Playing below the poverty line: Investigating an online game as a way to reduce prejudice toward the poor
Vol.10,No.2(2016)
A plethora of research indicates that viewing media can reduce prejudice. Emerging work on computer gaming shows that games can also influence social attitudes. The present studies investigated the influence of an interactive computer game about living in poverty on attitudes and beliefs about the poor. Playing the poverty game was compared to playing a control game and merely observing the poverty game. In Study 1, playing an interactive poverty game did not influence attitudes while watching someone else play the game increased positive attitudes, empathic concern, and support for government-funded anti-poverty policies. In Study 2, meritocracy beliefs moderated the influence of the game; people lower in meritocracy showed less positive attitudes toward the poor after playing the poverty game. This effect was mediated by an increase in the belief that poverty is personally controllable. Future directions for and implications of studying the unique intergroup effects of games are discussed.
Prejudice/stereotyping; controllability; media; poverty; attitude change
Gina Roussos
Department of Psychology, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA
Gina Roussos, M.S. is a social psychology graduate student at Yale University, studying with Dr. John Dovidio and Dr. Yarrow Dunham. She is interested in the antecedents and consequences of prejudiced attitudes and beliefs and how these attitude and beliefs can ultimately be changed. She examines attitudes toward a number of stigmatized groups, including women, poor people, over-weight people, and people of color. She is currently a Graduate Policy Fellow with the Institute for Social and Policy Studies at Yale.
John F. Dovidio
Department of Psychology, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA
John F. Dovidio, Ph.D. is a Carl Iver Hovland Professor of Psychology and Public Health and Dean of Academic Affairs of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences at Yale University. His work centers around issues of social power and social relations, both between groups and between individuals. He explores both conscious (explicit) and unconscious (implicit) influences on how people think about, feel about, and behave toward others based on group membership.
Adachi, P. J. C., Hodson, G., Willoughby, T., & Zanette, S. (2014). Brothers and sisters in arms: Intergroup cooperation in a violent shooter game can reduce intergroup bias. Psychology of Violence, 5, 455-462. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0037407
Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Alwin, D. F. (1997). Feeling thermometers versus 7-point scales: Which are better? Sociological Methods & Research, 25, 318-340. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/ 30049124197025003003
Anderson, C. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: A meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychological Science, 12, 353-359. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1467-9280.00366
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173-1182. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173
Batson C. D. & Moran T. (1999). Empathy-induced altruism in a prisoner's dilemma. European Journal of Social Psychology, 29, 909-924.
Batson, C. D., & Ahmad, N. (2001). Empathy‐induced altruism in a prisoner's dilemma II: what if the target of empathy has defected. European Journal of Social Psychology, 31, 25-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.26
Batson, C. D., Sager, K. Garst, E., Kang, M., Rubichinsky, K., & Dawsong, K. (1997). Is empathy-induced helping due to self-other merging? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73, 495-509. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022- 3514.73.3.495
Belman, J., & Flanagan, M. (2010). Designing games to foster empathy. International Journal of Cognitive Technology, 15(1), 5-15.
Bishaw, A. & Fontenot, K. (2014). Poverty: 2012 and 2013. U.S. Census Bureau Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2014/acs/acsbr13-01.pdf
Burgess, M. C., Dill, K. E., Stermer, S. P., Burgess, S. R., & Brown, B. P. (2011). Playing with prejudice: The prevalence and consequences of racial stereotypes in video games. Media Psychology, 14, 289-311. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2011.596467
Cameron, L., Rutland, A., Hossain, R., & Petley, R. (2011). When and why does extended contact work? The role of high quality direct contact and group norms in the development of positive ethnic intergroup attitudes amongst children. Group Processes and Intergroup Relations, 14, 193-207. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1368430210390535
Chen, X., Ender, P., Mitchell, M. and Wells, C. (2003). Regression with Stata. Retrieved from http://www.ats.ucla.edu/stat/stata/webbooks/reg/default.htm
College Board. (n.d). Interpreting and using SAT scores. Retrieved from http://www.collegeboard.com/prod_downloads/counselors/hs/sat/resources/handbook/4_InterpretingScores.pd f
Cozzarelli, C., Wilkinson, A. V., & Tagler, M. J. (2001). Attitudes toward the poor and attributions for poverty.
Journal of Social Issues, 57, 207-227. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/0022-4537.00209
Dixon, J., Durrheim, K., & Tredoux, C. (2007). Intergroup contact and attitudes toward the principle and practice of racial equality. Psychological Science, 18, 867-872. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01993.x
Dovidio, J. F., ten Vergert, M., Stewart, T. L., Gaertner, S. L., Johnson, J. D., Esses, V. M., ... & Pearson, A. R. (2004). Perspective and prejudice: Antecedents and mediating mechanisms. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 30, 1537-1549. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0146167204271177
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A.-G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41, 1149-1160.
Flanagan, M., Howe, D. C., & Nissenbaum, H. (2005). Values at play: Design tradeoffs in socially-oriented game design. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 751-760). ACM.
Flandez, R. (2011, February 14). Online game draws attentions – and money – for the needy. The Chronicle of Philanthropy. Retrieved from http://philanthropy.com/blogs/prospecting/online-game-draws- attention%E2%80%94and-money%E2%80%94for-the-needy/28750
Foster, M. D., Sloto, L., & Ruby, R. (2006). Responding to discrimination as a function of meritocracy beliefs and personal experiences: Testing the model of shattered assumptions. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 9, 401-411. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1368430206064641
Games for Change. (2015). About Games for Change. Retrieved from http://www.gamesforchange.org/about/
Gehlbach, H., Marietta, G., King, A. M., Karutz, C., Bailenson, J. N., & Dede, C. (2015). Many ways to walk a mile in another’s moccasins: Type of social perspective taking and its effect on negotiation outcomes. Computers in Human Behavior, 52, 523-532. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.035
Gorski, P. C. (2011). Unlearning deficit ideology and the scornful gaze: Thoughts on authenticating the class discourse in education. In R. Ahlquist, P. C. Gorski, & T. Montano (Eds.), Assault on kids: How hyper-accountability, corporatization, deficit ideologies, and Ruby Payne are destroying our schools (pp.152-176). New York, NY: Peter Lange.
Graham, S., Weiner, B., & Zucker, G. S. (1997). An attributional analysis of punishment goals and public reactions to OJ Simpson. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 23, 331-346. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0146167297234001
Green, M. C., & Brock, T. C. (2000). The role of transportation in the persuasiveness of public narratives. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 701-721. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.79.5.701
Greitemeyer, T., & Osswald, S. (2010). Effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 98, 211-221. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0016997
Greitemeyer, T., Osswald, S., & Brauer, M. (2010). Playing prosocial video games increases empathy and decreases schadenfreude. Emotion, 10, 796-802. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0020194
H2 Gambling Capital (2016). Size of the online gaming market from 2003 to 2015 (in billion U.S. dollars). Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved from http://www.statista.com/statistics/270728/market-volume-of-online-gaming- worldwide/
Hague, A. L., & White, A. A. (2005). Web-based intervention for changing attitudes of obesity among current and future teachers. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, 37, 58-66. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1499- 4046(06)60017-1
Huey, E. V. (2013). Games for change: The ever-evolving industry [PowerPoint slides]. Retrieved from http://www.slideshare.net/gamesforchange/
Jenkins, H. (2003). Game design as narrative architecture. In P. Harrington & N. Wardrip-Fruin (Eds.), First person: New media as story, performance, and game (pp.118-130). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Jones, E. E., & Nisbett, R. E. (1972). The actor and the observer: Divergent perceptions of the causes of behavior. In E. E. Jones, D. E. Kanouse, H. H. Kelley, R. E. Nisbett, S. Valins, & B. Weiner (Eds.), Attribution: Perceiving the causes of behavior (pp. 79-94). Morristown, NJ: General Learning.
Jones, E. E., Farina, A., Hastorf, A. H., Markus, H., Miller, D. T., & Scott, R. A. (1984). The dimensions of stigma: The psychology of marked relationships.
Kain, E. (2012, April 19). As video game sales climb year over year, violent crime continues to fall. Forbes Magazine. Retrieved from http://www.forbes.com/sites/erikkain/2012/04/19/as-video-game-sales-climb-year- over-year-violent-crime-continues-to-fall/
Kampf, R. (2015). Computerized simulations of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and attitude change: Peacemaker vs. Global Conflicts. eLearning Papers, 43, 3-12.
Kampf, R. & Cuhadar, E. (2015). Do computer games enhance learning about conflicts? A cross-national inquiry into proximate and distant scenarios in Global Conflicts. Computers in Human Behavior, 52, 541-549. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.08.008
Kaufman, G., & Flanagan, M. (2015). A psychologically “embedded” approach to designing games for prosocial causes. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 9(3), article 5. http://dx.doi.org/10.5817/CP2015-3-5
Kinder, D. R., & Drake, K. W. (2009). Myrdal's prediction. Political Psychology, 30, 539-568. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9221.2009.00714.x
Klimmt, C., Hartmann, T., & Frey, A. (2007). Effectance and control as determinants of video game enjoyment.
CyberPsychology & Behavior, 10, 845-848. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2007.9942
Kluegel, J. R., & Smith, E. R. (1986). Beliefs about inequality: Americans' views of what is and what ought to be. New York: DeGruyter.
Lalonde, R. N., Doan L., & Patterson, L. A. (2000). Political correctness beliefs, threatened identities, and social attitudes. Group Processes and Intergroup Relations, 3, 317-336. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1368430200033006
Madsen, K. E. (2016). The differential effects of agency on fear induction using a horror-themed video game.
