A Preliminary Study Exploring Moderating Effects of Role Stressors on the Relationship Between Big Five Personality Traits and Workplace Cyberloafing
Vol.11,No.4(2017)
Cyberloafing—a type of counterproductive behavior—occurs when employees use the internet for personal use while at work. Past research shows that work role stressors (i.e., role conflict, role ambiguity, and role overload) and Big Five personality traits (i.e., neuroticism, conscientiousness, extraversion, and agreeableness) predict cyberloafing, but research has yet to explore interactions among these factors. The current study aimed to address this gap by examining whether work role stressors strengthen the relationship between personality and cyberloafing based on the Personal Resource Allocation (PRA) framework. In an online survey of employees from diverse occupations (N = 343), we replicated past work showing relationships among personality traits and cyberloafing. However, role conflict was the only stressor that predicted cyberloafing. Moderated multiple regression analyses suggested only three statistically robust findings in the expected direction: role conflict strengthening the positive association between neuroticism and cyberloafing, role conflict strengthening the negative association between agreeableness and cyberloafing, and role overload strengthening the negative association between conscientiousness and cyberloafing. Overall, this study implies mixed and somewhat weak support for PRA framework predictions, including a lack of consistency in a specific role stressor enhancing personality-cyberloafing relationships. Practical implications for personnel selection and employee training/development are also discussed.
Cyberloafing; work role stressors; personality traits; counterproductive work behavior
Lebena Varghese
Northern Illinois University, Dekalb, IL, United States
Lebena Varghese, PhD, is a Research Scientist at ACT.inc. Her research interests include promotion of gender
diversity, impact of counterproductive behaviours in the workplace, and survey research with a focus on
identifying factors that can enhance response rates of surveys.
Larissa K. Barber
Northern Illinois University, Dekalb, IL, United States
Organizational Psychology Program) at Northern Illinois University. Her research interests are in the areas of
occupational and health and organizational behavior, with a focus on the work-life interface, sleep, self-control,
and counterproductive behaviors in response to workplace stress.
Andreassen, C., Torsheim, T., & Pallesen, S. (2014). Predictors of use of social network sites at work - a specific type of cyberloafing. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 19, 906-921.
Arnold, T., Flaherty, K., Voss, K., & Mowen, J. (2009). Role Stressors and Retail Performance: The Role of Perceived Competitive Climate. Journal of Retailing, 85(2), 194-205. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jretai.2009.02.002
Ashton, M. (1998). Personality and job performance: the importance of narrow traits. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 19(3), 289-303. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1099-1379(199805)19:3<289::aid-job841>3.3.co;2-3
Barrick, M., Stewart, G., & Piotrowski, M. (2002). Personality and job performance: Test of the mediating effects of motivation among sales representatives. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(1), 43-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037//0021-9010.87.1.43
Bowling, N., & Eschleman, K. (2010). Employee personality as a moderator of the relationships between work stressors and counterproductive work behavior. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 15(1), 91-103.
Conlin, M. (2000). Workers, Surf at Your Own Risk. Businessweek.com. Retrieved 24 May 2015, from http://www.businessweek.com/2000/00_24/b3685257.htm
Connor-Smith, J., & Flachsbart, C. (2007). Relations between personality and coping: a meta-analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93, 1080-1107.
Donnellan, M. & Lucas, R. (2008). Age differences in the big five across the life span: Evidence from two national samples. Psychology and Aging, 23, 558-566. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0012897
Donnellan, M., Oswald, F., Baird, B., & Lucas, R. (2006). The mini-IPIP scales: Tiny-yet-effective measures of the Big Five factors of personality. Psychological Assessment, 18(2), 192-203.
Folkman, S., & Lazarus, R. (1988). Coping as a mediator of emotion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(3), 466.
Fox, S., Spector, P., Goh, A., & Bruursema, K. (2007). Does your coworker know what you're doing? Convergence of self- and peer-reports of counterproductive work behavior. International Journal of Stress Management, 14(1), 41-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/1072-5245.14.1.41
Fox, S., Spector, P. E., & Miles, D. (2001). Counterproductive work behavior (CWB) in response to job stressors and organizational justice: Some mediator and moderator tests for autonomy and emotions. Journal of vocational behavior, 59(3), 291-309.
Grawitch, M. J., Barber, L. K., & Justice, L. (2010). Rethinking the work–life interface: It's not about balance, it's about resource allocation. Applied Psychology: Health and Well‐Being, 2(2), 127-159.
Henle, C., & Blanchard, A. (2008). The interaction of work stressors and organizational sanctions on cyberloafing. Journal of Managerial Issues, 20, 383-400.
Hobfoll, S. (1989). Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44, 513-524.
Jackson, S. E. (1983). Participation in decision making as a strategy for reducing job-related strain Journal of Applied Psychology, 68(1), 3-19.
Jia, H., Jia, R., & Karau, S. (2013). Cyberloafing and personality: The impact of the big five traits and workplace situational factors. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 20, 358-365.
Johansson, A. & Gotestam, K. (2004). Internet addiction: Characteristics of a questionnaire and prevalence in Norwegian youth (12-18 years). Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 45, 223-229. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.2004.00398.x
John, O., & Srivastava, S. (1999). The Big Five trait taxonomy: History, measurement, and theoretical perspectives. Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research, 2, 102--138.
Kahn, R., Wolfe, D., Quinn, R., Snoek, J., & Rosenthal, R. (1964). Organizational stress: Studies in role conflict and ambiguity. New York, NY: John Wiley.
Koelega, H.S., 1992. Extraversion and vigilance performance: 30 years of inconsistencies. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 239–258.
