appearance looked worse than they thought, compared to the male participants, at p < .05 (Table 2). The results from the body dissatisfaction evaluation showed a strong gender effect on body image discrepancy post virtual experiment.
Table 2. Body Dissatisfaction Scores After Virtual Avatar Experience.
|
BSS Scale Item |
Overall |
Men |
Women |
t |
Sig. |
|
I became more satisfied with my body† |
3.27 (.91) |
2.94 (.90) |
3.67 (.75) |
-4.147 |
.000** |
|
My height looks shorter than I thought |
2.65 (1.06) |
2.37 (.77) |
2.98 (1.26) |
-2.837 |
.006** |
|
My waist looks bigger than I thought |
3.14(1.12) |
2.61 (.96) |
3.79 (.95) |
-5.911 |
.000** |
|
My stomach looks bigger than I thought |
3.18 (1.06) |
2.69 (.95) |
3.79 (.87) |
-5.772 |
.000** |
|
My thighs look larger than I thought |
3.14 (1.19) |
2.88 (1.19) |
3.45 (1.13) |
-2.346 |
.021* |
|
My buttocks look bigger than I thought |
2.73 (1.14) |
2.41 (1.04) |
3.12 (1.15) |
-3.105 |
.003** |
|
My hips look bigger than I thought |
2.83 (1.11) |
2.43 (.92) |
3.31 (1.14) |
-4.114 |
.000** |
|
My legs look bigger than I thought |
3.01 (1.22) |
2.73 (1.15) |
3.36 (1.23) |
-2.558 |
.012* |
|
My body proportions look better than I thought† |
3.065 (.95) |
2.73 (.83) |
3.48 (.94) |
-4.089 |
.000** |
|
My overall physical appearance look better than I thought† |
3.13 (.95) |
2.75 (.87) |
3.60 (.83) |
-4.798 |
.000** |
|
Note: † reversed items; ** p < .01, * p < .05.
|
|||||
Figure 5 visually summarizes the relationships between the overall trend and each of the gender data. With the line graph indicating the overall trend of the gender-combined data, it illustrates that all bars showing the female data are positioned above the line graph, while those showing the male data are below the overall line. This visual representation indicates that the female participants experienced higher body dissatisfaction with all body parts measured than the combined average, as well as the male participants’ scores, after examining their virtual avatar. That is, the female participants’ body satisfaction was negatively affected by having the experience of virtual avatar viewing, but the male participants showed neutral or moderately positive evaluations on their body after the experience.
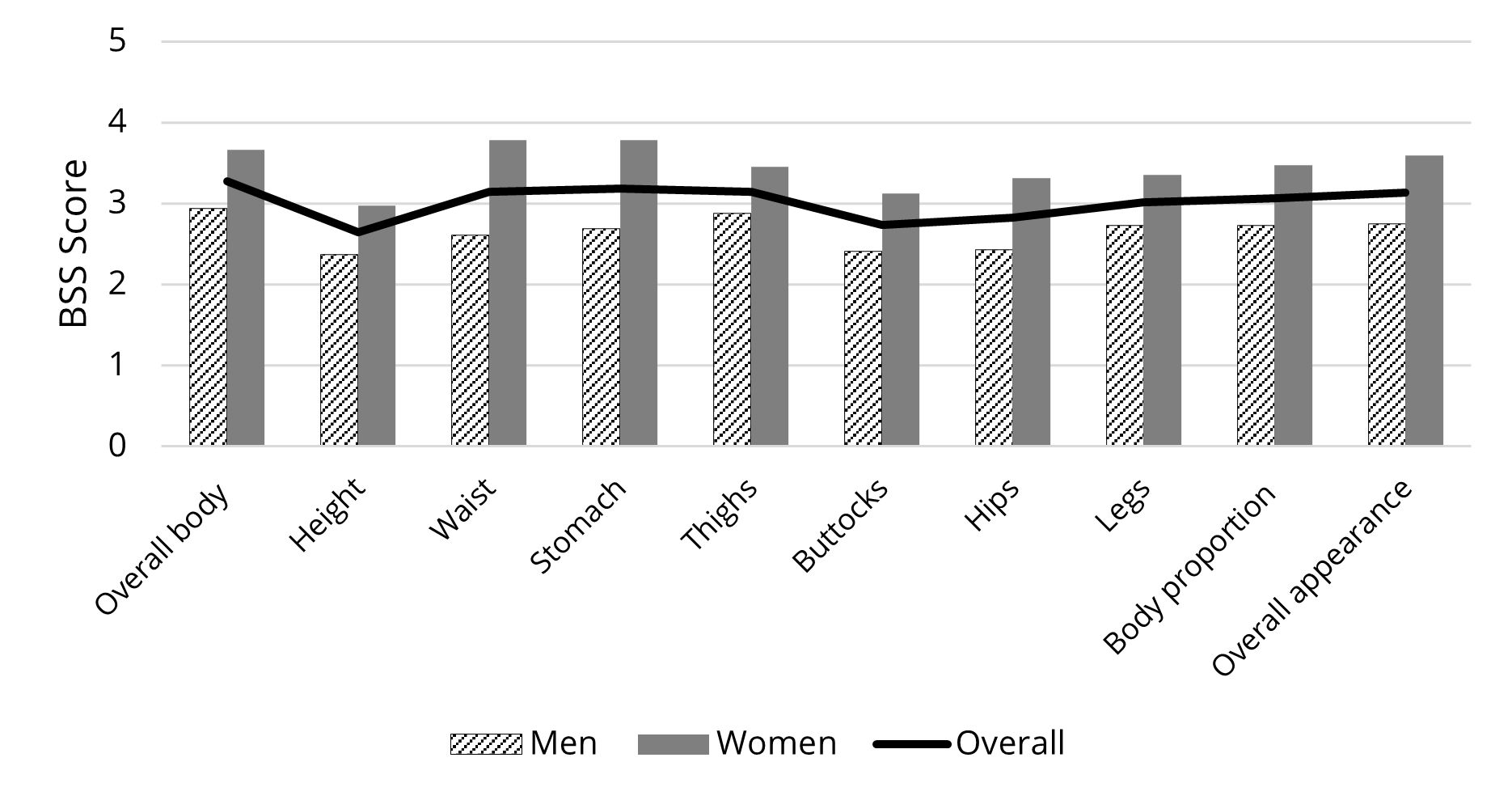
Figure 5. Gender comparison of body dissatisfaction scores after virtual avatar experience.