Computers in Human Behavior, 56, 142-146. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.11.041
Malle, B. F. (2006). The actor-observer asymmetry in attribution: A (surprising) meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 132, 895-919. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.132.6.895
Malle, B. F., Knobe, J. M., & Nelson, S. E. (2007). Actor-observer asymmetries in explanations of behavior: New answers to an old question. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93, 491-514. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.93.4.491
Mukherjee, S. (2013, July 30). Four ways that poverty hurts Americans’ long-term health. ThinkProgress. Retrieved from http://thinkprogress.org/health/2013/07/30/2381471/four-ways-poverty-impacts-americans-health/
Mutz, D. C., & Goldman, S. K. (2010). Mass media. In J. F. Dovidio, M. Hewstone, P. Glick, & V. M. Esses (Eds.), The Sage handbook of prejudice, stereotyping and discrimination (pp. 241-257). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Paluck, E. L. (2009). Reducing intergroup prejudice and conflict using the media: A field experiment in Rwanda. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 96, 574-587. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0011989
Pedersen, A., Beven, J., Walker, I., & Griffiths, B. (2004). Attitudes toward indigenous Australians: The role of empathy and guilt. Journal of community & applied social psychology, 14, 233-249. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/casp.771
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40, 879-891. http://dx.doi.org/10.3758/BRM.40.3.879
Puhl, R. M., & Brownell, K. D. (2003). Psychosocial origins of obesity stigma: Toward changing a powerful and pervasive bias. Obesity Reviews, 4, 213-227. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1467-789X.2003.00122.x
Rank, M. R., Yoon, H. S., & Hirschl, T. A. (2003). American poverty as a structural failing: Evidence and arguments. Journal of Sociology & Social Welfare, 30, 3.
Riggle, E. D., Ellis, A. L., & Crawford, A. M. (1996). The impact of “media contact” on attitudes toward gay men. Journal of Homosexuality, 31(3), 55-69. http://dx.doi.org/10.1300/J082v31n03_04
Schiappa, E., Gregg, P. B., & Hewes, D. E. (2005). The parasocial contact hypothesis. Communication Monographs, 72, 92-115. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/0363775052000342544
Shih, M., Wang, E., Bucher, A. T., & Stotzer, R. (2009). Perspective taking: Reducing prejudice towards general outgroups and specific individuals. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 12, 565-577. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1368430209337463
Soss, J. & Schram, S. F. (2007). A public transformed? Welfare reform as policy feedback. American Political Science Review, 101, 111-127. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0003055407070049
Stephan, W. G., & Finlay, K. (1999). The role of empathy in improving intergroup relations. Journal of Social Issues, 55, 729-743. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/0022-4537.00144
Stevenson, M. R., & Medler, B. R. (1995). Is homophobia a weapon of sexism? The Journal of Men's Studies, 4, 1-8. Storms, M. D. (1973). Videotape and the attribution process: Reversing actors’ and observers’ points of view. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 27, 165-175. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/h0034782
Tagler, M. J., & Cozzarelli, C. (2013). Feelings toward the poor and beliefs about the causes of poverty: The role of affective-cognitive consistency in help-giving. The Journal of Psychology, 147, 517-539. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2012.718721
Todd, A. R., Bodenhausen, G. V., Richeson, J. A., & Galinsky, A. D. (2011). Perspective taking combats automatic expressions of racial bias. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100, 1027–1042. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0022308
Tyrrell, A. C., Hetz, S. P., Barg, C. J., & Latimer, A. E. (2010). Exercise as stigma management for individuals with onset-controllable and onset-uncontrollable spinal cord injury. Rehabilitation Psychology, 55, 383-390. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0021539
United States Census Bureau. (2014). Households by size: 1960 to present [Table]. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/hhes/families/data/households.html
United States Census Bureau. (2015). Poverty thresholds for 2014 by size of family and number of related children under 18 years [Table]. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/hhes/www/poverty/data/threshld/
Urban Ministries of Durham. (2011). Spent, the online game about surviving poverty and homelessness reaches its millionth play and invites Congress to accept the challenge [Press release]. Retrieved from http://www.umdurham.org/assets/files/pdf/SPENT1mmRelease_FINAL.pdf
Vescio, T. K., Sechrist, G. B., & Paolucci, M. P. (2003). Perspective taking and prejudice reduction: The mediational role of empathy arousal and situational attributions. European Journal of Social Psychology, 33, 455-472. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.163
Wang, C. S., Ku, G., Tai, K., & Galinsky, A. D. (2013). Stupid doctors and smart construction workers: Perspective- taking reduces stereotyping of both negative and positive targets. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 5, 430-436. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1948550613504968
Weiner, B., Perry, R. P., & Magnusson, J. (1988). An attributional analysis of reactions to stigmas. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55, 738-748. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.55.5.738
Yale University. (2016). Yale facts. Retrieved from http://www.yale.edu/about-yale/yale-facts
Yang, G. S., Gibson, B., Lueke, A. K., Huesmann, L. R., & Bushman, B. J. (2014). Effects of avatar race in violent video games on racial attitudes and aggression. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 5, 698-704. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1948550614528008
Yeh, C. S. H. (2015). Exploring the effects of videogame play on creativity performance and emotional responses. Computers in Human Behavior, 53, 396-407. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.024
Introduction
The media has a profound impact on the way individuals think and feel about social groups (Mutz & Goldman, 2010). Past research on how media can influence social beliefs has focused on such traditional media forms as radio (Paluck, 2009), storybooks (Cameron, Rutland, Hossain, & Petley, 2011), television (Schiappa, Gregg, & Hewes, 2005), and film (Riggle, Ellis, & Crawford, 1996). Computer gaming, which engages people more actively and immerses them more in the events than does traditional media (Jenkins, 2003), has recently started to receive more research attention (cf. Burgess, Dill, Stermer, Burgess, & Brown, 2011) due its broad popularity (Kain, 2012). This recent work reveals that playing video and computer games can influence prosocial behavior and intergroup beliefs and attitudes (Adachi, Hodson, Willoughby, & Zanette, 2014; Anderson & Bushman, 2001; Gehlbach et al., 2015). For example, playing a violent video game as a Black (vs. White) avatar increases negative attitudes toward Black people and reinforces the stereotype that Black people are violent (Yang, Gibson, Lueke, Huesmann, & Bushman, 2014). When Israeli Jews and Palestinians played an educational game about the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, they showed a more nuanced understanding of the conflict and more positive attitudes toward the other group (Kampf, 2015; Kampf & Cuhadar, 2015). Studying the effects of gaming is even more important now because games are increasingly available for free to anyone with internet access (H2 Gambling Capital, 2015). The current research, consisting of two studies, examined how the fundamental aspects of online gaming can affect attitudes toward the poor.
A plethora of past research indicates that many Americans hold negative attitudes toward the poor (Cozzarelli, Wilkinson, Tagler, 2001; Tagler & Cozzarelli, 2013). The poor are consistently stereotyped as dishonest, lazy, and dependent (Gorski, 2011). Work by Rank, Yoon, and Hirschl (2003) reveals that when people are asked to explain why poverty exists, they make internal attributions (i.e., blaming the poor individuals) significantly more often than external attributions (i.e., blaming the government or society). People generally cite irresponsibility and laziness as reasons for poverty (Soss & Schram, 2007). This attribution of controllability to poverty is significant because stigmas perceived as more controllable elicit more negative attitudes (Graham, Weiner & Zucker, 1997).
Addressing individuals’ beliefs about poor people is important because these beliefs can have significant consequences for individuals living in poverty. For example, anti-poor attitudes affect policy-makers’ and politicians’ willingness to support government funded anti-poverty policies such as welfare and food stamps (Cozzarelli et al., 2001). These policies could significantly improve the lives of the current 15.8% percent of Americans living below the poverty line, considering that people in poverty have limited access to good food, health care, and clean air (Bishaw & Fontenot, 2014; Mukherjee, 2013). In the present research, we examined computer games as a possible way to reduce anti-poor attitudes.
In examining the literature on prejudice reduction, two contrasting perspectives emerge for how playing a computer game about poverty might influence attitudes toward the poor and support for policies that benefit poor people. The first perspective emphasizes how playing a computer game could promote empathic emotions (Greitemeyer, Osswald, & Brauer, 2010). Computer games are interactive and immersive in a way that narratives in traditional forms of media are not: Players both “perform [and] witness narrative events” (Jenkins, 2003, p. 124). Thus, one way playing computer games might reduce prejudice towards poor people is by allowing players to take on the perspective of a poor person. Stephan and Finlay (1999) showed that being instructed to adopt the perspective of a member of a stigmatized group can arouse a range of sympathetic emotions (see also Pederson, Beven, Walker, & Griffiths, 2004), and Batson et al. (1997) found that specifically inducing feelings of empathic concern (e.g., feeling sympathetic and compassionate) by instructing participants to imagine the feelings of a member of a stigmatized group produced more positive attitudes toward the group as a whole (see also Todd, Bodenhausen, Richeson, & Galinsky, 2011).
Computer games may be particularly effective at improving intergroup attitudes and reducing prejudice by inducing empathic concern given their interactive and engaging nature (Klimmt, Hartmann, & Frey, 2007). Games’ interactivity and immersiveness increase their ability to impact players’ emotions and cognitions (Madsen, 2016; Yeh, 2015). When the player becomes immersed in the game and in the lives of its characters, this helps the player see through the eyes of the character and imagine how a poor person feels (Batson et al., 1997; Mutz & Goldman, 2010). Past work shows that perspective-taking exercises in which participants observe the misfortunes of a member of an out-group leads to increased empathic concern and thus positive attitudes toward that out-group (Dovidio et al., 2004). Work by Gehlbach et al (2015) confirms that playing a perspective-taking computer game positively influences intergroup interactions. Thus, to the extent that playing an interactive computer game about the threat of experiencing poverty promotes empathic concern, it can lead to less prejudice toward poor people (Batson et al., 1997).