Kossek, E. E., Hammer, L. B., Kelly, E. L., & Moen, P. (2014). Designing work, family & health organizational change initiatives. Organizational dynamics, 43(1), 53-63. 10.1016/j.orgdyn.2013.10.007
Krischer, M., Penney, L., & Hunter, E. (2010). Can counterproductive work behaviors be productive? CWB as emotion-focused coping. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 15(2), 154-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0018349
Kraut, R., Olson, J., Banaji, M., Bruckman, A., Cohen, J., & Couper, M. (2004). Psychological research online: report of Board of Scientific Affairs’ Advisory Group on the Conduct of Research on the Internet. The American Psychologist, 59(2), 105–117.
Landers, N. R., Beherend, S. T. (2015). An inconvenient truth: Arbitrary distinctions between organizational, Mechanical Turk, and other convenience samples. Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 8(2), 142-164.
Lim, V. (2002). The IT way of loafing on the job: Cyberloafing, neutralizing and organizational justice. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 23(5), 675-694.
Matthews, G., 2008. Personality and information processing: a cognitive-adaptive theory. In: G.J. Boyle, G. Matthews and D.H. Saklofske, eds. Handbook of personality theory and assessment. Volume 1: Personality theories and models. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Matthews, G., & Campbell, S. E. (2009). Sustained performance under overload: personality and individual differences in stress and coping. Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science, 10(5), 417-442.
Minton, E., Gurel-Atay, E., Kahle, L., & Ring, K. (2013). Comparing data collection alternatives: Amazon Mturk, college students, and secondary data analysis. In AMA Winter Educators' Conference Proceedings (Vol. 24).
Mount, M., Ilies, R., & Johnson, E. (2006). Relationship of personality traits and counterproductive work behaviors: The mediating effects of job satisfaction. Personnel Psychology, 59(3), 591–622.
O’Neill, T., Hambley, L., & Bercovich, A. (2014). Prediction of cyberslacking when employees are working away from the office. Computers in Human Behavior, 34, 291-298. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.02.015
O’Neill, T., Hambley, L., & Chatellier, G. (2014). Cyberslacking, engagement, and personality in distributed work environments. Computers in Human Behavior, 40, 152-160. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.08.005
Pee, L., Woon, I., & Kankanhalli, A. (2008). Explaining non-work-related computing in the workplace: A comparison of alternative models. Information & Management, 45(2), 120-130. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2008.01.004
Peters, C., & Malesky Jr, L. (2008). Problematic usage among highly-engaged players of massively multiplayer online role playing games. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 11, 481-484.
Peterson, M. F., Smith, P. B., Akande, A., Ayestaran, S., Bochner, S., Callan, V., ... & Viedge, C. (1995). Role conflict, ambiguity, and overload: A 21-nation study. Academy of Management Journal, 38(2), 429-452.
Preacher, K., Rucker, D., & Hayes, A. (2007). Addressing Moderated Mediation Hypotheses: Theory, Methods, and Prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42(1), 185-227. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00273170701341316
Rizzo, J., House, R., & Lirtzman, S. (1970). Role conflict and ambiguity in complex organizations. Administrative Science Quarterly, 15, 150-163.
Runing, S., Hunik, S., & Cahyadin, M. (2012). The moderate effect of commitment to supervisor and internet expertise on work stressor and employee cyberloafing: The study on employee of local government of Surakarta. Journal of Indonesian Economy & Business, 27, 271-284.
Seo, M. & Hill, N. (2005). Understanding the human side of merger and acquisition: An integrative framework. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 41, 422-443. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0021886305281902
Siegrist, J. and Marmot, M. (2004). Health inequalities and the psychosocial environment – two scientific challenges. Social Science and Medicine, 58, 1463–1473.
Steffy, B. & Jones, J. (1990). Differences between full-time and part-time employees in perceived role strain and work satisfaction. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 11, 321-329. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/job.4030110407
Teo, T. & Lim, V. (1998). Usage and Perceptions of the Internet: What Has Age Got to Do With It?. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 1, 371-381. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cpb.1998.1.371
Tett, R. & Burnett, D. (2003). A personality trait-based interactionist model of job performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88, 500-517. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.3.500
Thoresen, C., Bradley, J., Bliese, P., & Thoresen, J. (2004). The Big Five Personality Traits and Individual Job Performance Growth Trajectories in Maintenance and Transitional Job Stages. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89, 835-853. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.89.5.835
Ugrin, J., & Michael Pearson, J. (2013). The effects of sanctions and stigmas on cyberloafing. Computers in Human Behavior, 29, 812-820
November 15, 2017 Accepted for publication:
November 20, 2017
Introduction
Cyberloafing is defined as the act of voluntarily checking personal emails and surfing websites that are not job-related by employees during stipulated work hours (Lim, 2002). Research estimates that employees spend 60-80% of their internet time during office hours browsing sites that have little to do with their work tasks or responsibilities (Urgin & Pearson, 2013), which reduces organizational performance (Conlin, 2000). Cyberloafing is also a pertinent counterproductive behavior to study because of the recent changes in office environments. It is becoming more common for employees to work remotely for organizations with low supervision, which are conducive to cyberloafing behaviors (O’Neill, Hambley, & Bercovich, 2014, O’Neill, Hambley, & Chatellier, 2014). Thus, understanding potential sources of cyberloafing is important to organizations as it would enable organizations to prudently select people with certain personality traits for certain professions in which working with computers may be inevitable (e.g. IT professions), allocate people with certain personality traits to work in remote work settings, and reduce overall costs associated with low productivity.