Weight regulation intention (H3 and H4). In order to understand the causal relationships of how the regulated behavioral intention is related with body image discrepancy and body dissatisfaction experienced by the participants after viewing their virtual avatar. We used regression analyses to determine the relationships between each of the independent variables, either body image discrepancy or body dissatisfaction, and the regulated intension for weight-related behavioral changes after virtual avatar experience.
Because body image discrepancy was presented in a single dataset, univariate regression analyses were performed defining body image discrepancy as an independent variable and each of the 3-item scale measures for regulated intentions (to lose weight, exercise, and do a nutritional diet) as a dependent variable. The results of the univariate regression analyses indicated that there was no significant relationship between the degree of body image discrepancy and weight regulation intention (p = .554, .518, and .748; the intention to lose weight, to exercise, and to do a nutritional diet respectively). These findings signified that no causal relationship was predicted with weight regulation intention even when a strong body image discrepancy was perceived after virtual avatar experience. Therefore, H3 was rejected. The regression results were consistent with gender at the 95% confidence interval.
On the other hand, the body satisfaction scale that we used in this study contained 12-items. Thus, multivariate regression analyses were performed to understand the causal effect of body dissatisfaction with regulated intention for weight-related behavioral changes. The result showed a strong linear relationship of body dissatisfaction with regulated intention for weight loss (R2 = .252, F = 3.114, df = 9, p = .003). That is, the extent to which the participants indicated dissatisfaction with their body after the virtual avatar experience predicted their regulated intention to lose weight. However, the analyses did not notice significant relationships between body dissatisfaction and the other two intentions for weight-related behaviors, including the intention to exercise (p = .187) or the intention to have a nutritional diet (p = .375). Therefore, H4 was partially supported.
