Discovering Unique Profiles of Adolescent Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Use: Are ICT Use Preferences Associated with Identity and Behaviour Development?
Vol.11,No.4(2017)
Over the course of the last seven years, the average weekly screen-time of youth has dramatically increased. The present study was designed to better understand how young people utilise multiple types of information and communication technology (ICT) in their everyday lives and how these preferences may be associated with key aspects of their development. To this end, the present study was designed to explore whether specific profiles of technology usage would be associated with key characteristics of identity and behaviour. To identify groups of adolescents who share similar technology use habits, a sample of 933 adolescents reported on their time spent interacting with various digital communication devices and associated platforms. Utilizing a latent profile analysis, four distinct profiles of technology use preferences emerged. Then, a series of linear regressions were calculated to investigate the degree to which class membership predicted indicators of identity and problem behaviours. The findings suggest that important concepts of both identity and behaviour are associated with individual ICT usage preferences. Acknowledging the cross-sectional nature of the data, it is suggested that the impact of clusters of communication technology use on adolescent development should be investigated with longitudinal data.
Technology; adolescence; identity; behaviour; development
Anna Kurek
Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand
Anna Kurek is a PhD candidate at Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand studying clinical and
developmental psychology. She previously received her Masters of Science in applied clinical psychology in the
UK. Anna’s research interest are focused on personality and cyber psychology, in particular how youth
development and identity formation is impacted by the use of Internet technologies.
Paul E. Jose
Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand
Paul Jose is a Professor of Psychology in the School of Psychology at Victoria University of Wellington in New
Zealand. He received his PhD in developmental psychology from Yale University in 1980, and has taught and
conducted research in the area of social development in his career. Recent work has included examination of
adolescents' use of digital communication platforms.
Jaimee Stuart
Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand
Jaimee Stuart is a Lecturer in the School of Applied Psychology at Griffith University, Australia and an Adjunct
Fellow at Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand. Jaimee's research areas span cultural and
developmental Psychology with a specific focus on adolescence identity in multicultural contexts and
interpersonal relationships for young people online and offline.
Bee, H. L. (1992). The developing child. London: HarperCollins.
Berusch, A. (2016). “You don’t want to seem more into the conversation”: Texting identity, conflict, and maintenance in early romantic relationships [Undergraduate Honors Theses]. Retrieved from https://scholar.colorado.edu/honr_theses/1176/
Broughton, J. M. (1981). The divided self in adolescence. Human Development, 24, 13-32. https://doi.org/10.1159/000272621
Brown, J. D., & Bobkowski, P. S. (2011). Older and newer media: Patterns of use and effects on adolescents' health and well-Being. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21, 95-113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532- 7795.2010.00717.x
Buckels, E. E., Trapnell, P. D., & Paulhus, D. L. (2014). Trolls just want to have fun. Personality and Individual Differences, 67, 97-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.01.016
Carli, V., Durkee, T., Wasserman, D., Hadlaczky, G., Despalins, R., Kramarz, E., … Kaess, M. (2013). The association between pathological Internet use and comorbid psychopathology: A systematic review. Psychopathology, 46, 1-13 https://doi.org/10.1159/000337971
Christensson, P. (2010, January 4). ICT Definition. Retrieved from https://techterms.com
Collishaw, S., Maughan, B., Goodman, R., & Pickles, A. (2004). Time trends in adolescent mental health. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45, 1350-1362. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00335.x
Crocetti, E., Rubini, M., Luyckx, K., & Meeus, W. (2008). Identity formation in early and middle adolescents from various ethnic groups: From three dimensions to five statuses. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 37, 983-996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-007-9222-2
Cyr, B., Berman, S. L., & Smith, M. L. (2012). The role of communication technology in adolescent relationships and identity development. HIM Child & Youth Care Forum, 44, 79-92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-014-9271-0
Dayton, T. (2009). Creating a false self: Learning to live a lie. Retrieved from http://www.huffingtonpost.com/dr- tian-dayton/creating-a-false-self-lea_b_269096.html
DeLisi, M., Vaughn, M. G., Gentile, D. A., Anderson, C. A., & Shook, J. J. (2012). Violent video games, delinquency, and youth violence. Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice, 11, 132-142. https://doi.org/10.1177/1541204012460874
Department of Health Washington State. (2002). Healthy Youth Survey 2002-2004. Retrieved from https://www.doh.wa.gov/Portals/1/Documents/Pubs/160-NonDOH-HealthyYouthSurvey-Form-a2002.pdf
Erikson, E. H. (1956). The problem with ego identity. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 4, 56-121. Erikson, E. H. (1963). Youth: Change and challenge. New York, NY: Basic books.
Fredriksen, K., Rhodes, J., Reddy, R., & Way, N. (2004). Sleepless in Chicago: Tracking the effects of adolescent sleep loss during the middle school years. Child Development, 75, 84-95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467- 8624.2004.00655.x
Garcia, D., & Sikström, S. (2014). The dark side of Facebook: Semantic representations of status updates predict the Dark Triad of personality. Personality and Individual Differences, 67, 92-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2013.10.001
Gentile, D. A., Choo, H., Liau, A., Sim, T., Li, D., Fung, D., & Khoo, A. (2011). Pathological video game use among youths: A two-year longitudinal study. Pediatrics, 127(2), 319-329. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-1353
Gil-Or, O., Levi-Belz, Y., & Turel, O. (2015). The "Facebook-self": Characteristics and psychological predictors of false self-presentation on Facebook. Frontiers in Psychology, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00099
Gini, G. (2006). Social cognition and moral cognition in bullying: What's wrong? Aggressive Behaviour, 32, 528-539. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20153
GLSEN, CiPHR, & CCRC. (2013). Out online: The experiences of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender youth on the Internet. New York: GLSEN.
Goth, K., Foelsch, P., Schlüter-Müller, S., Birkhölzer, M., Jung, E., Pick, O., & Schmeck, K. (2012). Assessment of identity development and identity diffusion in adolescence - Theoretical basis and psychometric properties of the self-report questionnaire AIDA. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health, 6(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1753-2000-6-27
Hickerson, B., & Mowen, A. J. (2012). Behavioral and psychological involvement of online video gamers: Building blocks or building walls to socialization? Loisir et Société / Society and Leisure, 35, 79-103. https://doi.org/10.1080/07053436.2012.10707836
Holtz, P., & Appel, M. (2011). Internet use and video gaming predict problem behaviour in early adolescence. Journal of Adolescence, 34, 49-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2010.02.004
Ito, M., Baumer, S., Bittanti, M., Cody, R., Stephenson, B. H., Horst, H. A., ... & Perkel, D. (2010). Hanging out, messing around, and geeking out: Kids living and learning with new media. Retrieved from https://dourish.com/~dourishc/classes/readings/HorstHerr-StephensonRobinson.pdf
Jose, P. E., Ryan, N., & Pryor, J. (2012). Does social connectedness promote a greater sense of well-being in adolescence over time? Journal of Research on Adolescence, 22, 235-251. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532- 7795.2012.00783.x
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social Media. Business Horizons, 53, 59-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2009.09.003
Kelishadi, R., Qorbani, M., Motlagh, M. E., Heshmat, R., Ardalan, G., & Jari, M. (2015). Relationship between leisure time screen activity and aggressive and violent behaviour in Iranian children and adolescents: The
CASPIAN-IV Study. Paediatrics and International Child Health, 35, 305-311. https://doi.org/10.1080/20469047.2015.1109221
Kernberg, O. F. (1985). Borderline conditions and pathological narcissism. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
Ko, C., Yen, J., Yen, C., Chen, C., & Chen, C. (2012). The association between Internet addiction and psychiatric disorder: A review of the literature. European Psychiatry, 27(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2010.04.011
Larson, R. W., Wilson, S., Brown, B. B., Furstenberg, Jr., F. F., & Verma, S. (2002). Changes in adolescents' interpersonal experiences: Are they being prepared for adult relationships in the twenty-first century? Journal of Research on Adolescence, 12, 31-68. https://doi.org/10.1111/1532-7795.00024
Lemmens, J. S., Valkenburg, P. M., & Peter, J. (2011). The effects of pathological gaming on aggressive behaviour. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 40, 38-47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-010-9558-x
Lenhart, A., Madden, M., Smith, A., Purcell, K., Zickuhr, K., & Rainie, L. (2011). Teens, kindness and cruelty on social network sites. Pew Internet and American Life Project. Retrieved from http://pewinternet.org/~/media//Files/Reports/2011/PIP_ Teens_Kindness_Cruelty_SNS_ Report_Nov_2011_FINAL_110711.pdf
Lenhart, A. (2015). Teens, Social Media & Technology Overview 2015. Pew Research Center. Retrieved from http://www.pewinternet.org/2015/04/09/teens-social-media-technology-2015
Marcia, J. E. (1966). Development and validation of ego-identity status. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 3, 551-558. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0023281
Martin K. (2011). Electronic overload: The impact of excessive screen use on child and adolescent health and wellbeing. Perth, Western Australia: Department of Sport and Recreation.