Research that focuses on identifying the various antecedents of cyberloafing is complex. Various factors such as emotions, attitudes, social factors, expectations of negative consequences to name a few have been identified as determinants of cyberloafing (Pee, Woon, & Kankanhalli, 2008). Additionally, recent research highlights both personality traits (Jia, Jia, & Karau, 2013; O’Neill et al., 2014) and work role stressors (Henle & Blanchard, 2008) as potential sources of cyberloafing. Although a fair amount of research (Jia et al., 2013; O’Neill et al., 2014; O’Neill et al., 2014) has looked at personality traits, research examining the influence of role stressors on cyberloafing tendencies is limited with the exception of Henle and Blanchard (2008) and Running, Hunik, and Cahyadin (2012). Furthermore, research related to cyberloafing has yet to explore the interaction between these two factors. Exploring these interactions is particularly important as various scholars who research the relationship between personality and job performance/counterproductive behaviors note that the strength of this relationship is modified by situational moderators (e.g. role stressors; Tett & Burnett, 2003). Role stressors are relevant situational moderators to consider because current work environments are dynamic and constantly changing. Employees often find themselves in situations in which they have to manage conflicting expectations (role conflict), deal with uncertainty (role ambiguity) and meet demands within a limited time period (role overload; Arnold, Flaherty, Voss, & Mowen, 2009). Moreover, understanding how personality traits interact with role stressors informs research related to selection of employees within organizations. Precisely, organizations actively select for certain personality traits. For example, extraverts are sought after because they strive for rewards and overtly show a desire to excel. Extraverts are specifically hired in client facing jobs such as retail and sales occupations (Barrick, Stewart, & Piotrowski, 2002). Hence, it is important to examine whether the positive association between certain personality traits and performance will diminish in the presence of role stressors.
The current research adds to the cyberloafing literature by examining how role stressors as situational moderators strengthen or weaken the relationship between personality traits and cyberloafing. As discussed above, a complex set of factors act as determinants of cyberloafing; we propose that examining interactions between primary predictors of cyberloafing will provide us with a nuanced understanding of the boundary conditions within which cyberloafing occurs. Using the personal resource allocation (PRA) framework, the current study examines whether work role stressors moderate the personality-cyberloafing relationships. This framework postulates that performance outcomes (including cyberloafing) can be viewed as an outcome of individual preferences to allocate resources while faced with demands in the workplace (Grawitch, Barber, & Justice, 2010). In the following sections, we discuss previous links between personality traits and cyberloafing, as well as work role stressors and cyberloafing. We then explain how role stressors are anticipated to moderate the effects of personality traits on cyberloafing.
Personality Traits as Antecedents of Cyberloafing
The past decade has seen a surge in studies examining the impact of personality traits on cyberloafing. Recent studies suggest that personality traits of conscientiousness and agreeableness are negatively related to cyberloafing (Andreassen, Torsheim, Pallesen, 2014; Jia et al., 2013). Conscientiousness refers to an individual’s disposition to follow rules and norms (John & Srivastava, 1999). The intrinsic desire to sustain and improve performance is likely to deter individuals high on trait conscientiousness from engaging in withdrawal or deviant behaviors like cyberloafing. Similarly, individuals who are agreeable demonstrate cooperative and trustworthy behavior. This trustworthiness dissuades them from breaching organizational policies and engaging in cyberloafing (Jia et al., 2013).
Alternatively, traits neuroticism and extraversion have been positively linked to cyberloafing (Andreassen et al., 2014; Jia et al. 2013). Individuals who are high on neuroticism tend to be emotionally unstable and anxious. Therefore, these individuals are likely to adopt coping strategies that are avoidant in nature, which may include cyberloafing to avoid work tasks (Andreassen et al., 2014). Extraverts are also vulnerable to cyberloafing because they are more likely to seek out social interactions (Donnellan, Oswald, Baird & Lucas, 2006). The need for being in socially stimulating environments may spur them to seek out social media sites or other sources of entertainment via cyberloafing. Based on these findings, we proposed the following set of hypotheses for personality predictors of cyberloafing:
Hypothesis 1: (a) Conscientiousness and (b) agreeableness are negatively associated with cyberloafing whereas (c) neuroticism and (d) extraversion are positively associated with cyberloafing.
Work Role Stressors as Antecedents of Cyberloafing
Role stressors are other antecedents of cyberloafing, as they are significantly related to a variety of counterproductive work behaviors (Bowling & Eschleman, 2010). According to role theory, balancing tasks due to competing work roles can be cumbersome for employees, resulting in employee stress (Kahn, Wolfe, Quinn, Snoek, Rosenthal, 1964). Specifically, role ambiguity (uncertainty regarding actions needed to fulfill a job role), role overload (excessive role demands in relation to available resources), and role conflict (incompatibility between multiple work expectations) are common workplace stressors. The mechanism by which stressors can lead to counterproductive behavior is via avoidant coping, in which employees attempt to alleviate stress by ignoring problems through distracting activities (Folkman & Lazarus, 1998). Thus, cyberloafing could be an avoidant coping strategy that helps employees temporarily distance themselves from stressful job activities (Henle & Blanchard, 2008).
Although multiple studies have linked these stressors to general counterproductive work behaviors (Bowling & Eschleman, 2010), little research specifically examines cyberloafing behavior. Two studies have shown that role ambiguity and role conflict have a positive correlation with cyberloafing (Running Sawitri, 2012; Henle & Blanchard, 2008), although relationships with role overload are mixed. Specifically, Runing Sawitri (2012) found no relationship between role overload and cyberloafing, while Henle and Blanchard (2008) found that role overload led to less cyberloafing. The negative relationship between role overload and cyberloafing may be due to the high amount of work and demanding deadlines deterring employees from taking breaks (Henle & Blanchard, 2008). Based on past research findings, we proposed the following set of hypotheses for role stressor predictors of cyberloafing:
Hypothesis 2: (a) Role conflict and (b) role ambiguity are positively associated with cyberloafing whereas (c) role overload is negatively associated with cyberloafing.
Work Role Stressors as Moderators of the Personality-Cyberloafing Relationship
Personality and work stressors may also have interactive effects on the occurrence of cyberloafing in the workplace. Research notes that personality traits dictates the manner in which individuals cope with their stressors, and coping strategies such as withdrawing effort (Fox, Spector, & Miles, 2001) are relevant to cyberloafing. Thus, certain personality traits may have different relationship with cyberloafing based on exposure to various work role stressors. To date, no research has examined the combination of personality and work stressor as antecedents that may trigger cyberloafing tendencies, which can provide us with a better understanding of the boundary conditions surrounding the effects of personality on cyberloafing behavior.