Additionally, we ran multivariate regression analysis in each sub group. As for gender, the same trend was not found. To explain, in the gender-split data, no significance was observed in the regulated intention for weight loss between the male and female participants (p = .141, .267 respectively). That is, overall body dissatisfaction strongly predicted regulated intention to lose weight, but the result was consistent across the gender groups. Interestingly the male participants, however, showed a strong intention to be involved in exercising (p = .004), but it was not observed in the female data (p = .289). Both the male and the female groups did not show a strong relationship between body dissatisfaction and intention for a nutritional diet (for males, p = .227; for females, p = .071). Although the significance was lower than .05, the data hinted that women might be more motivated to be on a nutritional diet than men after seeing their own avatar. However, the data of this study did not prove that, which suggests a further investigation with a larger sample.
Discussion
The findings of this study uncovered the effect of virtual avatar experience on body image discrepancy, body satisfaction, and weight regulation intention. Overall, data indicated an increase in body image discrepancy and a decrease in body satisfaction, after participating in a virtual avatar session, and those who showed higher body dissatisfaction exhibited a higher intention to be involved in behavioral change for healthy body weight. However, the increased body image discrepancy itself did not trigger a regulated intention for weight loss after virtual avatar experience.
Specifically in gender, this study demonstrated interesting differences between men and women in the explained variables. First, there was a strong gender difference in body image discrepancy and perceived body dissatisfaction, after experiencing their own virtual avatar. That is, after the virtual avatar experience, the female participants rated their body significantly larger and displayed much higher dissatisfaction with their body than the male participants did. In other words, the experience of virtual body experience negatively affected the female participants’ body size perception and the emotional state about their body (i.e., body dissatisfaction) much stronger in women than in men.
Another key finding of this study was that the gender effect of virtual avatar experience on weight regulation intention was also valid through body dissatisfaction, but not through body image discrepancy. This trend was consistent with the gender-combined data described earlier. Both male and female participants showed intentions to lose weight after having a virtual avatar experience. The finding explained that the study participants’ motivation toward healthy weight management was activated by dissatisfied perception of their body image, but it was not necessarily different by gender. Namely, when the participants, regardless of gender, experienced their body dissatisfaction altered in the negative direction after viewing their virtual avatar, they indicated their strong willingness to change their behavior toward healthy weight management. On the other hand, it was interesting that the male group exhibited a stronger intention to be involved in exercise than the female group, while the female group showed a relative preference to participate in a nutritional diet, compared to the male group. However, the relationship on a diet was not yet confirmed by statistical significance.
From the theoretical perspective, the findings supported Higgins’ (1987) argument in the SDT that people are regulated to reduce the self-discrepancy that causes emotional discomfort from their internalized self-evaluative standards. In this particular study, the self-discrepancy was measured by the difference between the perceived actual body sizes before and after viewing one’s own virtual avatar. Higgins, Bond, Klein, and Strauman (1986) determined that when an individual experiences high discrepancy in their value, the person tends to become emotionally vulnerable. Body dissatisfaction is negative perceptions and feelings that a person possesses about their body (McGuinness & Taylor, 2016), and various factors contribute to the adverse emotions about the body including body shape, appearance, attitudes toward weight gain, and cultural beauty ideal (Slade, 1994; Slevic & Tiggemann, 2011). Namely, in this study, the emotions evoked from having an experience of a virtual avatar were expressed in the form of body dissatisfaction. Further, the regulated intention for weight control predicted behavioral change to mediate negative feelings about the body by closing the discrepancy between their physical body and the sociocultural standards. Therefore, our findings validated the principles of the SDT, and added further insights to the theoretical framework with empirical data in the context of body image and virtual technology.
We may also look at the study findings from a motivational regulation angle. In this study, the participants were offered a private avatar experience session, in which they could control their viewing pace and mode (e.g., zoom-in and out, rotation, etc.). Another advantage of the virtual procedure was to avoid the need for personal interactions with clinicians, counselors, or other personnel in which an individual patient is often placed at healthcare services. Hence, the private setting was not only intended to facilitate a more self-controlled viewing environment, but also catalyze the internalization process by eliminating interpersonal interactions with healthcare personnel who often serve as an external driver for the patient’s regulation of health behavior change (i.e., extrinsic motivation) (Park, 2016). We recognize that the sociocultural standards of the body ideal is deeply embedded in contemporary Western society; therefore, it makes literally impossible for an individual in western culture to experience a complete sense of intrinsic motivation for behavioral change, when it comes down to body image. In other words, the motivational regulation for health-related behavior that we found in this study could not be the outcome of an intrinsically internalized motivation, because it is inevitable that the evoked emotions and regulated behavioral intention from body dissatisfaction are influenced by the cultural norms and standards of society that we live in.