McCain, J. L., Borg, Z. G., Rothenberg, A. H., Churillo, K. M., Weiler, P., & Campbell, W. K. (2016). Personality and selfies: Narcissism and the Dark Triad. Computers in Human Behaviour, 64, 126-133.
Menesini, E., Sanchez, V., Fonzi, A., Ortega, R., Costabile, A., & Lo Feudo, G. (2003). Moral emotions and bullying: A cross-national comparison of differences between bullies, victims and outsiders. Aggressive Behaviour, 29, 515-530 https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.10060
Messias, E., Castro, J., Saini, A., Usman, M., & Peeples, D. (2011). Sadness, suicide, and their association with video game and Internet overuse among teens: Results from the Youth Risk Behaviour Survey 2007 and 2009. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behaviour, 41, 307-315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1943-278x.2011.00030.x
Michikyan, M., Dennis, J., & Subrahmanyam, K. (2015). Can you guess who I am? Real, ideal, and false self- presentation on Facebook among emerging adults. Emerging Adulthood, 3, 55-64. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696814532442
Milani, L., Camisasca, E., Caravita, S. C., Ionio, C., Miragoli, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2015). Violent video games and children’s aggressive behaviours. SAGE Open, 5(3), 215824401559942. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244015599428
Muthén, B. & Muthén, L. (2000). Integrating person-centered and variable-centered analysis: Growth mixture modeling with latent trajectory classes. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 24, 882-891.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. (2015). Mplus: Statistical analysis with latent variables: User's guide (7th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Nyarko, K. (2012). The influence of peer and parent relationships on adolescents’ self esteem. Ife Psychologia, 20(2), 161.
O'Loughlin, J., Lambert, M., Gauvin, L., Kestens, Y., & Daniel, M. (2008). Many teens spend 30 hours a week on 'screen time' during high school. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/03/080312172614.htm
Ong, E. Y., Ang, R. P., Ho, J. C., Lim, J. C., Goh, D. H., Lee, C. S., & Chua, A. Y. (2011). Narcissism, extraversion and adolescents’ self-presentation on Facebook. Personality and Individual Differences, 50(2), 180-185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.09.022
Pew Research Center. (2015). Internet seen as positive influence on education but negative on morality in emerging and developing nations. Retrieved from http://www.pewglobal.org/2015/03/19/internet-seen-as-positive- influence-on-education-but-negative-influence-on-morality-in-emerging-and-developing-nations/
Ray, M., & Jat, K. R. (2010). Effect of electronic media on children. Indian Pediatrics, 47, 561-568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-010-0128-9
Rideout, V. J., Foehr, U. G., & Roberts, D. F. (2010). Generation M2: Media in the lives of 8- to 18-year-olds. Retrieved from http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED527859.pdf
Rideout, V., Pai, S., & Saphir, M. (2015). The Common Sense census: Media use by tweens and teens. Common Sense Media. Retrieved from: https://www.commonsensemedia.org/sites/default/files/uploads/research/census_researchreport.pdf
Romer, D., Bagdasarov, Z., & More, E. (2013). Older versus newer media and the well-being of United States youth: Results from a national longitudinal panel. Journal of Adolescent Health, 52, 613-619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2012.11.012
Rosen, L.D., Whaling, K., Rab, S., Carrier, L.M., & Cheever, N.A. (2013). Is Facebook creating ‘‘iDisorders’’? The link between clinical symptoms of psychiatric disorders and technology use, attitudes and anxiety. Computers in Human Behaviour, 29, 1243-1254.
Rosenberg, M. (1965). Society and the adolescent self-image. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Rubin, A. M. (1994). Media uses and effects: A uses-and-gratifications perspective. In J. Bryant & D. Zillmann (Eds.), LEA's communication series. Media effects: Advances in theory and research (pp. 417-436). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Sartain, A. Q., North, A. J., Strange, J. R., & Chapman, H. M. (1973). The self and behaviour. In Psychology: Understanding human behaviour (pp. 88-126). Retrieved from https://archive.org/stream/psychologyunders033255mbp/psycho logyunders 033255 mbp_djvu.txt
Scott, J., & Porter-Armstrong, A. P. (2013). Impact of multiplayer online role-playing games upon the psychosocial well-being of adolescents and young adults: Reviewing the evidence. Psychiatry Journal, 2013, article 464685. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/464685
Schwartz, S. J., Beyers, W., Luyckx, K., Soenens, B., Zamboanga, B. L., Forthun, L. F., & Waterman, A. S. (2011). Examining the light and dark sides of emerging adults’ identity: A study of identity status differences in positive and negative psychosocial functioning. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 40, 839–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-010-9606-6
Schwartz, S. J., Zamboanga, B. L., Weisskirch, R. S., & Rodriguez, L. (2009). The relationships of personal and ethnic identity exploration to indices of adaptive and maladaptive psychosocial functioning. International Journal of Behavioural Development, 33, 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025408098018
Scott, J., & Porter-Armstrong, A. P. (2013). Impact of multiplayer online role-playing games upon the psychosocial well-being of adolescents and young adults: Reviewing the evidence. Psychiatry Journal, 2013, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/464685
Shyam, R., & Bhoria, A. (2011). Information technology (Internet): Effects on social participation and well-being of users. Journal of the Indian Academy of Applied Psychology, 37, 157-162.