Based on the personal resource allocation framework (Grawitch et al., 2010) and conservation of resources theory (Hobfoll, 1989), we expected that role stressors may strengthen the relationship between personality traits and cyberloafing. In efforts to cope with workplace stress, individuals will have fewer resources to override personality tendencies in managing stress. For example, the traits of conscientiousness and agreeableness both have negative links to disengagement strategies (Connor-Smith & Flachbart, 2007). These traits should be more strongly related to less cyberloafing behavior when individuals are under stress. For instance, a conscientious individual is likely to appraise his/her personal resources to fulfill both looming deadlines and completion of projects in the near future (Grawitch et al., 2010). Work stressors are likely to trigger neurotic individuals to adopt disengagement coping strategies. The PRA framework would suggest that these individuals are less likely to have control over personal resources when pressed with demands. They are likely to succumb to actions such as online shopping and playing online games (Peters & Malesky, 2008). However, the link between extraversion and cyberloafing is potentially more complicated, as extraversion is not associated with disengaged coping. But, extraverted employees tend to adopt more social support engagement coping strategies, which may be facilitated by non-work-related communications (i.e., cyberloafing) through social media sites. Based on the PRA framework, we proposed that role stressors (conflict, ambiguity, and overload) moderate the relationship between each personality trait and cyberloafing per the hypotheses listed below.
Hypothesis 3: Role conflict strengthens the relationship between cyberloafing and (a) neuroticism, (b) conscientiousness, (c) extraversion, and (d) agreeableness.
Hypothesis 4: Role ambiguity strengthens the relationship between cyberloafing and (a) neuroticism, (b) conscientiousness, (c) extraversion, and (d) agreeableness.
Hypothesis 5: Role overload strengthens the relationship between cyberloafing and (a) neuroticism, (b) conscientiousness, (c) extraversion, and (d) agreeableness.
Method
Participants and Procedure
This study used an online survey made available on Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk). MTurk is a platform used by researchers to collect data via crowd-sourcing. A few reasons accompany our decision to use Mturk as a platform and to adopt an anonymous survey design to collect data. Firstly, Mturk produces comparable data to other convenience samples in organizations or universities (Landers & Behrend, 2015). Furthermore, in comparison to college samples, Mturk samples closely match the U.S. census data. This representativeness enhances the external validity and the generalizability of the findings obtained from an Mturk sample (Minton, Gurel-Atay, Kahle, & Ring, 2013). Secondly, an anonymous, online survey design may be best suited for soliciting honest responses for sensitive research questions like counterproductive behavior (Kraut, Olson, Banaji, & Bruckman, 2004). Given that counterproductive behaviors are often carried out privately (i.e., employees anticipate punishments from supervisors for such behavior; Ashton, 1998), administering anonymous surveys helps capture better information regarding the actual engagement in these behaviors. Furthermore, past research shows that the results obtained using self-report or other-report (i.e. peer or supervisor ratings) measures of counterproductive behaviors tend to converge (r = .89; Fox, Spector, Goh, & Bruursema, 2007).
Individuals who responded to the survey were provided $0.25 for completing the survey. Measures were introduced in the order of role stressors, cyberloafing items, personality items, and then demographic variables. The final analysis included 343 respondents from an initial recruitment of 373 participants. Twenty-five participants did not respond to all measures, one participant responded “1” to all questions, and four people were removed for indicating they were currently unemployed at the end of the survey (after they were promised compensation regardless of honest responses). The final sample was comprised of both full-time (295; 86.0%) and part-time working adults, and slightly over half of respondents were women (177; 51.6%). The racial composition of the sample was as follows: 242 Whites (70.6%), 30 African Americans (8.7%), 25 Hispanic (7.4%), 31 Asians (9.0%), and 15 Other (4.4%). The average age of participants was 32.45 years (SD = 9.93) and participants’ age ranged from 18 to 68 years. Most respondents reported that they worked in an office environment (309; 90.1%), did not work from home at least some of the time (274; 79.9%), and were not in a managerial role (227; 66.2%).
Measures
Role Stressors. Role conflict and role ambiguity was measured using the validated Role Questionnaire (Rizzo, House and Lirtzman, 1970). The role conflict subscale comprises of eight items (α = .86; e.g., “I work with two or more groups who operate quite differently”). The role ambiguity subscale comprises of six items (α = .86; e.g. “I know what my responsibilities are”-reverse coded item). The response scale ranges from 1 = Strongly disagree to 5 = Strongly agree. Role overload was measured using a role subscale developed by Peterson et al (1995). This measure constitutes of five items (α = .93; e.g. “There is a need to reduce some parts of my role”). The response scale ranges from 1 = Strongly disagree to 5 = Strongly agree. These measures were validated by Rizzo et al., (1970). Role conflict scale was positively associated with conflict and inconsistency scale (r =.50); role ambiguity was negatively correlated with constructs such as goal consensus and clarity (r = -0.49); role overload was validated across countries by Peterson et al., it positively correlated with role conflict (r = 0.33) and role ambiguity (r = 0.44) in samples from 21 different countries.
Cyberloafing. This construct was measured using 21 items (α = .94; e.g. “Viewed sports related websites”) which were previously used by Henle and Blanchard (2008). The response options for each subscale range from 1 = Never to 5 = Constantly. This scale is widely used to measure cyberlaofing behaviors in the workplace (Lim & Chen, 2012) and has sound psychometric properties.
Personality. The subset of the 20-item IPIP measure developed by Donnellan et al., (2006) was used in this study to measure the following Big Five personality traits: neuroticism (4 items; α = .68), conscientiousness (4 items; α = .74), extraversion (4 items; α = .82), and agreeableness (4 items; α = .78). Openness was excluded given it was not relevant to this study’s hypothesis. Participants were required to indicate their responses on response scale that ranges from 1 = Very inaccurate to 5 = Very accurate. The mini-IPIP subscales were validated by Donnellan et al., (2006). The convergent validity between mini-IPIP subscales and the IPIP-FFM subscales are as follows: Extraversion (r = 0.93); Agreeableness (r = 0.89); Conscientiousness (r = 0.90); Neuroticism (r = 0.92).