According to the Organismic Integration Theory (OIT), a sub-theory of self-determination, people’s motivation can be measured by the degree to which an activity or behavior is self-determined (Ryan & Deci, 2002). Largely, the locus of causality of the behavior can be categorized between extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. More specifically, within extrinsic motivation, there are distinctive forms of instrumentality on a spectrum of motivational states from not-self determined (external regulation) to partially self-determined (introjected, identified, and integrated regulation) to self-determined (intrinsic regulation). The completely self-determined motivation, also known as intrinsic motivation, is the purest form of motivation and the behavior is in line with an individual’s self values. On the other hand, the external regulation is considered the least autonomous, and the external rewards are not internalized at all. Among the partially self-determined regulations, the intention for weight regulation observed in this study could be understood as identified regulation, the most autonomous type of external regulation. To further explain, although the regulated intention for weight control was not the result of complete autonomy, it was still autonomously regulated based on their personally believed values, goals, and needs. In a study that applied this motivation concept in health promotion (Ryan, Williams, Patrick, & Deci, 2009), the researchers determined that the more internalized extrinsic motivation, the more autonomous the person will be when enacting the behavior. Given, the intention for behavioral change regulated from experiencing their own avatar, which is internally regulated, has potential to sustain their behavior over time. This topic was beyond the present study’s scope and thus is left for future research.
As a cautionary measure, we recruited the non-clinical group for this study. Considering the increased body image discrepancy and body dissatisfaction after the virtual avatar experience, the selection of the samples was deemed appropriate for this exploratory phase of the study. On a positive note, our previous study (Park, 2018) affirmed that, irrespective of their emotional responses (positive or negative) to viewing their virtual avatars, people showed their willingness to participate in a future session of virtual avatar viewing. Furthermore, many researchers (e.g., Kuo et al., 2016; Manzoni et al., 2016; Riva, 2002, 2005; Rothbaum et al., 2014; Serino et al., 2016) have evinced potential positive benefits of using virtual technology in clinical settings. However, in order to practice this virtual avatar approach with clinical samples, additional research must be preceded to identify contributing factors to the negative trends in body image and body satisfaction and find creative solutions to mitigate the issues. It is imperative to ensure that adequate subject protection is guaranteed and privacy is secured in the clinical trial environment.
Another limitation of the present study was to use the study participants who represented the U.S. adult population. In order to substantiate the study findings, we will need to recruit the participants with a wider range of demographic profiles such as age, ethnicity, sexual orientation, etc. It will also be useful to conduct a cross-cultural study to compare the results across various cultures, in which the hegemonic body ideals are different. Additionally in this study, we offered one session of virtual avatar experience. It will be beneficial to evaluate longitudinal effects of the virtual avatar experience, when virtual avatars are experienced over time, on the psychological and behavioral measures related to body image. While we recognize that continuous research is essential to validate the outcomes of the virtual avatar approach in diverse contexts with various populations, we believe that this study discovered potential consequences of having people experience their own virtual avatars developed based on their actual body physique. That is, the negative affective responses that our study participants indicated must be carefully examined to find creative solutions to mitigate the potential adverse effect of the virtual avatar approach in its real-world applications. For example, game developers must be mindful of potential negative outcomes of using virtual avatars in online computer games, because adolescents who are the dominant users yet vulnerable to the development of poor body image are known to have unhealthy behavioral problems than those who do not play computer games (Shokouhi-Moqhaddam et al., 2013; Zamani, Kheradmand, Cheshmi, Abedi, & Hedayati, 2010). On the other hand, if the motivational intention for weight regulation is properly used, it could generate positive outcomes in people who can shift their virtual avatar experience to behavioral changes for healthy lifestyles.
In conclusion, virtual technology has offered us new opportunities. At the same time, it has challenged us to find ways to use the technology to make positive impacts in our lives. There are still many unknowns and incongruence in current literature as we observed in Cornelissen et al.’s (2017) study vs. Mölbert et al.’s (2018) study. We feel the finding of this study shed little light on the scientific communities that are curious and interested in using virtual technology in an optimized way.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in party by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) through the Colorado Agricultural Experiment Station Hatch Funds under Grant [COL00224].

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2018 Juyeon Park