Tsang, J. (2002). Moral rationalization and the integration of situational factors and psychological processes in immoral behaviour. Review of General Psychology, 6, 25-50. https://doi.org/10.1037//1089-2680.6.1.25
Weir, K. F., & Jose, P. E. (2010). The perception of false self scale for adolescents: Reliability, validity, and longitudinal relationships with depressive and anxious symptoms. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 28, 393-411. https://doi.org/10.1348/026151009x423052
Woods, H. C., & Scott, H. (2016). #Sleepyteens: Social media use in adolescence is associated with poor sleep quality, anxiety, depression and low self-esteem. Journal of Adolescence, 51, 41-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.05.008
Editorial Record:
First submission received:
May 30, 2017
Revision received:
November 11, 2017
Accepted for publication:
December 15, 2017
Introduction
It has long been reported that young people’s lives are shaped by the interactions they maintain within their multiple social worlds (Ito et al., 2010; Larson, Wilson, Brown, Furstenberg, & Verma, 2002). Today, as a result of the proliferation of communication technology, many of these social worlds exist online. Research indicates that the average weekly screen-time of youth has increased by 43 hours in the last few years, suggesting that adolescents now spend approximately 11 hours a day interacting with a digital media device (O’Loughlin, Lambert, Gauvin, Kestens, & Daniel, 2008; Rideout, Foehr, & Roberts, 2010; Rideout, Pai, & Saphir, 2015). Some research has showcased the social and educational benefits that come from teenager technology use (GLSEN, CiPHR, & CCRC, 2013; Hickerson & Mowen, 2013; Pew Research Center, 2015), however, more numerous studies have attributed negative and deteriorating mental health to the increasingly ubiquitous digital media consumption amongst adolescents (Martin, 2011; Messias, Castro, Saini, Usman, & Peeples, 2011; Rosen, Whaling, Rab, Carrier, & Cheever, 2013). Despite these initial and, in some cases, mixed findings, current understanding of how access to, and interaction with, technology impacts on our youth’s development is impoverished. The present study was designed to help fill this gap in the literature, and investigate whether adolescents’ involvement with digital media is harmful, helpful, or perhaps benign.
Young people’s ability to access and interact with media content and person-to-person communication through internet-enabled digital devices, applications, and services is vast and seems to be continually increasing. Indeed, the expansion of digital devices in the home, school, and wider community has enabled a variety of new entertainment and socialization options, all of which have led children and youth to be far more digitally connected than the generations before them. The steady proliferation of the use of the Internet in daily life has resulted in earlier childhood exposure to the use of digital devices such as tablets and smartphones, as well as a wide number of services and applications like digital online games, video messaging software such as Facetime and Skype, and social media outlets such as Facebook and Instagram. This exposure is often facilitated through parenting behaviours involving educational software or posting photos of the family or offspring on social media. One can thus speculate that this exposure, as well as parental media behaviours, may facilitate a primary interest or preference towards particular digital media usage, which may then be further shaped throughout adolescence by individual peer groups.
Impacts of Technology Use on Youth Mental Health
In recent years a niche area of research has begun to document digital communication and media use among youth in an attempt to identify how usage patterns impact on relevant outcomes. Information and communication technology (ICT) primarily focuses on different modes of Internet use, cell phones, and other mobile and communication mediums (Christensson, 2010). ICT preferences have recently been documented by Lenhart (2015) and show that while some adolescents spend more time accessing social networking sites, others show a predilection towards video games, streaming videos, or consuming large amounts of other digital media. Moreover, 91% of American teens aged between 12 and 15 years report using their mobile device to go online, and just as many send text messages (Lenhart, 2015). These data suggest that unique profiles of preferences might exist for specific patterns or styles of ICT use among adolescents. Associations of these preferences with behavioural outcomes, however, remains relatively understudied. Some existing research, however, suggests that social media activity can contribute to anxiety, depression, and low self esteem in adolescence (Fredriksen, Rhodes, Reddy, & Way, 2004; Woods & Scott, 2016). Specific Facebook activities, such as status updates and frequency of likes and comments, have exhibited significant relationships with social anxiety and extraversion (Garcia & Sikström, 2014; Ong et al., 2011). Other social media activities like taking and posting pictures of oneself (i.e., selfies) have been linked to elevated rates of narcissism (McCain et al., 2016).
Social media use, however, is only one dimension of adolescent digital media consumption, and research into the effects of gaming suggests that there are psychological and behavioural impacts of video game usage during adolescence. For example, engagement in violent video game play has been linked to antisocial behaviour, higher degrees of externalizing behaviours, aggression, depression, reduced academic performance, as well as elevated psychopathy among adolescent samples (DeLisi, Vaughn, Gentile, Anderson, & Shook, 2012; Milani et al., 2015). Other research has linked cyber-trolling activity (i.e., unprovoked hostile, destructive, or disruptive online behaviour) to indices of sadism, deriving pleasure from other people’s pain or humiliation, and Machiavellianism, where personal gain is put above normative societal principles of equality (Buckels, Trapnell, & Paulhus, 2014).
The research on social media, particularly hostile social cyber behaviour, and online gaming provides important preliminary findings that illustrate the significance of understanding the interconnectedness between adolescent well-being and the digital world they inhabit. This research suggests that ICT use may be significantly associated with individual identity as well as a variety of behavioural outcomes of adolescents. The present study was motivated by the ‘uses and gratifications’ approach that emphasizes the importance of viewing the adolescent as an active consumer of ICT and media (Paik et al., 2001; Rubin, 1993) and the belief that what is presently missing in the field is a person-centered analysis to determine how specific ICT behaviours may or may not cluster together and predict important outcomes. The present study was designed to better understand how young people utilise multiple types of ICT in their everyday lives and how these preferences may be associated with important indices of development.
Information and Communication Technology and Identity Development
Identity is the process of defining oneself as an individual who knows and understands who they are, what they value, and their unique direction in life (Erikson, 1956). Securing a strong self-identity can be accomplished through the creation of personal relationships outside of the family unit, developing awareness of one's sexual orientation, and by exploring the impact of ethnic and cultural identity. Forming awareness and understanding of these various facets of self in adolescence are an integral component of identity commitment (Erikson, 1956; Marcia, 1966) and they ensure that teens avoid identity confusion, lack of direction, and an ill definition of self. Decreasing identity confusion during the developmental stage of adolescence prepares youth for emerging adult experiences and responsibilities by setting the necessary foundation for future stages of adulthood (Erikson, 1956).
The process of reaching self-understanding in adolescence requires a coming together of separate traits into larger, abstract ones, with an aim to gradually combine these characteristics into one holistic organized system (Bee, 1992; Erikson, 1963). The mechanism by which this system is achieved includes identity exploration, the process of trying out different roles, activities, or interests, while actively questioning and evaluating a multitude of identity options. These dynamics are seen to eventually lead to identity commitment, the point at which the adolescent commits to certain aspects of the self (Marcia, 1966).
While there are several benefits associated with identity commitment, such as higher self esteem, life satisfaction, and decreased symptoms of depression and anxiety (Crocetti, Rubini, Luyckx, & Meeus, 2008; Schwartz et al., 2011), studies have shown that identity exploration is frequently associated with identity confusion and a lack of certainty about one’s identity (Schwartz et al., 2011; Schwartz, Zamboanga, Weisskirch, & Rodriguez, 2009). This lack of certainty can result in the creation of a false self, a protective mask meant to diffuse the discrepancy between the adolescents’ perceptions of who they are as opposed to how they believe they are perceived by other important people (Broughton, 1981; Dayton, 2009; Goth et al., 2012; Kernberg, 1985). The false self may initially be used to ward off anxiety or feelings of inferiority, but in some instances can become so well accepted that it is compulsive and unconscious as the adolescent loses sight of rectifying the discrepancies between the false and true selves (Dayton, 2009; Sartain, North, Strange, & Chapman, 1973).
Communication technology provides adolescents with a growing number of options for self-exploration, and studies have begun to suggest that the integrity of adolescent self-concept can greatly influence the way youth represent themselves online, specifically on the social networking platform Facebook (Gil-Or, Levi-Belz, & Turel, 2015). For example, identity state and psychosocial well-being in particular have been found to be negatively associated with presentations of the ideal and false selves through Facebook activity, whereas, for example, self esteem has been reported as being positively associated with representations of the authentic self on Facebook (Gil-Or et al. ; Michikyan, Dennis, & Subrahmanyam, 2015). Today’s youth spend a significant amount of time online, and recent research has suggested that this involvement may lend itself to living two different lives, with some youth confessing to sharing a different self offline (i.e., face-to-face) compared to the one they believe they share online (Kaplan & Haenlein, 2010). The developmental implications of living and managing these two separate identities remains relatively unexplored.