Control variables. Past research shows that certain demographic variables predict cyberloafing tendencies. Precisely men are more likely to cyberloaf than women (Lim & Chen, 2012); adolescents and young adults are more likely to spend time on the internet when compared to their mature counterparts (Teo & Lim, 1998) and finally full-time employees report higher frequency of engaging in cyberloafing behaviors than part-time employees (Johansson & Gotestam, 2004). Similarly, these demographic variables tend to be associated with our primary predictors and moderators. For instance, some research shows that part-time workers perceive higher levels of work stress in comparison to full-time workers (Steffy & Jones, 1990); younger individuals are likely to be more extraverted and agreeable than their older counterparts (Donnellan & Lucas, 2008). Thus, we anticipated including demographic variables in exploratory analyses if they were associated with both cyberloafing and any of the predictors.
Results
Preliminary Analyses
We conducted all statistical analyses using SPSS software (version 21). Correlations between all variables in the study are reported in Table 1, along with descriptive statistics. In preliminary analyses with demographic variables, only three characteristics (age, gender, and full-time status) were significantly associated with cyberloafing. Age (r = -.18, p < .001) and full-time status (r = .12, p = .013) were negatively associated with cyberloafing. Also, men were more likely to cyberloaf than women (r = .25, p < .001). Additionally, age was positively associated with conscientiousness (r = .16, p = .002) and women reported higher trait neuroticism than men (r = -.19, p <.001). Cyberloafing was not significantly associated with ethnicity, office environment status, working from home status, or managerial status. Thus, only age, full-time status, and gender were included as covariates in the regression analysis for exploratory analyses for hypothesis testing.
Table 1. Correlations and Means/Standard Deviations for All Study Variables.
|
|
Mean |
SD |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
1. Role Conflict |
3.08 |
0.87 |
0.86 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Role Ambiguity |
2.13 |
0.78 |
0.37* |
0.86 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Role Overload |
2.71 |
1.12 |
0.60* |
0.34* |
0.93 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. Neuroticism |
2.65 |
0.88 |
0.30* |
0.24* |
0.30* |
0.68 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. Conscientiousness |
3.70 |
0.88 |
-0.27* |
-0.26* |
-0.25* |
-0.29* |
0.74 |
|
|
|
|
|
7. Extraversion |
2.85 |
1.04 |
-0.09* |
-0.21* |
-0.18* |
-0.25* |
0.07 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
|
8. Agreeableness |
3.66 |
0.86 |
-0.22* |
-0.15* |
-0.24* |
-0.16* |
0.25* |
0.38* |
0.78 |
|
|
|
8. Cyberloafing |
2.11 |
0.75 |
0.24* |
0.07 |
0.21* |
0.16* |
-0.25* |
0.05 |
-0.31* |
0.94 |
|
|
Notes: *p < .05 using one-tailed significance tests for directional hypotheses. Cronbach’s alpha coefficients are reported along the diagonal. N = 343. |
|||||||||||
Hypothesis Testing
We conducted moderated multiple regression analysis for all hypothesis testing. To improve the statistical robustness of our findings, we conducted our analyses both without (Model 1) and with (Model 2) covariates (see Table 2). Only consistent results across both types of analyses were interpreted for hypothesis testing. For both models, we entered personality traits together in a step (tests of Hypothesis 1), role stressors in a step (tests of Hypothesis 2), and mean-centered interaction terms simultaneously in a step (tests of Hypothesis 3-5). Interaction terms were all entered at the same time to (a) determine the unique contribution of each interaction when accounting for all other interactions and (b) reduce Type I error associated with individual tests of interactions in 12 separate regression models.1Simple slope analyses for probing statistically significant moderator effects for were conducted using the Process macro in SPSS (Preacher, Rucker, & Hayes, 2007). We report the simple slope results for Model 1.
Table 2. Moderated Multiple Regression Analyses Predicting Cyberloafing.