Although the research on empathic concern paints a rosy picture for how computer games might be used to reduce prejudice (Mutz & Goldman, 2010; Wang, Ku, Tai, & Galinsky, 2013), research in the area of stigma controllability suggests that these games might have the opposite effect (Weiner, Perry, & Magnusson, 1988). This second perspective emphasizes how playing a game about poverty might lead players to believe that poverty is personally controllable. Computer games arouse a sense of personal agency and control (Klimmt et al., 2007). They involve a series of decisions and behaviors; they are “enacted” stories that emphasize the role of decisions and choices on outcomes (Jenkins, 2003). A player in game feels that they have complete control over the game outcomes, because the game outcomes are a direct result of their decisions. Past research has established that when a stigma is perceived to be controllable (implying that stigmatized members are to blame for their situation), that stigma elicits more negative attitudes than when a stigma is perceived to be uncontrollable (Puhl & Brownell, 2003; Tyrrell, Hetz, Barg, & Latimer, 2010). Thus, to the extent that playing a computer game emphasizes personal control and thus the blameworthiness of the stigma (in this case, poverty), it can lead to more negative attitudes.
It is important to study how online games influence intergroup attitudes because of a current trend to create games with the intention of reducing bias and increasing empathy. While many of these prosocial games are based on psychological research and have had their effects empirically tested (Belman & Flanagan, 2010; Flanagan, Howe, & Nissenbaum, 2005; Kaufman & Flanagan, 2015), many other games are created and disseminated without having their ability to reduce bias tested. For example, Gamesforchange.org is a website launched in 2004 with the mission of “catalyzing social impact through digital games” (Games for Change, 2015). The website currently hosts over 100 games that address topics such as poverty, mental illness stigma, and illegal immigration. These games are being promoted as a new method of attitude change despite the lack of evidence that they actually work. In the present research, in two studies, we investigated one of the games hosted on Gamesforchange.com called SPENT and how it influences attitudes toward the poor.
Study 1
Study 1 examined how playing a game about poverty can uniquely influence attitudes toward the poor by comparing participants who played a poverty game to participants who watched a video of the poverty game as well as to participants in a control condition. SPENT is an interactive poverty simulation game in which players start out with $1,000 and engage in daily financial decisions with the goal of making it to the end of 30 days with money left in their bank account. Participants in the Game condition played SPENT whereas participants in the Observation condition watched a video recording of someone else playing SPENT. Participants in the Control condition played a game about preparing for natural disasters.
As noted earlier, playing a computer game about poverty could have two different, and potentially countervailing effects. On the one hand, playing a game about poverty could increase empathic concern for the poor, which could reduce prejudice against poor people (Batson & Moran, 1999). On the other hand, playing a game about poverty, because it emphasizes decision-making by the player, could increase perceptions of the personal controllability of poverty, thus increasing stigmatization of the poor (Tyrrell et al., 2010). We therefore examined how the playing a computer game about poverty affects people’s empathic concern for the poor, beliefs about the controllability of poverty, attitudes toward the poor, and support for anti-poverty government policies. While attitudes toward out-groups and support for government policies to help those out-groups are correlated, past work has shown them to be conceptually distinct (Dixon, Durrheim, & Tredoux, 2007).
To the extent that observing the unique challenges that members of stigmatized groups experience encourages perspective taking (Shih, Wang, Bucher, & Stotzer, 2009) and arouses empathic concern (Batson & Moran, 1999), both participants who watch a video of the poverty game and those who play the poverty game themselves were expected to experience higher levels of empathic concern than participants in the control condition. Greater empathic concern, in turn, was expected to lead to more positive attitudes toward the group and efforts to benefit members of the group (Batson et al., 1997).
In addition, because playing the game actively engages participants directly in making economic decisions and seeing contingent outcomes, we expected that participants who played the game would also believe that poverty is more controllable than would participants in the control condition. Greater attribution of controllability of a group for its stigmatized condition predicts more negative attitudes toward the group (Graham et al., 1997) and less support for government-funded policies to improve the condition of the group (Cozzarelli et al., 2001).
By contrast, we expected that, because perspective taking leads to more external attributions for another’s condition, participants who observed the game could potentially show a weaker belief in the personal controllability of poverty compared to participants in the control condition. Although observing someone else play the game in the role of a person in poverty could lead to stronger dispositional attributions, which people often make when they observe others (Jones & Nisbett, 1972; cf. Malle, 2006; Malle, Knobe, & Nelson, 2007), Vescio, Sechrist, and Paolucci (2003) demonstrated that adopting, the perspective of a member of another group leads to less prejudice not only because of increased empathic concern but also because of increased situational attributions (i.e., decreased internal attributions; see Storms, 1973) for the adversity faced by members of the out-group.
Taken together, these lines of reasoning suggest that compared to participants in the control condition, observing the poverty game (SPENT) would lead to more positive attitudes toward the poor and more support for policies benefiting the poor because these participants would experience higher levels of empathic concern (Batson & Ahmad, 2001) and possibly, based on Vescio et al.’s 2003 paper, believe that poverty is less personally controllable. However, compared to the control condition, playing the poverty game (SPENT), could increase empathic concern for the group but at the same time, because of the salience of personal economic choices in the game, also increase belief in the personal controllability of poverty. Because empathic concern produces more positive orientations whereas controllability beliefs produce more negative orientations, playing SPENT may not influence attitudes toward the poor and support for policies to benefit the poor, relative to the control condition. We thus investigated not only the outcomes (attitudes toward the poor and support for policies to alleviate the negative impact of poverty) but also the processes leading to these outcomes.
Method
Participants. American Mechanical Turk workers over 18 were recruited on Mturk.com to participate in a study entitled “Online Gaming and Thought Processes.” There were 227 participants. Of these 227, 51.5% were men. Fifty-five percent held a two or four-year college degree and 27.3% completed some college but did not get a degree. Average age was 35 years (SD=11 years) and ages ranged from 18 to 72 years. Average income was $36,964 (SD=$37,596). Using an $18,850 yearly salary as the poverty cut-off value for the average American household (US Census Bureau, 2014, 2015), 27% (n=62) of participants were impoverished. Seventy-seven point one percent of participants identified as White, 7.9% were African American, another 7.9% were Hispanic, and 5.3% were Asian or Pacific Islander. All participants who completed the study were included in the analyses. We arrived at our sample size by conducting a power analysis using G*power (Faul, Erdfelder, Buchner, & Lang, 2009). Setting a medium effect size, f= .25, the power analysis indicated that to examine mean differences between three groups we would need a sample size of 252. Our final sample size of 227 approached this number.
Experimental Conditions. Participants played different games in the experimental conditions. In the control condition, participants played the online game Stop Disasters created by the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction. In this game, participants are given a population and are told to put structures (like hospitals) and plant-life (like trees) in place to protect the population from an impending natural disaster (such as a flood). After preparing the town, participants start the disaster and see how well the town holds up. The game takes about ten minutes to play. After finishing the game, participants answered a number of comprehension check questions such as “what type of natural disaster are you trying to protect the town from?” This game was chosen as the control because we found it is as engaging and interactive as SPENT and because it shared SPENT’s focus on making decisions to achieve a certain outcome.
In the game-playing condition, participants played the interactive online poverty game, SPENT. SPENT was chosen as the treatment game because it is a highly popular computer game (played over one million times as of 2011; Urban Ministries of Durham, 2011) presented as an effective way to reduce prejudice against the poor. It was designed by an advertising agency in 2011 with the goal of promoting empathy and liking for the poor. The group created the game’s situations with input from local case workers and people living in homeless shelters (Flandez, 2011). It is an interactive and immersive way for participants to come to understand the struggles of living in poverty.
In SPENT, participants took on the role of an unemployed single parent with $1000 in their bank account. Participants begin the game by choosing a job to apply for. Next they select a place to live. The rest of the game consists of the participants making day-to-day financial decisions and seeing the consequences of those actions. For example, participants may encounter a scenario in which their car breaks down and they need to decide whether to pay for it to be fixed or to just start using the bus instead. After they make a decision, they are shown the consequences of that decision. In this scenario, they may be presented with a text box indicating that taking bus to save money makes them late for work too often, and as a consequence they are fired from their job for frequent tardiness. However, if participants instead decided to pay for the damages, the text box might say that they no longer have money to pay their rent and are subsequently evicted.
The objective of the game is to make to the end of 30 days without running out of money and hopefully with enough money to pay next month’s rent (~$1,000). We note that in many of these scenarios the decision that leads to more money in reserve (e.g., foregoing a needed root canal) is not necessarily the best decision when other factors (e.g., physical or mental health) are considered. In this way, SPENT poignantly depicts the many challenges that people in poverty face. Participants were instructed to play until they either ran out of money or reached the end of the month.
In the present research, the game took 11 minutes, on average, to complete. While participants played the game they answered a number of comprehension check questions to ensure that they were paying attention. Questions included multiple choice questions such as, “Which job requires admin experience?” and open-ended questions such as, “Describe one of the situations encountered during the game.” Forty-five percent of participants who played the game made it to the end of the month, but no participants succeeded in saving enough money to pay the next month’s rent.
In the observation condition, participants watched one of four videos. Each of these videos was a screen recording of one of four confederates (one man) between the ages of 21 and 35 playing SPENT. While watching the screen recordings, participants answered the comprehension check questions used in the game-playing condition. Participants did not receive any special instructions regarding how they should view the video. Forty-one percent of participants viewed a video in which the player made it to the end of the month; this percentage did not significantly differ from the percentage of participants in the game condition who made it to the end of the month.
Measures. Before playing the game or watching the video, participants responded to a number of demographics items including gender (male vs. female), age, race (White, African American, Asian/Pacific Islander, Native American, Hispanic), and annual income. Conservatism was measured by having participants indicate their political ideology on a scale 1=very liberal to 7=very conservative.