Alongside the impact on identity confusion, research has suggested that certain types of ICT use are positively correlated with relationship difficulties (Nyarko, 2012; Shyam & Bhoria, 2011). Evidence for this association is illustrated in a study of college students in which individuals who reported low identity coherence were shown to use texting as a means of peer avoidance (Berusch, 2016). Similarly Cyr, Berman, and Smith (2012) showed that time spent using ICT was significantly correlated with identity distress and existential anxiety among a sample of high school students. Although these investigations have provided tantalizing suggestions that the use of ICT may adversely affect identity achievement, these conclusions are limited by often being correlational in nature and failing to broadly survey a wide range of ICT behaviours. The personal identity of each adolescent should result in a coherent sense of self in emerging adulthood, and investigating how communication technology preferences may be associated with identity is a necessary next step in understanding the impact of ICT use on adolescent development. The present work took a person-centred approach in exploring how not only Facebook use but also other ICT use preferences may be associated with maladaptive adolescent identity.
Youth Problem Behaviours and ICT
The effects of ICT have also been found to extend beyond youth’s development of identity, impacting on adolescent behaviour. For example, increases of overt aggression, aggressive feelings, and social isolation among youth have been attributed to lengthy screen time (Ray & Jat, 2010). Reports indicate that the number of youth who develop or display conduct problems during adolescence have more than doubled over the last 25 years (Collishaw, Maughan, Goodman, & Pickles,2004). This fact should provide motivation to investigate whether increased ICT involvement is responsible for this increase in externalising behaviour. Moreover, ICT activities such as heavy video game usage, irrespective of content, has consistently been shown to be associated with depression, externalizing and internalizing problems, social phobia, withdrawal, anxiety, delinquency and aggressive behaviours (Brown & Bobkowski, 2011; Gentile et al., 2011; Holtz & Appel, 2011; Lemmens, Valkenburg, & Peter, 2011; Romer, Bagdasarov, & More, 2013; Scott & Porter-Armstrong, 2013). Web surfing and general Internet use has also been linked to negative outcomes in adolescence, i.e., conduct disorders, attention deficit disorder, impulsivity, obsessive-compulsive disorder, hostility, and antisocial behaviours (Carli et al., 2013; Ko, Yen, Yen, Chen, & Chen, 2012). Investigations into clusters of ICT usage preferences coupled with time spent accessing particular outlets of technology could shed more light on how different types of media consumption are associated with specific behavioural concerns.
Research Questions
Given the background evidence demonstrating the impact of ICT in adolescence, the present study was designed to explore whether specific profiles of technology usage would be associated with key characteristics of identity and problem behaviour. Our first research question sought to determine whether adolescents would fall into a small number of distinct ICT usage profiles (RQ1). The second research question was posed to investigate whether significant differences would be documented between ICT usage profiles on a range of self-reported aspects of identity such as false self, authentic self, self-image satisfaction, and self esteem (RQ2). Lastly, it was anticipated that significant differences would be documented among ICT usage profiles on a range of self-reported problem behaviours such as bullying, victimization, trouble with friends, externalization, and immoral behaviour (RQ3).
Methods
Participants
In 2006, a large initial sample (N = 2,174) of adolescents was recruited from 78 schools across the North Island of New Zealand to start the Youth Connectedness Project (YCP), a longitudinal study examining adolescent behaviour and adjustment. The participants were drawn from schools with a range of socio-economic backgrounds, yielding a mean that approximated a middle-class status. The geographical distribution included 61% urban schools, 33% suburban schools, and 6% rural schools. A total of 933 young people took part in the fourth and last wave of data collection for the YCP study in 2015, and this sample served as the basis for the present study because the previous time points did not include questions assessing adolescent ICT, particularly the social media outlet Facebook.
At T4 the sample was composed of 336 males (36%) and 597 females (64%) ranging in age from between 17 and 22 years old. Participants also reported on their cultural background, and were permitted by the question to identify with more than one ethnicity. Most respondents (85%; n = 588) identified as New Zealand European, the majority cultural group in New Zealand. Other ethnicities were Maori (23%; n = 156), Pacific Islander (6.9%; n = 48), Asian (3%; n = 23), and 18% (n = 123) identified as Other. Ethical approval was obtained from the Victoria University of Wellington Human Ethics Committee, and all adolescents consented to the study’s procedures prior to data collection at T4.
Procedure
As part of the longitudinal Youth Connectedness Project (see Jose, Ryan, &Pryor, 2012), adolescents were recruited from high schools across the North Island of New Zealand through a stratified random sampling method, yielding a nationally representative sample of school types. Over time the research team attempted to retain all of the previous adolescent participants from preceding time points, however, many contact details ceased to be current or accurate. This lack of contact information resulted in an attrition rate of 57% between time point 1 (T1) in 2006 and time point 4 (T4) in 2013. All participants at T4 received an email notification with an online hyperlink inviting them to complete the survey online. Each participant was compensated with a $10 voucher for his or her participation. All participants at T4 were 16 years of age or older and consent was obtained from each participating individual.
Measures
To assess the impact of technology use on identity, the study included measures of both authentic and false self, self-esteem, and self-image satisfaction. In order to measure problem behaviour, measures of bullying behaviours, victimization, trouble with friends, immoral behaviour, and externalization were obtained.
Perceptions of False Self. To assess adolescent false self-conceptions three items measuring false sense of self were taken from the Perceptions of False Self scale (POFS) (Weir & Jose, 2010). Participants were asked to rate how much each statement applied to them: ‘I don’t let people see the real me’, ‘What I say on the outside is different to what I think on the inside’, and ‘I hide the real me by looking like others’. Responses were marked on a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) where higher scores indicated increased levels of false sense of self. The total scale internal consistency for the present dataset was good (α = .78).
Perceptions of Authentic Self. To measure participant’s levels of authentic self, participants were asked to respond to three reverse-coded items of the POFS scale (Weir & Jose, 2010) dedicated to measuring levels of authenticity (‘I say what I think even if it is different to the opinions of others’, ‘I act in ways that express who I really am’, and ‘I can talk openly to others about my feelings’). Responses were marked on a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) where higher scores indicated increased levels of authentic self. An additional 2 items, using a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (very difficult) to 5 (very easy), assessed degrees of perceived authenticity by asking participants to indicate how easily they could be themselves around different individuals, (e.g., your best friend, other friends). The total scale internal consistency was good (α = .74).
Self Esteem. In order to measure participant’s self esteem, the Rosenberg Self Esteem Scale (Rosenberg, 1965) was employed. A total of six self-report items were used (e.g., 'I feel that I am a person of worth, at least on an equal plane with others' and 'On the whole, I am satisfied with myself’). Responses were measured using a 5-point Likert scale ranging between 1 (strongly disagree) and 5 (strongly agree) with higher scores indicating higher levels of self-reported self-esteem. The total scale internal consistency was high (α = .85).
Immoral Behaviour. Utilizing 3 items from the Morality of Action scale adapted from the Washington Healthy Youth Survey (Department of Health Washington State, 2002) participant’s level of immoral behaviour (e.g., 'I think it is ok to take something without asking as long as you get away with it' and 'I think sometimes it is ok to lie rather than tell the truth') was measured. The measure employed a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (strong disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) with higher scores indicating higher levels of immoral behaviour. The total scale internal consistency was good (α = .74).