|
Model 1: Simultaneous Interactions Without Covariates |
Model 2: Simultaneous Interactions With Covariates |
|||||||
|
Predictors |
β |
B |
SE |
t |
β |
B |
SE |
t |
|
Age |
-0.17 |
-0.01 |
0.01 |
-3.26* |
||||
|
Gender |
0.25 |
0.38 |
0.08 |
4.94* |
||||
|
Work Status |
-0.12 |
-0.26 |
0.11 |
-2.34* |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 1 |
F(3,339) = 13.73* ΔR2 = .108 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Neuroticism |
0.12 |
0.10 |
0.05 |
2.29* |
0.16 |
0.14 |
0.05 |
3.12* |
|
Conscientiousness |
-0.14 |
-0.12 |
0.05 |
-2.71* |
-.011 |
-0.09 |
0.04 |
-2.05* |
|
Extraversion |
0.22 |
0.16 |
0.04 |
4.07* |
0.19 |
0.14 |
0.04 |
3.49* |
|
Agreeableness |
-0.34 |
-0.30 |
0.05 |
-6.23* |
-0.28 |
-0.24 |
0.05 |
-5.02* |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Step 1 |
F(4,338) = 17.85* ΔR2 = .174 |
Step 2 |
F(4,335) = 13.90* ΔR2 = .127 |
|||||
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Role Conflict |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.06 |
1.78* |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.05 |
1.82* |
|
Role Ambiguity |
-0.06 |
-0.05 |
0.05 |
-1.02 |
-0.05 |
-0.04 |
0.05 |
-0.84 |
|
Role Overload |
0.07 |
0.04 |
0.04 |
1.04 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
0.04 |
0.87 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Step 2 |
F(3,335) = 2.70* ΔR2 = .019 |
Step 3 |
F(3,332) = 2.48* ΔR2 = .017 |
|||||
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Neuroticism X Conflict |
0.12 |
0.11 |
.063 |
1.70* |
0.13 |
0.12 |
0.06 |
1.94* |
|
Neuroticism X Ambiguity |
-0.13 |
-0.14 |
.066 |
-2.08* |
-0.13 |
-0.14 |
0.06 |
-2.20* |
|
Neuroticism X Overload |
0.01 |
0.01 |
.045 |
0.11 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
0.04 |
0.17 |
|
Conscientiousness X Conflict |
0.03 |
0.03 |
.069 |
0.45 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
0.07 |
0.64 |
|
Conscientiousness X Ambiguity |
0.06 |
0.06 |
.062 |
0.98 |
0.04 |
0.04 |
0.06 |
0.64 |
|
Conscientiousness X Overload |
-0.12 |
-0.09 |
.053 |
-1.69* |
-0.13 |
-0.10 |
0.05 |
-1.88* |
|
Extraversion X Conflict |
0.11 |
0.08 |
.053 |
1.52 |
0.14 |
0.10 |
0.05 |
1.98* |
|
Extraversion X Ambiguity |
-0.06 |
-0.05 |
.058 |
-0.84 |
-0.07 |
-0.06 |
0.06 |
-1.05 |
|
Extraversion X Overload |
0.12 |
0.07 |
.042 |
1.69* |
0.09 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
1.30 |
|
Agreeableness X Conflict |
-0.24 |
-0.22 |
.067 |
-3.30* |
-0.26 |
-0.24 |
0.07 |
-3.64* |
|
Agreeableness X Ambiguity |
0.02 |
0.02 |
.070 |
0.24 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.07 |
0.28 |
|
Agreeableness X Overload |
0.14 |
0.10 |
.054 |
1.94* |
0.17 |
0.12 |
0.05 |
2.32* |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Step 3 |
F(12,323) = 3.02* ΔR2 = .081 |
Step 4 |
F(12,320) = 3.22* ΔR2 = .081 |
|||||
|
|
||||||||
|
Full Model Statistics |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
F(19, 323) = 2.77* R2 = .275 |
|
F(22,320) = 7.25* R2 = .333 |
||||||
|
Notes: *p < .05 using one-tailed significance tests for directional hypotheses. For gender, men were coded as 1 and women were coded as 0. For full-time status, 1 = working full time and 0 = working part time. N = 343. |
||||||||
Hypothesis 1a and 1b were supported. Conscientiousness and agreeableness were negatively associated with cyberloafing. Hypothesis 1c and 1d were also supported. Neuroticism and extraversion were positively associated with cyberloafing. Among the workplace stressors, only role conflict emerged as significant positive predictor of cyberloafing. Thus, Hypothesis 2b was supported, but Hypotheses 2a (role ambiguity) and 2c (role overload) were not supported.
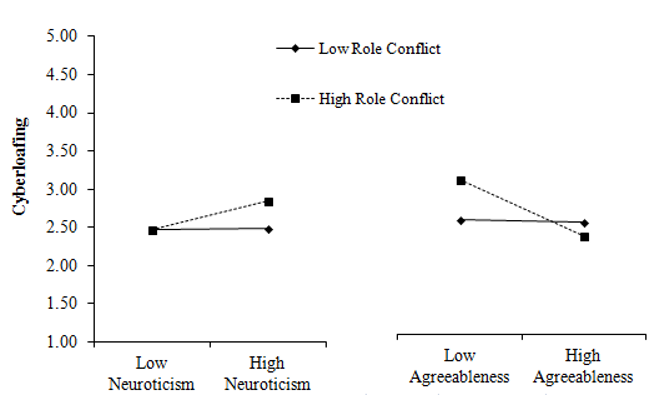
Hypotheses 3-5 proposed interactions between personality traits and role stressors in predicting cyberloafing. First, role conflict moderated the relationship between two personality traits and cyberloafing (see Table 2, Figure 1): neuroticism and agreeableness.2 Specifically, neuroticism was more strongly linked to cyberloafing among those who experienced high role conflict (β = .17, p = .023) compared to those with low role conflict (β = -.03, p = .662). Agreeableness was also more strongly linked to cyberloafing among those reporting high role conflict (β = -.54, p < .001) compared to those with low role conflict (β = -.10, p = .222). Thus, there was some support for Hypothesis 3a (neuroticism x role conflict interaction) and 3d (agreeableness x role conflict interaction). However, 3b (extraversion x role conflict interaction3) and Hypothesis 3b (conscientiousness x role conflict interaction) were not supported.
Figure 1: Role conflict moderating the effect of two personality traits
(neuroticism and agreeableness) on cyberloafing. Simple slopes effects are plotted
at one standard deviation above and below the mean.
Role ambiguity only moderated the relationship between neuroticism4 (see Table 2, Models 1 and 2); however, the moderation effect was the opposite of what was expected (see Figure 2). Specifically, neuroticism was more strongly linked to cyberloafing among individuals experiencing low role ambiguity (β = .19, p = .016) than those experiencing high ambiguity (β = -.05, p = .499). Thus, there was a lack of evidence supporting Hypothesis 4a-d; none of the personality traits interacted with role ambiguity to predict cyberloafing in the expected direction.