After watching the video or playing the game, to first assess their emotional responses, participants rated how much (from 1=not at all to 5=very much) of various emotions they were currently experiencing. Eight of these items (warm, softhearted, moved, tender, concerned, touched, compassionate, and sympathetic) represented empathic concern, which has predicted positive intergroup attitudes in previous research (Batson et al., 1997). Ten other items (frustrated, alert, scared, upset, happy, hopeless, irritable, attentive, interested, and alert) were included to obscure the purpose of the study. Factor analyses on the eighteen items indicated three components. All of the empathic concern items factored onto one component (eigenvalue=5.39), with factor loadings ranging from .60 to .87. Responses to the eight empathic concern items were averaged to for an empathic concern measure (α=.93, M= 2.89, SD= 1.05).
Next, participants in the game-playing and observation conditions responded to three items measuring perceived personal agency in the game; these items served as a manipulation check of condition assignment. Participants responded using a scale from 1=strongly disagree to 6=strongly agree to the following items: “I felt I had control over the outcomes in the scenarios presented”; “The outcomes in the scenarios presented were a direct result of my personal choices”; and “I felt I could not control the outcomes in the scenarios presented.” Responses were reverse-coded as needed and averaged to create a Perceived Personal Agency variable (α=.79, M= 3.08, SD= 1.11).
The main dependent measures in this study were belief in the controllability of poverty, support for government-funded poverty-alleviating programing, and attitudes toward the poor. The scale assessing beliefs about poverty contained 10 items measuring the extent to which people believe that poverty is controllable and that poor people should be blamed for their plight. Items included, “Poor people cannot fully control what happens to them” (reverse-scored), and “Poor people are personally to blame for their situation.” Participants indicated their agreement on a scale of 1=strongly disagree to 6=strongly agree, and items were scored such that higher scores indicated a stronger belief that poverty is controllable. Responses to these items were averaged to create a Poverty Controllability Beliefs measure (α=.90, M= 3.05, SD= 0.86).
A scale measuring support for government-funded policies to reduce poverty instructed participants to indicate how much they might support four hypothetical policies using a scale from 1=strongly oppose to 6 =strongly support. Items included, “Establishing more soup kitchens, this would be funded by a 0.3% increase in income tax” and “Increasing the minimum wage to $10.00/hour nation-wide.” We came up with these items after conducting a web search for anti-poverty policies being put in place at the local, state, or federal government level. We added the “this would be funded by...” to items as needed in order to clarify how the policies would be enacted. The four items were averaged to create a Policy Support variable (α=.82, M= 4.40, SD= 1.24).
Feeling thermometers, which have been shown to be both reliable and valid measures of social attitudes (Alwin, 1997; Kinder & Drake, 2009), assessed participants’ attitudes toward ten different groups: Asian people, Black people, clowns, journalists, drug addicts, factory workers, lawyers, poor people, homeless people, and fast food workers. The groups were presented in random order. Participants indicated how warmly they felt toward each of these groups on a scale of 1=very cold to 50=very warm using a slider that was centered at 25. Poor people, homeless people, and fast food workers were included to represent groups in or near poverty; the other seven groups were included to obscure the purpose of the study. Factor analysis confirmed that ratings for poor, homeless, and fast food workers all loaded onto the same factor (eigenvalue=3.93), with loadings of .84, .72, and .79, respectively. The thermometer ratings for poor, homeless, and fast food workers were combined and averaged to create an Attitudes toward the Poor variable (α=0.87, M= 34.03, SD= 9.58).
Procedure. Participants completed all measures online using the survey tool Qualtrics. The experiment took 24 minutes on average and participants received $1.01 as compensation. First, participants completed the demographic items described above. Next, participants were randomly assigned to one of three conditions. In the control condition, participants are instructed to play Stop Disasters. In the game-playing condition, participants were instructed to play SPENT. In the observation condition, participants were randomly assigned to watch one of four screen recordings of someone playing SPENT. After exposure to either SPENT or Stop Disasters, participants responded to items measuring their emotions, including emotions related to empathic concern. Additionally, participants in the observation and game conditions responded to items measuring their feelings of perceived personal agency while playing or observing SPENT. Finally, participants in all conditions completed the three scales measuring the main dependent variables: belief that poverty is personally controllable, attitudes toward the poor, and support for government-funded anti-poverty policies.
Results
All continuous variables were centered at zero. To examine the effects of condition, we used the standard method for analyzing categorical variables with three levels (Chen, Ender, Mitchell, & Wells, 2003) to create two dummy variables: Game vs. Control (in which Game=1, Control=0, and Observation= 0) and Observation vs. Control (in which Observation=1, Game= 0, and Control= 0). Before investigating the effects of condition, we first examined the demographics variables (age, race, gender, etc.)1. We found that conservatism, age, gender, and income significantly predicted one or more dependent measures. Therefore, the following variables were included as covariates in all analyses: gender (male vs. female), age, conservatism, and income. For a summary of observed and covariate-adjusted means broken down by condition for participants’ perceived personal agency, empathic concern, controllability beliefs, attitudes toward the poor, and policy support, see Table 1. See Table 2 for a matrix of the correlations between controllability beliefs, empathic concern, attitudes toward the poor, and policy support in each condition and collapsing across condition.
Table 1. Study 1 Observed and Covariate-adjusted Means and Standard Deviations Broken Down by Condition for Participants’ Perceived Personal Agency, Empathic Concern, Controllability of Poverty Beliefs, Attitudes toward the Poor, and Policy Support.
|
Variable/Condition |
Game |
Control |
Observation |
|||
|
Mean Type |
Obsv. |
Adj. |
Obsv |
Adj. |
Obsv. |
Adj. |
|
Perceived Personal Agency |
3.41 (1.12) |
3.42 1.04) |
- - |
- - |
2.53 (.87) |
2.53 (1.05) |
|
Empathic Concern |
2.98 (.98) |
2.98 (.97) |
2.49 (1.00) |
2.48 (.97) |
3.46 (.97) |
3.49 (.97) |
|
Controllability Beliefs |
3.03 (.87) |
3.01 (1.01) |
3.18 (.89) |
3.21 (0.78) |
2.85 (.77) |
2.86 (.80) |
|
Attitudes toward the Poor |
34.23 (9.35) |
34.34 (9.15) |
32.54 (9.13) |
32.40 (9.08) |
36.30 (10.42) |
36.43 (9.18) |
|
Policy Support |
4.39 (1.35) |
4.44 (1.00) |
4.23 (1.19) |
4.18 (1.00) |
4.72 (1.10) |
4.72 (.15) |
|
Note: covariate-adjusted means take into account gender, age, income, and conservatism. |
||||||
Table 2. Study 1 Partial Correlations (Controlling for the Effects of: Conservatism, Age, Income, and Gender) and Zero-Order Correlations between Poverty Controllability Beliefs, Empathic Concern, Attitudes toward the Poor, and Support of Government Policy in Each Condition and Across Condition.
|
Condition |
Measure |
Policy Support |
Attitudes to. Poor |
Empathic Concern |
|
Observation |
Controllability Beliefs |
-.58** (-.72**) |
-.36* (-.49**) |
-.27† (-.31**) |
|
Empathic Concern |
.35* (.56**) |
.48** (.54**) |
|
|
|
Attitudes to. Poor |
.59** (.68**) |
|
|
|
|
Control |
Controllability Beliefs |
-.39** (-.56**) |
-.08 (-.20†) |
-.001 (-.03) |
|
Empathic Concern |
.14 (.14) |
.37** (.39**) |
|
|
|
Attitudes to. Poor |
.31** (.40**) |
|
|
|
|
Game |
Controllability Beliefs |
-.21† (-.35**) |
-.16 (-.17) |
-.35** (-.37**) |
|
Empathic Concern |
.46** (.51**) |
.26* (.33**) |
|
|
|
Attitudes to. Poor |
.42** (.45**) |
|
|
|
|
|
Controllability Beliefs |
-.38** (-.51**) |
-.21** (-.27**) |
-.23** (-.25**) |
|
Overall |
Empathic Concern |
.36** (.37**) |
.39** (.42**) |
|
|
|
Attitudes to. Poor |
.44** (.49**) |
|
|
|
Note: **p< .01, *p< .05, †p< .10. |
||||
Participants’ Perceived Personal Agency. As a manipulation check, we examined participants’ feelings of perceived personal agency in the observation and game-playing conditions. As expected, we found that participants who played SPENT (M=3.42, SD=1.11) felt more personal agency over the game’s outcomes than participants who observed SPENT2 (M=2.53, SD=.87), F (1,119)=21.40, p< .oo1, ηp2=.15.
Effects of Game Outcome. We conducted supplementary analyses testing whether, among participants who played SPENT in the study, there were differences in effects as a function of whether the player “won” the game. As indicated previously, 45% of participants who played SPENT “won” the game (made it to the end of 30 days with money still in their bank account). To examine the effect of performance on the game, we created a dichotomous variable indicating whether or not a participant made it to the end of 3o days. Making it to the end of 30 days was associated with marginally more support of government policies to reduce poverty, r(67)= .22, p=.084, and marginally more empathic concern, r(67)=.21, p=.081. There were no other effects. In the observation condition (in which 62% of participants watched a screen recording of a player who made it to the end of 30 days), game outcome was unrelated to empathic concern, policy support, liking, or controllability beliefs.
Empathic Concern. Participants in both the observation condition (b=1.01, SE=.18, β=.401, p<.001, 95% CI[.65, 1.36]) and the game condition (b=.49, SE=.16, β=.225, p=.002, 95% CI[.18, .80]) felt more empathic concern after the condition manipulation when compared to participants in the control condition. These results are in line with our prediction that both observing and playing SPENT would promote greater feelings of empathic concern feelings than participating in the control condition. However, an additional comparison revealed that the observation condition tended to elicit more empathic concern than did the game condition, b=.19, SE=.10, β=.134, p=.057.
Poverty Controllability Beliefs. When the covariates and two condition dummy variables are used to predict the belief that poverty is personally controllable, participants in the observation condition showed less belief that poverty is controllable when compared to participants in the control condition, b=-.35, SE=.15, β=-.171, p=.018, 95% CI[-.64, -.06]. Participants in the SPENT condition did not differ significantly from those in the control condition, b=-.20, SE=.13, β=-.110, p=.127, 95% CI[-.45, .06]. This result is inconsistent with our predictions: Playing SPENT did not increase controllability beliefs as we expected (see Table 1).