Self-Image Satisfaction. A number of items were specifically created for the Youth Connectedness Project (YCP) to measure adolescent health. Among these were items aimed at measuring health and self-image satisfaction within the sample. A total of 4 items were used to assess participant’s self-image satisfaction (e.g., 'Happy with how I look'; 'Happy with my weight') using a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). Higher scores indicated higher levels of self-image satisfaction. The total scale internal consistency was good (α = .77).
Bullying. Rates of bullying behaviour within different contexts were measured for the previous four weeks. A total of 7 items were created for the YCP, and using a 5-point Likert scale ranging between 1 (Never/Does not apply) and 5 (Almost daily/daily) participants responded to a total of 7 items regarding their bullying behaviour (e.g., 'Have you bullied others in the last month?', ‘How often in the last month have you bullied: Online?’). Higher scores indicated a higher frequency of bullying in the previous month. The total scale internal consistency was good (α = .73).
Victimization. Rates of victimization from bullying were also measured for the previous four weeks. A total of 7 items created for the YCP were employed, and using a 5-point Likert scale ranging between 1 (Never/Does not apply) and 5 (Almost daily/daily) participants responded to the items regarding their experiences of victimization (e.g., ‘Have you been bullied in the last month?'; How often in the last month have you been bullied: Online?'). Higher scores indicated a higher frequency of victimization in the previous month. The total scale internal consistency was high (α = .82).
Trouble with Friends. Employing a total of 3 items generated specifically for the study, the tendency to get into trouble with friends (e.g., 'How many of your close friends get into trouble?; How often do your friends pressure you to do things that can get you into trouble?') was measured using a 5-point Likert scale ranging between 1 (Never) and 5 (All of the time). Higher scores indicate an elevated frequency of negative peer pressure from friends. The total scale internal consistency was good (α = .79).
Externalizing. A total of 3 items created for the study were employed to assess externalizing behaviours (e.g., 'I get into fights or argue with people', ‘I hurt somebody that does not have anything to do with the problem’, 'I yell and scream') were measured using a 5-point Likert scale ranging between 1 ('Never/Almost Never') and 5 ('Always/Almost Always'). Higher scores indicate an elevated frequency of externalization. The total scale internal consistency was good (α = .73).
ICT Use and Exposure
In addition, questions about technology were included to measure adolescent use, exposure, and involvement with different outlets of information and communication technology. At the time of data collection, the social media network Facebook was gaining in popularity amongst adolescents and thus, the research team believed it was an important cyber-social phenomenon to measure in the present study. A total of seven questions were constructed for the present study to measure participant use, preferences, and engagement with the popular social media platform. Responses were reported on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). In addition, alternative response options were used that ranged from 1 (never) to 5 (all the time) to questions such as ‘How often do you visit Facebook (to update your status, read your friend’s posts, etc.)?’ or ‘Your Facebook profile gives an accurate picture of your life’.
In addition to adolescent Facebook engagement and use details, we included measures that would assess how much time youth were spending using Facebook as well as other ICT activities. From the perspective that all youth are different, we assumed that measuring time spent using various technologies might illuminate different youth preferences. Loosely following the Pew Research Center Internet and Technology (Lenhart, 2015) report, we selected items that previous research had identified as relevant for adolescents. As such, in order to assess our sample’s time spent engaging with different outlets of ICT on a daily basis, participants’ responses were reported on 6-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (0 hours) to 6 (10+ hours) to questions such as ‘How many hours a day, on average, would you say you spend playing video games?’ and ‘How many hours a day, on average, would you say you spend surfing the Internet?’ where higher self reports indicated more time spent using that particular digital medium. A complete list of items used in the ICT use and exposure section is outlined in Table 1. Taken together, these items were deemed representative of the existing technological trends and ICT preferences among youth.
Table 1. ICT Use and Exposure Items in the Adolescent Sample.
|
ICT Outlet |
Item Details |
Scale Used |
|
|
|
How many of your Facebook friends do you consider your close friends? (FB1) |
1 (None) to 5 (All of them) |
|
|
Other people's Facebook profiles give an accurate picture of their lives. (FB2) |
1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) |
||
|
Your Facebook profile gives an accurate picture of your life. (FB3) |
1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) |
||
|
When you compare yourself to others on Facebook, does it make you feel: (FB4) |
1 (Much worse) to 5 (Much better) |
||
|
Do you have a physical response (increased heart rate, stomach pain, sweating, headache, etc.) in response to information you see/receive on Facebook? (FB5) |
1 (Never) to 5 (All the time) |
||
|
How often do you visit Facebook to update your status, read your friends' posts, etc.?(FB6) |
1 (Never) to 6 (I am on most of the time) |
||
|
Keeping up to date with Facebook (messages, posts, links, photos) interferes with my daily life (eating a meal, doing assignments/chores, going out) (FB7) |
1 (Never) to 5 (All the time) |
||
|
Time spent using Facebook (TimeFB) |
1 (0 hrs) to 6 (10+ hrs) |
||
|
Internet |
Time spent surfing the Internet (TimeNet) |
1 (0 hrs) to 6 (10+ hrs) |
|
|
Video Games |
Time spent playing video games (TimeVG) |
1 (0 hrs) to 6 (10+ hrs) |
|
|
Mobile Phone |
Time spent making phone calls or texting (TimePhon) |
1 (0 hrs) to 6 (10+ hrs) |
|
Data Analysis
As we were interested in identifying groups of adolescents who share similar ICT use habits, latent profile analysis (LPA), a statistical method used to identify latent class membership among participants using continuous observed variables, was used. Latent profile analysis is a person-centered technique that considers responses to a set of variables and then defines groups of individuals who endorse these variables in similar ways. LPA is distinguished from factor analysis, which is a variable-centered technique that assumes that latent clusters of variables exist (Muthén & Muthén, 2000). The person-based groups that are identified with the LPA technique are referred to as latent classes in that they are not directly observed but instead are inferred from the data. The optimal number of profiles is determined by estimating models with an increasing number of classes and comparing fit indices between these models (Muthén & Muthén,).
Identification of communication technology classes. The variables used to construct the LPA were the 12 items assessing ICT use, such as Facebook use, time spent surfing the Internet, playing video games, making phone calls, and texting. Using these variables, it was expected that a small number of distinct user profiles would emerge within the sample population, illustrating the various ways in which youth interact with ICT. The classes were derived using Mplus version 7.2 (Muthén & Muthén, 2015). Classification quality was assessed using recommended indices, including the Akaike information criterion, the Bayesian information criterion, as well as the Lo-Mendell-Rubin likelihood ratio test and normalized entropy criterion. It was anticipated that at minimum, three latent profiles would emerge reflecting average, high, and low users of ICT, but fewer and more possibilities were examined as well.
Regression models predicting outcomes. Upon identification of the ICT user profiles, a series of linear regressions were then used to assess whether class membership was associated with aspects of identity and aggressive behaviour. It was expected that variations between outcomes based on class membership would be identified.
Results
Descriptive Analysis
Table 2 presents correlation coefficients, descriptive statistics, and Cronbach’s αs for all of the variables used in the study.