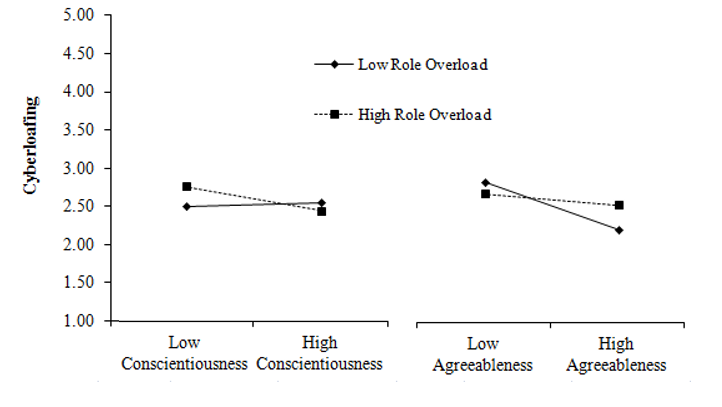
Finally, role overload moderated the relationships between two personality traits and cyberloafing (see Table 2, Figure 3): conscientiousness and agreeableness.5 As expected, conscientiousness was more strongly associated with cyberloafing among individuals experiencing high role overload (β = -.23, p = .007) compared to those with low overload (β = -.001, p = .988). However, the moderation effect was the opposite of what was expected for agreeableness. Agreeableness was more strongly linked to cyberloafing among individuals experiencing low role overload (β = -.46, p < .001) compared to those experiencing high role overload (β = -.19, p = .030). Thus, only Hypothesis 5b (conscientiousness x role overload interaction) was supported. Hypothesis 5c (extraversion x role overload interaction6), Hypothesis 5a (neuroticism x role overload interaction) and 5d (agreeableness x role overload interaction) were not supported.
Figure 2: Role ambiguity moderating the effect of neuroticism on cyberloafing.
Simple slopes effects ar plotted at one standard deviation above and below the mean.
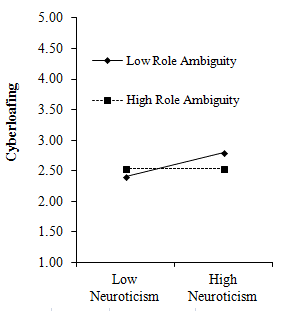
Figure 3: Role overload moderating the effect of two personality traits
(conscientiousness and agreeableness) on cyberloafing. Simple slopes effects are plotted
at one standard deviation above and below the mean.
Discussion
Cyberloafing is a prevalent and often counterproductive behavior in today’s work environment. Thus, it is important to understand factors that are associated with this type of behavior. The existing literature has suggested that some personality traits and role stressors predict cyberloafing. Consistent with past research (Jia et al., 2013; O’Neill et al., 2014), our findings replicate results showing that trait neuroticism and trait extraversion positively predicted cyberloafing, whereas trait conscientiousness and agreeableness negatively predicted cyberloafing. Also, similar to past research (Henle & Blanchard, 2008; Running & Cahyadin, 2012) our results replicated the finding that role conflict positively predicts cyberloafing. However, the two other role stressors (role ambiguity and role overload) did not emerge as significant predictors of cyberloafing in our study. Thus, more work is needed to determine if role ambiguity and role overload can be reliably linked to cyberloafing behavior in future research samples.
Past research cautions us that the link between personality traits and job performance/counterproductive behavior tends to be weak and inconsistent (Koelega, 1992; Matthews, 2008). These scholars speculate that these weak and inconsistent relationships could be attributed to the possibility that a host of moderators (e.g. role stressors) influences these relationships. They note that testing interactive effects is key to theory building. The strongest contribution of this study was our focus on investigating potential interactions among personality traits and role stressors. Such investigations are warranted to gain a better understanding of the role stressor conditions under which personality traits are more likely be linked to cyberloafing behavior. Based on the PRA framework, we expected that role stressors (i.e., conflict, ambiguity, and overload) would strengthen the relationship between personality traits (i.e., neuroticism, conscientiousness, extraversion, and agreeableness) and cyberloafing. However, our findings found mixed and often weak support for PRA framework predictions. Out of twelve potential interactions, only three interactions were statistically robust in the expected direction: role conflict strengthening the positive association between neuroticism and cyberloafing, role conflict strengthening the negative association between agreeableness and cyberloafing, and role overload strengthening the negative association between conscientiousness and cyberloafing. Three other interactions (role conflict x neuroticism, role conflict x extraversion, and role overload x agreeableness) received support in some analyses but not others (i.e., when testing all interactions simultaneously or individually with or without covariates). Thus, we interpret these results with more caution. Altogether, these findings provide only weak support for the PRA framework assertion individuals with certain personality traits allocate their resources differentially based on role stressors.
It is also worth noting that two interaction results were in the opposite direction than anticipated based on the PRA framework. More role ambiguity tended to weaken the positive relationship between neuroticism and cyberloafing. That is, workers high on neuroticism were less likely to cyberloaf under conditions of high ambiguity. A plausible reason for Additionally, high role overload weakened the negative relationship between agreeableness and cyberloafing. Given that these results are counter to predictions, they must be interpreted with caution until they are replicated in future research.
Implications for Theory and Practice
The findings of this study provide some preliminary yet mixed support for PRA framework and role theory by illustrating that some personality tendencies that predict cyberloafing behavior are exacerbated by the influence of organizational stressors. One theoretical implication is that there was a lack of consistency regarding what specific role stressor enhanced personality-cyberloafing relationships. Role conflict, role ambiguity, nor role overload emerged as a stressor that reliably produced the proposed effects. Another theoretical implication from our results is that we observed rather weak interaction effects in terms of effect sizes; even the statistically robust findings ranged from .13 to .26. Given that many less robust findings were also in the anticipated direction according to theory, it is possible that the expected effects could be detected in extremely large sample sizes. Nevertheless, such weak effects may be of limited practical significance when they are difficult to detect in even a large sample sizes such as this study (i.e., well over 300 participants). Future researchers wishing to test the PRA framework with similar methodology and measures should consider larger sample sizes to replicate these results.
In terms of practical implications, the findings of the current research can inform personnel selection by suggesting that stressors in the work environment may change how personality traits are linked to counterproductive work behavior—specifically cyberloafing. Organizations often use personality testing as a way to select top performers, including trying to detect and exclude individuals likely to engage in counterproductive behaviors (Mount, Ilies, & Johnson, 2006). Although, past research shows that traits such as agreeableness predict less counterproductive behavior (Thoresen, Bradley, Bliese, & Thoresen, 2004), our results suggest that these links may be weaker when employees experience more role stressors such as role ambiguity (but stronger under high conditions of role conflict).