Attitudes toward the Poor. In the model predicting attitudes toward the poor using the aforementioned covariates and the two condition dummy variables, participants in the observation condition showed more favorable attitudes toward the poor than did participants in the control condition, b=4.03, SE=1.69, β=.177, p=.018, 95% CI[.69, 7.37]. Participants in the SPENT game condition did not differ in their attitudes toward the poor compared to those in the control condition, b=1.94, SE=1.48, β=.098, p=.191, 95% CI[-.97, 4.85]. Overall, the findings for attitudes toward the poor are consistent with our hypotheses.
Policy Support. Using the same model as before to predict support of government funded anti-poverty policies, the observation condition again produced more policy support than the control condition (b=.55, SE=.19, β=.184, p=.004, 95% CI[.18, .91]), while the effect of game condition was non-significant, b=.26, SE=.16, β=.101, p=.110, 95% CI[-.06, .58]. As with attitudes toward the poor, these findings are consistent with our hypotheses.
Examining the Intergroup Effects of Condition. To more directly examine the intergroup effects of playing or observing SPENT (that is, the effect SPENT has on participants who are not poor themselves compared to its effect on poor participants), we classified participants as poor or not poor using the poverty cut-off value identified in the most recent US Census statistics on average household income (US Census Bureau, 2014, 2015). We then analyzed the influence of poverty status, condition (as in the previous analyses, analyzing the effects of the three conditions with two dummy-coded variables representing Game vs. Control and Observation vs. Control comparisons), and all interactions between poverty status and condition on the four main dependent measures. The effect of condition was not moderated by poverty status, with one notable exception. Analyses revealed a game (playing SPENT vs. playing the Control game) x poverty status interaction on attitudes toward the poor (b=6.25, SE= 3.30, β=.200, p=.060, 95% CI[-.26, 12.75]).
To further investigate this interaction, we examined the effect of playing SPENT on attitudes toward the poor separately for participants with incomes below and above the poverty line. Among participants classified as poor based on their income, playing SPENT led to significantly more positive attitudes toward the poor, b=7.04, SE=2.5, β=.395, p=.007, 95% CI[1.98, 12.11]). Non-poor participants’ attitudes were not influenced by playing SPENT (b=. 12, SE= 1.82, β=.006, p=.946, 95% CI[-3.48, 3.72]). All other analyses listed in the results section were conducted using the full sample, collapsed across poverty status, with supplementary analyses conducted separately for non-poor participants.
Indirect Effects: Attitudes toward the Poor. Based on past work examining the effects of observation of the adversity of a member of a stigmatized group, we predicted that both empathic concern and controllability beliefs would partially account for the relationship between condition and attitudes toward the poor. We first examined the indirect effect of the observation condition on positive attitudes toward the poor. We tested this model, illustrated in Figure 1, using Preacher and Hayes’ (2008) bootstrapping macro (model 4) using 10,000 bootstraps. As previously mentioned, participants in the observation condition experienced greater empathic concern (b=1.01, SE=.18, β=.401, p<.001) and believed that poverty was less controllable than participants in the control condition, b=-.35, SE=.15, β=-.171, p=.018. Empathic concern additionally significantly predicted more positive attitudes toward the poor (b=3.42, SE=.58, β=.377, p<.001) and controllability beliefs predicted more negative attitudes toward the poor, b=-2.41, SE=.81, β=-.216, p=.003. The indirect effect of observation condition on positive attitudes was partially accounted for both by empathic concern, b=3.18, SE=.83, 95% CI[1.76, 5.03], and controllability beliefs, b=.50, SE=.36, 95% CI[ .01, 1.50].
Figure 1. Study 1 Indirect Effect of Observation Condition on Attitudes toward the Poor through Empathic
Concern and Belief about the Controllability of Poverty (top panel) and Study 1 Indirect Effect of Observation
Condition on Support of Government-funded Anti-Poverty Policies through Empathic Concern and Belief
about the Controllability of Poverty (bottom panel).

Non-poor participants showed the same pattern of effects. Non-poor participants in the observation condition experienced greater empathic concern (b=.86, SE=.19, β=.38, p<.001) and believed that poverty was less controllable than participants in the control condition, b=-.29, SE=.16, β=-.15, p=.069. Empathic concern predicted more positive attitudes toward the poor (b=4.0, SE=.64, β=.38, p<.001) and controllability beliefs predicted more negative attitudes toward the poor, b=-3.56, SE=.83, β=-.30, p<.001. The indirect effect of observation condition on positive attitudes was significant through empathic concern, b=2.65, SE=.85, 95% CI[1.26, 4.66], whereas the effect through controllability beliefs was only trending, b=.30, SE=.34, 95% CI[-.11, 1.27] (p = .144).
Next we tested this model among all participants but only within the game condition. Note that playing SPENT led to more empathic concern, b=.49, SE=.16, β=.225, p=.002, but did not influence controllability beliefs, b=-.20, SE=.13, β=-.110, p=.127. Using the same bootstrapping macro as before, the indirect effect of game condition on positive attitudes toward the poor through empathic concern was significant, b=1.57, SE=.61, 95% CI[.58, 3.02]. Controllability beliefs did not account for this indirect effect, b=.28, SE=.30, 95% CI[-.04, 1.21]. Thus, our hypothesis was partially supported: Empathic concern significantly accounted for the indirect effect of condition on positive attitudes toward the poor in both game and observation conditions, whereas controllability beliefs only accounted for the indirect effect of observation condition.
Indirect Effects: Policy Support. Based on past work on controllable stigmas and correlates of support of anti-poverty policies, we predicted that indirect condition effects on policy support would occur through both empathic concern and controllability beliefs. As before, we first examined the indirect effect of observation condition on policy support through empathic concern and controllability beliefs. We tested this model, presented in Figure 1, using Preacher and Hayes’ (2008) bootstrapping macro (model 4) using 10,000 bootstraps. Recall that observation condition predicted both empathic concern and controllability. Further, both empathic concern (b=.35, SE=.07, β=.300, p<.001) and controllability beliefs (b=-.48, SE=.09, β=-.334, p<.001) predicted policy support. Both empathic concern, b=.27, SE=.09, 95% CI[.12, .49], and controllability beliefs, b=.14, SE=.06, 95% CI[.04, .29], significantly partially accounted for the influence of observation condition on policy support. When we examined the game condition, empathic concern again accounted for the indirect effect on policy support, b=.13, SE=.06, 95% CI[.05, .27], whereas controllability beliefs did not, b=.08, SE=.06, 95% CI[-.02, .23].
In this case, our hypothesis was fully supported when examining the influence of observing SPENT. Observing SPENT led to more policy support in part because it also led to increased empathic concern and decreased belief in the controllability of poverty. Our hypothesis was only partially supported when examining the Game condition. Here, only empathic concern accounted for the indirect effect of condition on policy support.
Discussion
In Study 1, we examined the influence of playing a poverty simulation game, observing a poverty simulation game, and playing a control game on attitudes and beliefs about the poor. We hypothesized that playing the game would lead to both more empathic concern and more belief that poverty is personally controllable relative to playing a game unrelated to poverty. Playing SPENT produce greater empathic concern but did not lead to more belief in the controllability of poverty. Overall, compared to playing the control (disaster) game, playing SPENT did not influence attitudes toward the poor or support for policies benefitting the poor.
We further hypothesized that observing the game would positively influence attitudes toward the poor. Indeed, we found that observation evoked empathic concern, increased positive attitudes toward the poor, led to more support of government funded anti-poverty policies, and decreased the belief that poverty is personally controllable. Lastly, we predicted that empathic concern and controllability beliefs would significantly account for the indirect effects of condition on both attitudes toward the poor and policy support. This hypothesis was partially supported. While both greater empathic concern and weaker controllability beliefs accounted for the indirect effect of observation condition on policy support, only empathic concern accounted for the indirect effect of observation condition on attitudes toward the poor.
Overall, these data show that observing the adversity of members of a stigmatized group has a variety of positive effects on intergroup attitudes and beliefs. Our findings support past work indicating that observation of adversity can evoke empathic concern and other positive emotions (Shih et al., 2009). Furthermore, our data do not support the prejudice-reducing claims put forth by the creators of SPENT (Urban Ministries of Durham, 2011). In our study, playing SPENT had no positive effect on attitudes toward the poor.
Our prediction that playing SPENT would lead to higher controllability beliefs was not supported. In fact, playing SPENT had no main effect on controllability beliefs. It’s possible that SPENT’s effects on attitudes and beliefs are moderated by personal ideology, such as belief in meritocracy. Past work shows that individuals high in meritocracy beliefs more strongly believe that poverty is personally controllable and thus hold especially negative attitudes toward the poor (Kluegel & Smith, 1986). Although these results generally support our hypotheses, other influences could be involved. For example, it is possible that playing (vs. observing) SPENT did not positively influence attitudes because game players were more distracted, more self-focused, or more physically aroused than game observers. However, further examination of emotions relating to alertness (mean of how alert, attentive, and interested participants felt after playing/observing the game; α=.90) revealed no differences between the Observation, Game, and Control conditions, F(2, 222)= .41, p= .665, suggesting that these results cannot be readily explained by differences in distraction or arousal levels.
Moreover, the small percentage of participants in the game condition who reached the end of game (45%) could have influenced SPENT’s ability to positively impact attitudes toward the poor. While playing SPENT in general had no significant effect on attitudes or beliefs, players who played the game until the end (i.e., made effective enough decisions to make it through the end of 30 days with money still left in their bank account) tended to display more empathy, more support of government programs to reduce poverty, and less belief that poverty is personally controllable. Had a larger percentage of participants “won” SPENT, the game condition might have had a more positive effect on poverty beliefs and attitudes.