Table 2. Youth Reports of Identity and Behaviour Variables: Correlations and Descriptive Statistics.
|
Variables |
FS |
AS |
SE |
IMM |
SIS |
BULLY |
VICT |
TRBF |
EXTN |
|
AS |
-.58** |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SE |
-.54** |
.54** |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IMMO |
.36** |
-.22** |
-.26** |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIS |
-.31** |
.35** |
.50** |
-.07* |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
BULLY |
.29 |
.14 |
-.07 |
.35 |
.29 |
- |
|
|
|
|
VICT |
.50** |
.19 |
-.21 |
.56** |
-.15 |
.85** |
- |
|
|
|
TRBF |
.20** |
-.11** |
-.15 |
.36** |
-.04 |
.24 |
.61** |
- |
|
|
EXTN |
.27** |
-.19** |
-.36** |
-.21** |
-.24** |
.10 |
.43** |
.22** |
- |
|
M |
2.29 |
3.94 |
3.00 |
1.82 |
3.39 |
1.55 |
1.59 |
1.69 |
1.82 |
|
SD |
.80 |
.56 |
.56 |
.75 |
.80 |
.68 |
.57 |
.68 |
.77 |
|
α |
.78 |
.74 |
.85 |
.74 |
.77 |
.73 |
.82 |
.79 |
.73 |
| Note: **p < .01, *p < .05. FS = False Self, AS = Authentic Self, SE = Self Esteem, IMM = Immorality, SIS = Self Image Satisfaction, BUL = Bullying, VIC = Victimization, TRF = Trouble with Friends, EXN = Externalizing Behaviours. (N = 933). | |||||||||
Identifying ICT Profiles with Latent Profile Analyses
Four latent profile models, representing 2-, 3-, 4-, and 5-profile solutions were fitted to the data. The 2-profile model, while achieving statistical significance (p < .001), was not sufficiently representative of the data, and resulted in a relatively low entropy (.78), the chief measure of the distinguishability of the classes. When fitting the 3-profile model, the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) scores significantly decreased from the 2-profile model, while the entropy increased (to .89), indicating improved model fit. At the next step, the fit indices for the AIC and BIC showed a sufficient decrease between the 3- and 4-class models (> 100), and entropy increased to .90 and remained significant (p = .03). When attempting to fit the 5-profile model, the Lo-Mendell Rubin likelihood ratio test rejected the model (p = .17). Taken together, these LPA results indicated support of a 4-class model.
The four profiles are depicted in Figure 1 with ICT profile membership descriptive statistics outlined in Table 3. Upon initial analysis of the ICT model, we saw limited variability between classes for the first five variables focused on Facebook perceptions (namely FB1 to FB5). As a result we focused our profile analysis on the remaining six ICT items. The first and largest ICT profile, distinguished by overall average levels of ICT use, was labeled the Average Use group, and it represented 46.3% (n = 434) of youth in the sample. The smallest group was constituted by 6.1% (n = 57) of the total sample size, and it was defined by a higher amount of time spent engaging with video games (M = 3.43) compared to other types of ICT use. This group also manifested lower average levels of social media use (M = 1.11) than the other profiles. Consequently this group was termed the High Video Game/Low Social Media class. The third class, dominated by individuals who reported high levels of ICT usage, namely reporting significantly high amounts of time using all forms of communication technology, was designated the Elevated ICT Use class, and it made up 40.8% (n = 383) of the sample across all of the categories. The final profile included 6.3% (n = 59) of youth in the sample, and they spent a higher than average amount of time using social media (M = 5.29) and surfing the net (M = 4.75), but little time engaged with video games, phone calls, or texting, and as such this group was consequently labeled the High Social Media and Net Use class. Thus, these results support the intent behind RQ1 by identifying a small number of discrete ICT use profiles.
Table 3. ICT Usage Profile Membership Descriptive Statistics.
|
Average |
|
Elevated |
|
HVG-LSM |
|
HSM-Net |
|||||
|
|
M |
SD |
|
M |
SD |
|
M |
SD |
|
M |
SD |
|
Surfing the Internet |
2.65 |
0.89 |
|
3.48 |
0.83 |
|
3.2 |
1.38 |
|
4.75 |
0.95 |
|
Using Facebook |
1.96 |
0.27 |
|
3.36 |
0.49 |
|
1.11 |
0.32 |
|
5.29 |
0.46 |
|
Playing Video Games |
2.67 |
1.07 |
|
2.95 |
1.08 |
|
3.43 |
1.18 |
|
3.88 |
1.56 |
|
Mobile Texting & Calls |
2.27 |
0.88 |
|
2.86 |
1.05 |
|
1.94 |
0.83 |
|
3.89 |
1.56 |
| Note: Average = Average ICT Use Group, Elevated = Elevated ICT Use Group, HVG-LSM = High Video Game-Low Social Media Group, HSM-Net = High Social Media and Net Use G. | |||||||||||
Figure 1. Technology Use Preferences by ICT Profile Membership.
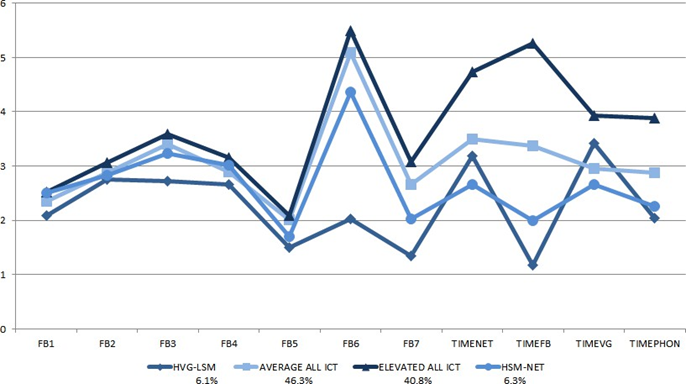
Note. FB1 = Number of Facebook friends, FB2 = Other Facebook profiles accurate,
FB3 = Own Facebook profile accurate, FB4 = Compare self to others on Facebook,
FB5 = Physical response, FB6 = Facebook visit frequency, FB7 = Keep up with Facebook,
TimeNet = Time on Internet, TimeFB = Time on Facebook,
TimeVG= Time playing video games, TimePhon = Time on phone
Associations between ICT Profile Membership and Outcomes
Controlling for age and gender, a series of linear regressions were calculated to investigate the degree to which class membership predicted indicators of identity, namely, false self, authentic self, self image satisfaction, and self esteem, as well as problem behaviours, such as bullying, victimization, trouble with friends, immoral behaviour, and externalization. To this end, profile membership in the High Video Games-Low Social Media, Elevated ICT, and High Social Media-Net groups were dummy coded and as a result the regressions are interpreted in comparison to the reference category of the Average ICT Use profile.
Differences in identity. The second research question (RQ2) involved examination of differences in identity among the obtained classes. Table 4 shows that membership in the elevated ICT group (β = .15, p < .001), as well as in the high video game profile (β = .11, p < .001), were associated with higher levels of false self-perceptions in comparison to the average usage profile. Similar results were found for authentic self, but in the opposite direction, where participants in the high video game profile (β = -.14, p < .001) and elevated ICT use group (β = -.09, p < .01) reported significantly lower levels of authenticity in comparison to the average usage profile. No significant differences were noted between the high social media and net use profile and the average use profile for rates of false self (p = .44) or authenticity (p = .58).
In comparison to the average group, results indicated that belonging to the elevated ICT use profile (β = -.13, p < .001) and high video game group (β = -.07, p < .05) predicted significantly lower self-image satisfaction. Moreover, self-esteem was found to suffer if participants belonged to the elevated ICT use group (β = -.10, p < .01) and high video game profile (β= -.16, p < .001) in comparison to the average group. No significant effect, however, was noted between the high social media and net use profile and the average use groups for self-image satisfaction (p = .25) or self-esteem (p = .11).