These findings are also important for organizational training and development because work role stressors are ubiquitous. For example, major changes within the organization tend to alter the existing job roles for many employees leading to more role ambiguity, conflict, and overload (Seo & Hill, 2005; Marks & Mirvis, 1992). Hence organizations may want to invest in role stressor interventions that can help alleviate issues surrounding employee cyberloafing. For example, allowing employees to participate in decision making (Jackson, 1983) may effectively reduce role conflict in the workplace. Primary interventions targeting how work is structured, including clear guidelines and policies, can also help reduce role overload and role ambiguity (Kossek, Hammer, Kelly, & Moen, 2014).
Future Directions and Limitations
Although the current research highlighted a few interesting findings, this study is only compelling preliminary data. Thus, there are a number of limitations to consider when interpreting these findings. Our study used a convenience sample to examine the effects of personality traits and role stressors on cyberloafing behavior. Even though Mturk participants are more representative of the general population when compared to college students (Minton et al., 2013), it must be noted that some characteristics of the Mturk sample may not be consistent with the other aspects of the U.S. adult working population (i.e.., more internet users or technologically savvy individuals). Thus, there may have been characteristics of the Mturk sample that may have moderated or influenced the conclusions we present in this paper, which limits the extent to which we can generalize these results to all workers. Like other convenience samples, this sample is also prone to selection bias; it is possible participants who chose to participate based the recruitment statement are different than those who opted out of the study. To establish further confidence in these results, replication studies using other populations and methodologies are needed. Although having employees from a wide variety of organizational or occupational settings was a strength of the current sample, perhaps more systematic investigation into whether these results hold for different types of occupations would be illuminating. Future research can triangulate these results by conducting experimental studies that temporarily manipulate role stressors in a laboratory setting or observational studies that observe actual cyberloafing behaviors. For instance, a common method used to increase task/work overload is to subject participants to a “rapid information processing task”. In such a task, participants are required to process about 100-150 stimuli within a minute (Matthews & Campbell, 2009). Furthermore, we have made suggestions based on past theory and findings that role stressors promote emotional coping; however, we did not directly measure the style of coping among participants. Future research may focus on measuring styles of coping mechanisms in addition to administering self-report measures related to role stressors. Similarly, past research also emphasized the role of appraisal in engagement of counterproductive behavior. Research shows that the extent to which performance suffers is contingent on the extent to which individuals appraise the stressor as a threat, challenge or difficult to control (Siegrist and Marmot 2004). Hence, future research that investigates the role of appraisal in the moderating effects of role stressors on the personality and counterproductive behavior may help throw light on some of the inconsistent interaction effects we witness in this study. For instance, future research could possibly shed light on the inconsistent effect- individuals high on trait neuroticism were less likely to cyberloaf when faced with role ambiguity. It is possible that these individuals may perceive certain role stressors as a threat than as a challenge and hence direct all their resources towards coping with the stressor in a task focused manner.
Another limitation of this study is that we only explored cyberloafing behavior from the traditional perspective of a counterproductive work behavior. Yet some research (Lim & Chen, 2012; Krischer, Penny, & Hunter, 2010) suggests that there are sometimes positive consequences of engaging in these types of behavior. For instance, Lim and Chen (2012) found that browsing websites was associated with more positive affect among research participants. Similarly, temporarily withdrawing from work can employees alleviate emotional exhaustion (Krischer et al., 2010). Thus, future research should distinguish between cyberloafing behaviors that represent actual counterproductively versus short term breaks that could improve performance in the long-term.
Conclusion
In sum, this study provides partial support of the PRA framework in that some role stressors strengthened the relationship between some personality traits and cyberloafing behaviors. However, there was overall mixed and somewhat weak support for our predictions, including a lack of consistency in a specific role stressor enhancing personality-cyberloafing relationships. These preliminary results suggest that more work is needed to explore the interplay between personality and work stressors in predicting counterproductive behavior (i.e., cyberloafing) instead of focusing on main effects common in past research. An interactive approach can help provide more information regarding the boundary conditions under which personality tendencies lead to negative work behaviors.
Notes
1 For comparison, exploratory analyses for individual interaction effects analyses with and without covariates are also presented in the footnotes.
2 The role conflict-neuroticism interaction effect was not statistically significant in individual interaction models without (p = .178) nor with (p = .099) covariates. The role conflict-agreeableness interaction effect was also statistically significant in individual interaction models without (p = .012) and with (p = .009) covariates.
3 In Model 2 only, the interaction between role conflict and extraversion (p = .025) was also in the anticipated direction. Extraversion had a stronger relationship with cyberloafing among those who experienced high levels of role conflict (β = .35, p < .001) than those with low levels of conflict (β = .10, p = .092). The role conflict-extraversion interaction effect was also statistically significant in individual interaction models without covariates (p = .049), but not with covariates (p = .053).
4 The role ambiguity-neuroticism interaction effect was also statistically significant in individual interaction models without (p = .029) and with (p = .048) covariates.
5 The role overload-conscientiousness interaction effect was also statistically significant in individual interaction models with (p = .039) covariates, but not without covariates (p = .070). The role overload-extraversion was also statistically significant in individual interaction models without (p < .001) and with (p < .001) covariates. Lastly, the role overload-agreeableness interaction effect was not significant in individual interaction models without (p = .555) nor with (p = .516) covariates.
6 In Model 2 (Table 2), this interaction was statistically significant (p = .046) in the anticipated direction. Specifically, extraversion was also more strongly related to cyberloafing among individuals with high role overload (β = .38, p < .001) compared to those with low role overload (β = .15, p = .063). This finding also held in individual interaction models with and without covariates (p < .001).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2017 Lebena Varghese, Larissa K. Barber