Interestingly, these effects of game outcome are counterintuitive when considered in comparison with past work on perspective-taking (Shih et al., 2009). If playing SPENT in the role of a poor person leads the player to view his or her experiences as reflecting the experiences of the poor, performing well on the game should lead players to believe that poor people, like him or her, can lift themselves out of poverty just by making the right choices. The player’s controllability beliefs should be intensified, leading to less liking of the poor (Rank et al., 2003). Instead, we found the opposite effect-- doing well in the game was associated with more positivity toward the poor. These results suggest that SPENT’S ability to change attitudes and beliefs about the poor comes not from its role-playing aspect, but on its educational aspect. The more time that players spend learning about poverty in the game, the more likely they are to feel positively toward the poor and to support poverty reducing policies. However, it’s likely that this effect wouldn’t be seen for players who begin the game already holding strong beliefs about the personal controllability of life success.
To the extent that perceptions of perceived controllability is an important factor in the effects of playing the computer game (SPENT) on attitudes toward poor people, the effects of playing the game would be expected to be more pronounced among people for whom personal controllability is more central to their social values and attitudes. We investigated this possibility in Study 2.
Study 2
Study 2 further investigated the influence of playing a computer game about poverty (SPENT) on attitudes toward the poor by considering individual differences in meritocracy beliefs as a moderator of the game’s effects. Beyond replicating the relationships observed in Study 1, we hypothesized that the effect of SPENT on attitudes would be moderated by meritocracy beliefs. In particular, to the extent that playing a game about poverty (SPENT), compared to playing a game about recycling, makes personal controllability of poverty salient (as we found in Study 1), playing SPENT may have a less positive impact on attitudes toward the poor among people for whom the personal controllability of poverty is not typically salient – that is, for people lower in meritocracy. Thus, we predicted that whereas people high in meritocracy would tend to believe that poverty was personally controllable and thus hold generally negative attitudes toward the poor (Cozzarelli et al., 2001), among people low in meritocracy, playing the game about poverty (SPENT) would lead them to believe that poverty is more personally controllable, and thus lead to less positive attitudes toward the poor.
Method
Participants. Participants were American undergraduate students over the age of 18, who participated to fulfill a course option. The sample size was determined by collecting data from as many students as possible in one semester. A total of 54 students participated, but because there was missing data for seven of them, the final sample size was 47. In this final sample, 26 were men, and 21 were women. Seventy-nine percent of the participants indicated a childhood socioeconomic status (SES) of middle class or higher. Age information was not collected but given that the sample was made up entirely of undergraduates, it is likely that the participants were between the ages of 18 and 22.
Experimental Conditions. Participants played different online games in the different experimental conditions. In this study, we used an online game about recycling, Garbage Dreams, as the comparison game in the control condition. In this game, participants took on the role of the Zaballeen people in Cairo who are responsible for disposing of Cairo’s garbage. The point of the game is to earn money by recycling as much of the garbage as possible. Participants can buy the ability to recycle different types of waste. Participants were instructed to play for ten minutes. During the game, participants responded to several attention-check questions. For example, they were asked how much money they made from recycling in their first month.
Garbage Dreams is similar to SPENT in that it involves taking on the role of a disadvantaged group member, making financial decisions, and seeing the consequences of those decisions. We chose a game similar to SPENT to ensure that the effects found in Study 1 were unique to SPENT and could not be elicited by playing just any immersive online game involving financial decisions and a disadvantaged group of people. Garbage Dreams differs from SPENT in a way that makes it a meaningful comparison game: the goal of Garbage Dreams is not to make users understand the struggles of the impoverished Zaballeen people. Instead, the emphasis is on understanding the job of the Zaballeen. The game does not mention the struggles faced by the Zaballeen or the short or long-term effects of the financial decisions made by players. By contrast, SPENT’s emphasis is on understanding the life of the poor. SPENT focuses on the challenges faced by the poor and the outcomes of their financial decisions. SPENT is meant to increase empathy for the poor, and so uses language, graphics, and music to achieve that goal. Garbage Dreams is merely a game about recycling. Thus, we concluded that Garbage Dreams would act as a better control than the game used in Study 1 (Stop Disasters).
In the experimental condition, participants played SPENT. Participants spent an average of 11 minutes playing SPENT. While they were playing the game, participants responded to several attention-check questions such as “Which job did you choose”; “How much was your rent?” and “Did you make it to the end of the month? If so, how much was in your bank account at the end?” Eighty percent of participants made it to the end of the month and one-third of those participants ended with $250 or more in their bank account. No participants ended the game with enough money to pay the next month’s rent. The amount of money participants had at the end of the month (categorized as zero, small, medium, or large) did not significantly influence poverty controllability beliefs, F(3, 22)=1.53, p=.234, ηp2=.173, or attitudes toward the poor, F(3, 22)=1.21, p=.330, ηp2=.141. Note that in this study there was no observation condition.
Measures. Before playing either Garbage Dreams or SPENT, participants completed Lalonde, Doan, and Patterson’s (2000) Meritocracy Beliefs Scale. In this scale, participants rated their agreement with seven statements on a range of 1=strongly agree to 5=strongly disagree. Sample items are, “Many people from minority groups do not reach positions of importance because they are not ambitious enough,” and “Our present social system works to the disadvantage of people from visible minorities” (reverse scored). An overall meritocracy score was created by averaging participant responses on each of the items, reverse-coding negatively worded items (M=2.50, SD=.51). Past studies using this meritocracy scale found a Cronbach alpha close to .71 (Foster, Sloto, & Ruby, 2006)3. In this study the Cronbach alpha was .57.
After playing either SPENT or Garbage Dreams, participants first indicated the degree to which they felt the empathic concern emotions moved, warm, softhearted, tender, compassionate, sympathetic, concerned, and touched from Batson et al.’s (1997) Empathic Concern scale (α= .90, M=2.88, SD= 0.84), the same scale used in Study 1. Next, participants completed the main dependent measures in this study, attitudes toward the poor and beliefs about the poor. The attitude measure was the same feeling thermometer used in Study 1, except that participants indicated warmth ratings on a scale from 1=very cold to 11=very warm instead of a scale from 1 to 50 and there were fewer additional groups (lawyers, clowns, drug addicts, journalists, and Black people). Factor analysis revealed three components. The warmth ratings for poor people, homeless people, and fast food workers all loaded onto component one (eigenvalue= 2.86) with factor loadings of .90, .88, and .68. An Attitudes toward the Poor variable was created by averaging the warmth ratings for these three groups (α=.82, M=6.30, SD= 1.57).
The beliefs measure was Stevenson and Medler’s (1995) Economic Beliefs scale, which was designed to measure classist beliefs. Participants indicated their agreement with items such as, “People who stay on welfare have no desire to work” and “Homeless people should get their acts together and become productive members of society” using a scale from 1=strongly disagree to 5=strongly agree. Factor analysis indicated a subscale accounting for 24.9% of the variance and containing four items that correlated .50 or more. These items mainly reflected the view that the poor’s defective choices were to blame for their poverty (e.g., “Most poor people are lazy”). These four “personal blame” items were averaged to create a Controllability Belief variable (α=.77, M=1.93, SD= 0.74). We used a different (and previously validated) measure of controllability beliefs in Study 2 to examine the convergent validity of the measure we created for Study 1.
Finally, a modified version of Green and Brock’s (2000) Narrative Engagement scale was used to confirm that the two games were equally engaging and interactive. Participants rated their agreement with such statements as “During the game, my body was in room, but my mind was inside the world created by the game” using a scale from 1=strongly disagree to 5=strongly agree. The five items were averaged to create an overall engagement score (α= .73, M=3.37, SD= .75).
Procedure. Participants, who signed up for a study described as “Online Social Decision Making” were contacted electronically to complete, embedded in other items purportedly assessing participant opinions, a measure of meritocracy beliefs. At least one week later, participants came into the lab to complete the second half of the study. They were told the first thing they had to do was play a game on the computer. Participants were randomly assigned to play one of two online games: SPENT or Garbage Dreams. After playing one of the two games, participants completed an empathy measure as well as measures of their attitudes and beliefs towards poor people. Lastly, participants completed a measure assessing their engagement with the game they played.
Results
In all analyses, continuous variables were centered at zero. In investigating interactions, “high” and “low” levels of a continuous variable refer to one standard deviation above and below the mean. To measure the effect of game, we used a dummy code (SPENT vs. Garbage Dreams). Demographic variables (gender and childhood SES) did not influence any of the dependent measures so they were not included in subsequent analyses. When the one participant who indicated his or her childhood SES as “poor” is excluded from the analyses, the results are the same. See Table 3 for a list of zero-order correlations among the variables Attitudes toward the Poor, Controllability Beliefs, Empathic Concern, and Meritocracy Beliefs across and between the two conditions.
Table 3. Study 2 Zero-Order Correlations between Poverty Controllability Beliefs, Empathic Concern,
Attitudes toward the Poor, and Meritocracy Beliefs in Each Condition and Across Condition.
|
Condition |
Variable |
Merit Beliefs |
Attitudes to. Poor |
Empathic Concern |
|
SPENT |
Control. Beliefs |
.21 |
-.27 |
-.13 |
|
Emp. Concern |
.17 |
.38* |
|
|
|
Att. to. Poor |
.23 |
|
||
|
Garbage Dreams |
Control. Beliefs |
.76** |
-.56** |
.23 |
|
Emp. Concern |
.16 |
.32 |
|
|
|
Att. to. Poor |
-.48* |
|
||
|
Overall |
Control. Beliefs |
.51** |
-.40** |
.04 |
|
Emp. Concern |
.17 |
.36** |
|
|
|
Att. to. Poor |
-.08 |
|
||
|
Note: **p< .01, *p< .05, †p< .10. |
||||
Engagement. We predicted that SPENT and Garbage Dreams would be equally engaging. Analysis confirmed this assumption (SPENT: M=3.62, SE=.48; Garbage Dreams: M=3.15, SE=.90; t(19)=1.49, p=.152, Cohen’s d=0.682). Level of engagement with the game did not predict more attitude change in either condition.