These findings indicate that the models, including covariates and ICT class membership, explained a significant amount of the variance in these identity variables, in support of RQ2. These results suggest that ICT class membership in youth was significantly associated with key variables of identity development.
Table 4. Standardized Regression Weights of the Three Non-Reference ICT Classes Relative
to the Reference Class of Average ICT Use in Predicting Identity Variables.
|
|
|
IDENTITY BLOCK |
||
|
Covariates |
FS |
AS |
SIS |
SE |
|
Age |
.00 [-.03, .03] |
.05 [-.01, .04] |
.03 [-.01, .05] |
.10** [.01, .05] |
|
Gender |
-.05 [-.20, .01] |
.04 [-.01, .15] |
-.21*** [-.44, -.23] |
-.11*** [-.18, -.04] |
|
ICT Profiles |
|
|
|
|
|
Elevated |
.15*** [.09, .31] |
-.09** [-.16, -.01] |
-.13*** [-.29, -.08] |
-.10** [-.14, -.01] |
|
HVG-LSM |
.11*** [.05, .48] |
-.14*** [-.45, -.13] |
-.07* [-.34, -.01] |
-.16*** [-.47, -.17] |
|
HSM-Net |
.03 [-.26, .16] |
.02 [-.04, .27] |
-.04 [-.24, .20] |
-.05 [-.20, .10] |
|
R² |
.03 |
.03 |
.06 |
.05 |
| Note: *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001. Square brackets indicate 95% Confidence Intervals. FS = False Self, AS = Authentic Self, SIS = Self Image Satisfaction, SE = Self Esteem, HVG-LSM = High Video Game – Low Social Media, HSM-Net = High Social Media and Net Use. | ||||
Differences in negative behavioural outcomes. Similar analyses were performed exploring the associations between class memberships with self-reported negative behavioural outcomes. The findings, as indicated in Table 5, suggest that user profiles significantly predicted important indicators of problem behaviours, in support of RQ3. Specifically, it was found that belonging to the elevated ICT use class (β = .15, p < .01) and the high social media and net use group (β = .09, p < .01) significantly predicted greater externalizing behaviours than if participants were part of the average use profile. We also found that membership in the elevated ICT use profile (β = .08, p < .01) and the high social media and net use group (β = .09, p < .01) predicted higher levels of problematic behaviours with friends as compared with the average user group. Furthermore, belonging to the elevated ICT use profile predicted significantly higher levels of immoral behaviour (e.g., lying and stealing) when compared to the average use group (β = .08, p < .05). However, no significant predictive effect was found for self-reported immoral behaviour for the high video game (p = .25) or high social media and net user groups (p = .32) when compared against the average ICT use profile members. There were also no significant differences identified between the high video game/low social media group and the average use group on externalization (p = .27) or problematic behaviours with friends (p = .42).
Notably, in comparison to the average use group, membership in the high social media and net use (β = .48, p < .001) predicted increased overall victimization, while no significant differences were observed between the average group and the elevated ICT use group or the high video game play members. The rates of bullying behaviour were similar across the high social media and net use group (p = .16), the high video game profile (p = .60), and the average use group. On the other hand, belonging to the elevated ICT use group significantly predicted fewer bullying behaviours (β = -.54, p < .05) in comparison to the average class.
Table 5. Standardized Regression Weights of the Three Non-Reference ICT Classes Relative
to the ReferenceClass of Average ICT Use in Predicting Behaviour Variables.
|
BEHAVIOUR BLOCK |
|||||
|
Covariates |
BUL |
VIC |
TRF |
EXN |
IMB |
|
Age |
.17 [-.11, .21] |
-.04 [-.12, .06] |
-.26*** [-.10, -.05] |
-.11*** [-.08, -.03] |
.01 [-.02, .03] |
|
Gender |
-.30 [-.77, .34] |
-.23 [-.75, .02] |
-.18*** [-.44, -.26] |
.15*** [.14, .34] |
-.27*** [-.51, -.32] |
|
ICT Profiles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Elevated |
-.54* [-1.08, -.16] |
-.15 [-.60, .04] |
.08** [.00, .17] |
.15** [.10, .30] |
.08* [.00, .20] |
|
HVG-LSM |
-.11 [-1.50, 1.55] |
-.04 [-.61, .60] |
-.02 [-.30, .07] |
.04 [-.20, .21] |
.04 [-.14, .26] |
|
HSM-Net |
-.36 [-.88, .57] |
.48*** [.74, 2.15] |
.09** [.04, .39] |
.08* [.05, .35] |
.03 [-.16, .23] |
|
R² |
.21 |
.37 |
.12 |
.06 |
.08 |
| Note: *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001. Square brackets indicate 95% Confidence Intervals. BUL = Bullying, VIC = Victimization, TRF = Trouble with Friends, EXN = Externalizing Behaviours, IMB = Immoral Behaviour, HVG-LSM = High Video Game – Low Social Media, HSM-Net = High Social Media and Net Use. | |||||
Overall, the covariates and ICT class membership explained a significant amount of the variance among these particular behavioural variables. These findings suggest that ICT preferences and usage habits were significantly associated with behavioural outcomes. The results indicate that important concepts of both identity and behaviour are affected, and that these identity characteristics are correlated with individual ICT usage preferences. The most interesting results were the significant associations between elevated ICT use with the variables of adolescent positive and negative self-perceptions, self-esteem, self-image satisfaction, immoral behaviour, externalizing behaviours, and trouble with friends.
Discussion
In this study we achieved two major goals: first, we identified four distinct classes of ICT use among a large sample of adolescents and early adults; and second, the analyses identified a number of reliable differences between classes associated with maladaptive identity and problem behaviour variables. Among the four unique ICT use profiles, the majority of the sample fell into the average ICT use class, while three other groups were also identified: elevated ICT use, high social media and net use, and high video game use. Using the average technology use profile as the reference category, the effects of class membership on both identity and behaviour among adolescents were explored.
Class Differences in Maladaptive Identity
In comparison to the average ICT use group, several classes displayed higher levels of compromised identity variables. For example, individuals in the elevated ICT use group were significantly more likely to exhibit increased levels of false self-perceptions and, in turn, lowered authenticity when compared to the average ICT user group. Similar results were identified for the high video game users, with participants showing significantly higher rates of false self-perceptions and decreased authenticity. Further to these findings, individuals belonging to either of these classes also reported significantly decreased self-image satisfaction as well as lowered self-esteem compared to peers belonging to the average technology user profile.
The high social media and net use profile, however, did not evidence any significantly worse identity outcomes when compared to the average use group. Rates of false self, authenticity, self-image satisfaction, and self-esteem did not significantly differ between those belonging to the high social media and net use profile when compared to the average user group. The noted differences between ICT use group membership on maladaptive identity supports the hypothesis that ICT use preferences are significantly associated with important indices of youth’s identity formation.
Class Differences in Maladaptive Behaviour
When comparing all ICT profiles against the average user group, adolescents and early adults who exhibited elevated rates of ICT use, or who frequently interacted with social media and the web, were more likely to report rebellious, defiant, aggressive, and antisocial behaviours characteristic of externalizing behaviours. Moreover, these digital preferences were also significantly associated with a higher likelihood of problematic behaviours with friends (e.g., getting pressured into doing things that could get one into trouble and an increased frequency of getting into risky situations with friends). Further, the rates of victimization by bullying were found to be significantly higher for individuals belonging to the high social media and net use profile. Bullying behaviours, however, were significantly less likely among youth who belonged to the elevated ICT use profile compared to the average use group. Results further indicated that participants belonging to the elevated ICT use profile demonstrated significantly higher levels of immoral thoughts and behaviours, suggesting that perhaps adolescents who display these immoral tendencies have graduated from bullying tactics and are using ICT for different means. Future studies should explore how immoral behaviour might present via ICT use and whether these immoral tendencies are manifested through trolling (i.e., starting arguments or posting inflammatory comments on profiles or forums), catfishing (i.e., the luring of someone into a relationship through a fake online persona), or even phishing (i.e., using social engineering to ascertain people’s personal information such as passwords or credit card information with malicious intent). The current differences in ICT use group membership found in association with maladaptive behaviour supports the hypothesis that significant associations exist between ICT use preferences and maladaptive youth behaviour.