Effects of Game Outcome. Eighty percent of participants in the SPENT condition made it to the end of 30 days. This lack of variation in game outcome makes it difficult to ascertain how game performance influenced attitudes and beliefs. Game outcome, measured using a dichotomous variable (made it to the end of 30 days vs. ended before 30 days), did not predict any dependent measures.
Empathic Concern. We predicted that SPENT would lead to more empathic concern when compared to Garbage Dreams. A linear regression model in which game condition predicted empathic concern showed no significant effect of game, b=-.05, SE=.23, β=-.031, p=.824, 95% CI[-.64, .39]. However, empathic concern was positively associated with more positive attitudes toward the poor, b=.67, SE=.25, β=.357, p=.009.
Controllability Beliefs. As predicted, meritocracy had a significant direct effect on controllability beliefs, such that those high in meritocracy saw poverty as more personally controllable, b=1.21, SE=.25, β=.847, p< .001, 95% CI[.71, 1.71]. The interaction between game and meritocracy was also significant, b=-.95, SE=.34, β=-.476, p=.009, 95% CI[-1.64, -.26]. This interaction (see Figure 2) was further investigated using simple slopes analysis (Aiken & West, 1991).
Figure 2. Study 2 Mean Controllability Beliefs across Meritocracy Levels, Broken Down by Game.

In the Garbage Dreams condition, meritocracy has a significant effect on controllability beliefs such that those lower in meritocracy showed lower controllability beliefs, b=1.21, SE=.23, β=.757, p< .001. By contrast, among people who played SPENT, there was no significant relationship between meritocracy and controllability beliefs, b=.26, SE=.26, β=.212, p=.321. Examining the data by low versus high meritocracy, when people low in meritocracy played SPENT, they indicated more belief that poverty is personally controllable when compared to low meritocracy people who played Garbage Dreams, b=.62, SE=.25, β=.432, p=.016. People high in meritocracy showed no effect of game condition on their controllability beliefs, b=-.33, SE=.24, β=-.240, p=.177.
Attitudes toward the Poor. We predicted that playing SPENT might lead to more negative attitudes towards the poor due to its emphasis on agency and that this relationship would be moderated by meritocracy. Although analyses indicated no significant direct effect of the game or meritocracy on attitudes toward the poor, there was a significant interaction between the meritocracy and game, b=1.97, SE=.80, β=.496, p=.018, 95% CI[.35, 3.59], see Figure 3.
Figure 3. Study 2 Mean Positive Attitudes toward the Poor across Meritocracy Levels, Broken Down by Game.
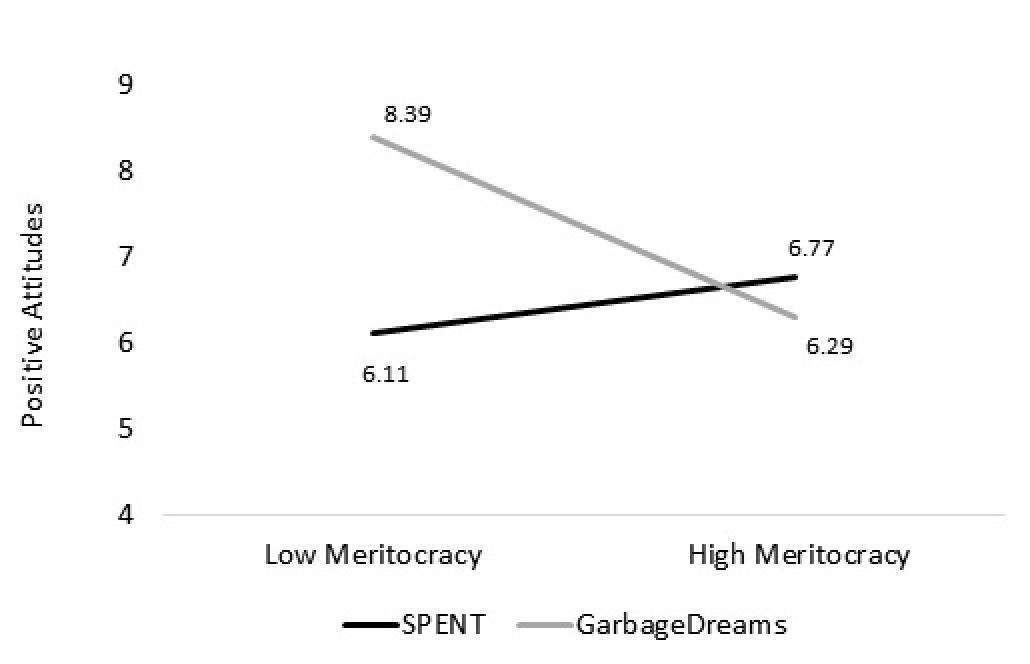
Simple slopes analysis revealed that, in the Garbage Dreams (control) condition, meritocracy had a significant effect on attitudes: Those higher in meritocracy showed less positive attitudes toward the poor, b=-1.29, SE=.52, β=-.477, p=.021. In the SPENT condition, meritocracy had no effect on attitudes, b=.68, SE=.61, β=.232, p=.276. Breaking down the analysis by low and high meritocracy, we see that playing SPENT led low meritocracy participants to have less positive attitudes towards the poor when compared to Garbage Dreams, b= 1.48, SE=.57, β=.516, p=.013. By contrast, the attitudes of participants high in meritocracy were not affected by game condition, b=-.526, SE=.58, β=-.183, p=.366. Thus, playing SPENT (when compared to playing Garbage Dreams) led low meritocracy individuals to show more negative attitudes toward the poor. These results are in line with our prediction that if playing SPENT led to more negative affect, this would be most prominent for those low in meritocracy3.
Mediated Moderation. Preacher and Hayes’ (2008) bootstrapping macro (model 8) using 5,000 bootstraps was utilized to test whether or not the effect of the game by meritocracy interaction on attitudes toward the poor is in fact explained (mediated) by the effect of the game by meritocracy interaction on controllability beliefs. In this model, game condition was the independent variable, controllability beliefs was the mediator, attitudes toward the poor was the dependent variable, and meritocracy as the moderator for both the relationship between game condition and attitudes toward the poor and the relationship between game condition and controllability beliefs. When controllability belief is included as an independent variable in the model where game, meritocracy, and the game by meritocracy interaction are used to predict attitudes toward the poor, the interaction between game and meritocracy becomes non-significant, b=1.32, SE=.84, p=.124. Thus, among people low in meritocracy, playing SPENT lead to less favorable attitudes toward the poor because it lead people to believe that poverty is personally controllable, 95% CI[0.12, 2.01], see Figure 4.
Figure 4. Study 2 Flowchart Depicting How Meritocracy Beliefs Moderate the Relationship
between Playing SPENT and both Controllability Beliefs about Poverty and Attitudes toward
the Poor and How Controllability Beliefs Mediate the Relationship between
Playing SPENT and Attitudes toward the Poor.

Note: **p< .01, *p< .05, †p< .10
Mediation. We further investigated the effect of the game by meritocracy interaction on attitudes through controllability beliefs by examining only participants in the Garbage Dreams condition, in which we found significant effects of meritocracy on both attitudes and controllability beliefs. Following the steps for mediation (Baron & Kenny, 1986), linear regression showed that meritocracy predicted both attitudes toward the poor (b=-1.29, SE=.52, p=.021) and controllability beliefs, b=-1.21, SE=.23, p< .001. In a model containing controllability beliefs and meritocracy, controllability beliefs predicted attitudes toward the poor (b=-1.11, SE=.45, p=.021) while the effect of meritocracy was non-significant, b=-.05, SE=.71, p=.943.
Preacher and Hayes’s (2008) bootstrapping macro (model 4) utilizing 5,000 bootstraps was used to test whether controllability beliefs mediated the relationship between meritocracy and attitudes toward the poor in the Garbage Dreams condition, with meritocracy as the independent variable and controllability beliefs as a mediator. Indeed, controllability beliefs were a significant mediator, 95% CI[0.36, 2.77]. When no other variables were affecting individuals’ attitudes towards the poor, low meritocracy individuals showed more positive attitudes toward the poor because they believed poverty is less personally controllable
Discussion
Study 2 was designed to conceptually replicate and theoretically extend the findings from Study 1. In terms of conceptual replication, Study 2 tested the effect of playing an interactive poverty game versus another type of control condition, playing an interactive recycling game, on attitudes toward the poor. With respect to extending Study 1, Study 2 also examined meritocracy as a moderating variable and controllability beliefs as a mediating variable.
As in Study 1, compared to playing a computer game unrelated to poverty (Stop Disasters in Study 1, Garbage Dreams in Study 2), playing SPENT did not significantly affect attitudes toward the poor. However, as predicted, individual differences in meritocracy moderated the impact of playing the different computer games. Specifically, participants high in meritocracy were not significantly affected by SPENT; they had consistently relatively negative attitudes toward the poor. In contrast, playing SPENT compared to Garbage Dreams did affect participants low in meritocracy. In the control (Garbage Dreams) condition, participants low in meritocracy had relatively positive attitudes toward the poor, but after playing SPENT, their attitudes toward the poor were more negative. Moreover, controllability beliefs mediated the relationship between game playing and attitudes toward the poor among participants low in meritocracy. That is, the more negative attitudes toward the poor after playing SPENT versus Garbage Dreams occurred because playing SPENT produced stronger controllability of poverty beliefs among low meritocracy participants.