No significant differences were found for self-reported immoral behaviour for both the high video game and the high social media and net user groups when compared with the average ICT user group. Further, we also found no significant differences for the high video game/low social media group, or for the average ICT group for externalizing or trouble behaviours with friends. Participants belonging to the elevated ICT use, as well as the video game group, did not experience significantly higher rates of victimization. Similarly, we found no significant differences in rates of bullying across the high social media and net use members or those belonging to the high video game profile, when compared to the average user profile. These results suggest that unique ICT user profiles are associated with both positive and negative aspects of identity formation.
Comparing Our Findings with Existing Research
The findings on both identity and behaviour from the present study are generally consistent with results noted in previous research, however, the predominant approach taken by previous researchers has solely focused on one or two behaviours associated with a specific ICT platform such as Facebook or the use of video games, in isolation. The current study, however, took a person-centered approach, focusing on the adolescent as an active user over a range of ICT use preferences. This person-centred approach allowed for the identification of typical adolescent profiles of ICT usage not previously identified by researchers. Illuminating these unique profiles allowed us to examine ICT usage as a holistic whole embodied within individual adolescents, an approach that has not been previously undertaken in this area of research. This novel approach resulted in several new findings, which highlights the importance of growing existing literature in the field.
We further speculated that profile membership would be associated with problematic behaviours. The present findings on the predictive relationships between externalizing and problematic behaviours with friends in relation to elevated ICT, social media, and net use expand on previous research that has documented significant relationships between prolonged screen time and increased aggression and conduct disorders (Kelishadi et al., 2015; Ray & Jat, 2010). The manifestations of these antisocial and aggressive tendencies are further showcased when exploring rates of online victimization. The current findings are consistent with reports that 88% of adolescents aged between 12 and 17 years have witnessed ‘mean acts’ online or experienced some degree of victimization in their own lives (Lenhart et al., 2011). Our findings underscore that adolescents who spend a significant amount of time online, as well as using social media, are more likely to experience being bullied. Adolescents, however, who exhibit elevated levels of all ICT use showed no significant association with committing acts of bullying, suggesting that a unique relationship may exist specifically between social media and bullying.
Our study did find that elevated ICT use was significantly associated with increased rates of immoral behaviour, a finding that has not been previously identified in the research. While limited empirical evidence exists investigating the relationship between immoral behaviour and ICT use, research has suggested that externalizing and aggressive behaviour are directly related to moral sensibility (Gini, 2006; Menesini et al., 2003). Exposure to highly immoral content via Internet access, for example, could result in ‘routinization’ (a form of adaptation), which has been shown to prevent individuals from enacting moral actions and behaviour (Tsang, 2002). Although literature on the influence of ICT use on adolescent morality is relatively scarce, a recent public survey by the Pew Research Centre (2015) revealed that the vast majority of the public believes that active and frequent use of the Internet is likely to result in decreased morality. Future research should consider how morality may be affected by different modes of ICT use, and how ICT activity may be impacting on the development of moral thought and action among youth.
Implications
The findings of the present study suggest that diverse aspects of ICT use among teens may have unique implications for personal development. The findings also contribute to an emerging literature on the subject of communication technology and adolescent development by illustrating a need for a broader and more developmental approach to the study of youth information and communication technology use. The current cross-sectional study illustrates that ICT is significantly associated with identity and behavioural attributes in adolescence, and although we cannot infer causality with such data, the associations suggest that personal inclinations towards specific digital preferences in youth may have the ability to not only amplify and shape identity and behaviour but also may have a transformative effect on teen development. Moreover, identifying clusters of ICT use, rather than focusing research on individual media outlets one at a time, illustrates a more dynamic and diverse digital media consumption among youth. These findings suggest that the outlets that teens may choose to predominantly use could be satisfying specific and unique psychosocial needs by aiding youth to seek out particular social networks, establishing a sense of community outside of their immediate environment, and building support systems with similar-minded individuals. In the reverse direction, it may be that individuals who possess antisocial personality traits seek out particular ICT outlets and experiences that are congruent with their inner motivations. Future work will be needed to tease apart longitudinal and causal relations that the current cross-sectional study cannot illuminate fully.
The findings of the present study illustrate the need to focus on collective or holistic depictions of ICT usage preferences as a building block in research as a means to truly understanding the unique motivations behind adolescent ICT platform preferences. Moreover, the rapid acceleration of computer-mediated technology use as well as other communication technology advancements, such as virtual or augmented reality, illustrate a pressing need for researchers to take on innovative and holistic approaches to studying the impact of technology on youth development.
Future Directions and Limitations
By identifying unique adolescent profiles of communication technology use preferences, research can expand its scope to focus on clusters of ICT use and thereby improve our current understanding of the unique profiles of adolescent communication technology consumption. Future research should evaluate what motivates youth to gravitate towards specific clusters of ICT usage by expanding empirical work to include different themes and/or motivations that stimulate participation and involvement in new and existing digital media. The current findings showed that high social media use is significantly associated with increased rates of bullying and victimization. Future work could consider how high rates of malicious activity over several social networking platforms by youth may be associated with personality traits related to sadism, Machiavellianism, narcissism, or psychopathic tendencies. Research into these four ‘dark’ personalities in relation to online behaviour is relatively uncharted (but see Buckels et al., 2014), and with the paradoxical mix of decreasing privacy and digital anonymity, it is critical to distinguish the different types of antisocial personalities that may be liberated in unmonitored online behaviour.
It is also important to note that the present work did not include all of the communication technology platforms available today, and as such future studies should investigate a wider breadth of ICT usage in latent profile analyses such as involvement with Instagram, Twitter, ask.fm, Snapchat, Tumblr, Skype, Facetime, and the like. While the use of a latent profile analysis in this context is novel, we recognize, as noted above, that doing so with a concurrent sample limits the ability to explain how ICT use causes differences in identity and problem behaviours over time, and vice versa. In the present case we cannot discern the temporal nature of these relationships, and must instead consider the findings as illustrating specific concurrent associations between the variables, which, we would argue, signpost the use of certain variables in future longitudinal investigations. Lastly, the current sample was taken from a single Western country in the Southern hemisphere, and while some of the results attained are consistent with previous work that has illustrated an impact of communication technology on identity and behaviour in other countries, future work should strive to replicate our findings in other cultures and countries.
Conclusions
Applying a latent profile analysis on various adolescent communication technology use preferences has yielded evidence that distinct youth ICT user profiles not only exist, but also exhibit significant associations with various identity and behavioural outcomes. We argue that the present findings illuminate the importance of studying clusters of ICT use preferences and we hope it motivates researchers to evaluate how certain types of communication technology use in adolescence may have impacts on development. Although significant associations were found between ICT profile membership and both identity and behaviour, the discrepancies between the current findings and those found in select previous literature indicate that there is still much to understand about the complex influence of communication technology on youth and development.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2017 Anna Kurek, Paul E. Jose, Jaimee Stuart