One finding from Study 1 that was not replicated in Study 2 was the effect for playing SPENT on empathic concern. However, methodological factors – responses to the game used in the control condition – may account for this seeming discrepancy. Inspection of the data reveals that participants who played SPENT in Study 1 (M=2.98, SD=.98) had very similar levels of empathic concern compared to those who played SPENT in Study 2 (M=2.91, SD=.77). The responses to the control conditions differed: Those who played Stop Disasters in Study 1 showed less empathic concern (M=2.49, SD=1.00) than those who played Garbage Dreams in Study 2 (M=2.85, SD=.91). We note that we assessed empathic concern by asking participants about the emotions they were experiencing at the given moment, not specifically toward people in poverty.
Thus, it appears that the experience of playing the game about recycling while learning about a disadvantaged group of people in Egypt (Garbage Dream) in Study 2 was a stronger empathy-eliciting exercise than the game about limiting damage from natural disasters (Stop Disasters), which had a stronger focus on building structures, a weaker emphasis on the well-being of the people in the town, and was in generally less emotionally immersive. Of course, because this is a post-hoc explanation for the results on empathic concern, we cannot test its veracity. It is very possible that there exists a different explanation for why our two control games elicited different levels of empathic concern.
Another way Study 2 differed from Study 1 was the percentage of participants who “won” the game (that is, made it to the end of 30 days); 45% of Study 1 participants won the game whereas 80% of Study 2 participants won the game. This discrepancy cannot be explained by a difference in difficulty level or instructions. However, the participant populations in these two studies differed in likely relevant ways. Study 1 employed a Mechanical Turk sample; Study 2 involved participants who were undergraduates at an Ivy League university. Differences in analytic aptitude, on average, and incentive could both contribute to the higher success rate of participants in Study 2 than Study 1. Participants in Study 2 scored, on average in the top 5% in standardized test scores of applicants for college admission (College Board, n.d.; Yale University, 2016).
In terms of effort incentive, participants in Study 2 were paid $1.01 for being in the study. Participants in Study 2 chose to participate in research as one way of fulfilling a course research expectation, which was directly relevant to their elective course (Introductory Psychology). Moreover, despite the better performance in the game by participants in Study 2 than Study 1, as we noted earlier, (a) whether participants won the game did not have a strong or consistently significant effect on response to people in poverty, and (b) despite these between-study differences in game performance, the pattern of results in both studies are similar conceptually.
One limitation of Study 2 was that the sample size was relatively small, restricted by the availability of participants in the college-student pool at the time. Despite the limited statistical power associated with a small sample we were able to detect a significant interaction between the meritocracy and game for attitudes toward the poor, the outcome of primary interest, that reflected a moderate effect size (β=.496). Nevertheless, confidence in the stability of the effects we observed would be enhanced by replication with a larger sample.
Another limitation was that the meritocracy beliefs scale used in Study 2, although validated in previous research (Lalonde, Doan, & Patterson, 2000), had a relatively low Cronbach’s alpha and, overall, had a fairly strong association statistically (r = .51; see Table 3) and perhaps conceptually (e.g., items such as “Many people from minority groups do not reach positions of importance because they are not ambitious enough”) with controllability beliefs. Thus, while the relationship between meritocracy beliefs and beliefs about the controllability of poverty, which would be expected because of the importance of effort, investment, and motivation in meritocratic ideology, does not compromise the interpretation of the moderating effect of meritocracy beliefs on the type of game played, the additional mediation effect of perceived controllability of poverty on attitudes toward the poor should be interpreted with some caution.
General Discussion
Our two studies examined how playing a highly popular online game about poverty (Flandez, 2011) might influence attitudes and beliefs about the poor in order to understand whether active media forms (games) differentially influence social attitudes when compared to passive media forms (videos) and how these differences might come about. We found that because playing a game about poverty (and thus having control over one’s outcomes) led participants to believe that poverty is personally controllable, it did not positively influence attitudes toward the poor. The null main effect of SPENT occurred in both an online adult population (Study 1) and an in-lab undergraduate population (Study 2). Furthermore, personal ideology influenced the effectiveness of playing an agency-promoting poverty game. People low in meritocratic beliefs were more strongly and more negatively influenced by the game.
Future research might consider both methodological and conceptual issues relating to the effects of online games on social attitudes. Methodologically, we compared the effects to playing the game about poverty to two different games: one, in Study 1, about preparing for a disaster and the other, in Study 2, about recycling. The conceptual convergence of our findings across studies and the tests of moderating and mediating effects are consistent with our hypotheses and demonstrate support with strong ecological validity (i.e., with actual, popular online games). However, these games represent complex activities, and each game can have a range of different effects. To provide more methodological refinement, future researchers might develop an online game with the same basic structure but for which the elements of the task (e.g., about managing finances or making decisions in some other area, such as environmental conservation) can be specifically varied while holding other aspects of situation constant. Researchers could also examine games that are more about education and awareness than perspective-taking and empathy per se. Kampf (2015) was able to change the intergroup attitudes of Israeli Jews and Palestinian by having them play an educational awareness-raising game about the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Conceptually, future research might consider how online games and their elements (e.g., emphasis on controllability) affects responses to other social groups. Playing SPENT imbues the player with a sense of personal agency; the player extends this feeling to the impoverished character in the game and subsequently believes that people in poverty also have personal agency over their outcomes, which adversely affects attitudes toward poor people. This negative impact on attitudes may not occur for other social groups. Controllability beliefs form the basis of poverty-based prejudice (Gorski, 2011). By contrast, if the game had focused on a stigma that is not seen as personally controllable (such as physical disabilities), the negative effects of playing an online game on attitudes toward the group would likely be much more limited. Thus, future research might examine whether playing (vs. observing) games that emphasize player choice and autonomy would have greater negative impact on groups perceived to have more controllable stigmas (e.g., alcoholics, overweight people) than uncontrollable stigmas (e.g., victims of child abuse). Moreover, future research can examine how the context in which games are played influences intergroup attitudes. Recent work by Adachi and colleagues (2014) indicates that playing a multiplayer shooter game with an outgroup member greatly improves attitudes toward that outgroup.
It is important to continue to study the intergroup effects of computer and video gaming as these studies showed that active forms of media are uniquely different from more passive forms of media in certain ways, and these differences lead to diverse effects on intergroup attitudes and beliefs. Currently, psychologists know a great deal about how passive media (that is, television, films, radio, and books) influences social beliefs and which mechanisms cause these changes to take place (Mutz & Goldman, 2010). Less is known about how computer games influence social beliefs, although research in this area is currently on the rise (Flanagan & Nissenbaum, 2007; Kampf & Cuhadar, 2015). Considering the growing popularity of free online games with the goal of changing social beliefs and attitudes (Games for Change, 2015; H2 Gambling Capital, 2015) and the emerging evidence that gaming’s focus on personal agency could potentially cause game-based prejudice interventions to backfire, it is important to further understand how games influence attitudes.
While the current paper focused on games’ emphasis on personal agency, it is likely that other aspects (e.g., focus on wining vs. losing, degree of difficulty of the game) also affect games’ effectiveness as prejudice interventions. Kaufman and Flanagan (2015) in particular outline several novel strategies using their embedded design approach, Moreover, feelings of personal agency may not affect attitude change in all situations. The current paper examined poor people as the stigmatized group and specifically controllability beliefs about poverty, as controllability of a condition is a critical dimension determining the nature of group stigmatization (Jones et al., 1984). Past work has established that people tend to believe that poverty is personally controllable and that this belief fuels negative attitudes toward the poor (Soss & Schram, 2007). That is, assumptions about the personal agency of poor people is a known antecedent of anti-poor attitudes. For groups with stigmas that are not seen as personally controllable (e.g., gay people), beliefs about personal agency should not influence attitudes and a game involving personal agency might be able to increase positive attitudes toward that group by evoking empathic concern.
For addressing stigmas that are seen as personally controllable, future work could investigate ways that games could promote empathy while not increasing controllability beliefs. For example, a game in which players experienced the negative situations associated with poverty without being able to control those situations might be able to decrease prejudice because it lacks the agency component. Past work indicates that observing out-group adversity through the perspective of the stigmatized group can promote empathy and liking for that outgroup (Shih et al., 2009). Additionally, a game which explained to players how aspects of a certain stigma actually are personally uncontrollable could lead to more positive attitudes toward people with that stigma. Prejudice interventions in which participants are shown the genetic influences on weight have had some success at decreasing bias toward the overweight (Hague & White, 2005).
Continued work on the intergroup influences of computer games is important not only to increase understanding of how active media differs from passive media but also to aid in the creation of games which can positively influence intergroup attitudes and beliefs. As mentioned previously, games with the goal of increasing empathy and reducing bias toward out-groups are already being created and played by individuals all over the world (Games for Change, 2015). As of 2011, SPENT had been played by over one million people (Urban Ministries of Durham, 2011). More importantly, these games are potentially being played by individuals who have great power to influence the lives of disadvantaged group members. The creators of SPENT currently have a petition underway asking members of the U.S. Congress to play SPENT (Urban Ministries of Durham, 2011). Further, many of games hosted on Gamesforchange.org are described as being designed to be played by policymakers in order to influence their policy decisions (Huey, 2013).
This is problematic because the current paper suggests that interactive games have the potential to actually increase prejudice toward certain groups. Thus, if policymakers and members of Congress are encouraged to play one of these games that, due to some aspect of its design (e.g., focus on agency), promotes negative attitudes, it is possible that these games could lead to the passage of state or federal laws and policies that perpetuate or increase the inequalities faced by members of stigmatized groups.
The current paper offers novel insight into how the content of a perspective-taking online game influences intergroup attitudes and beliefs. Further work on gaming’s intergroup effects will contribute to psychologists’ understanding of how active and passive media forms diversely influence attitudes and will inform the creation of games that can reduce prejudiced attitudes and behavior.
Footnotes
- Participants who watched video 1 in the observation condition were removed from all analyses because video 1 was considerably shorter than the other videos and led to significantly less empathy, liking, and change in controllability beliefs.
- Note that the degrees of freedom are only 19 here because this measure was added to the study half-way through data collection.
- All results in Studies 1 and 2 remain significant if liking of groups besides the poor is included as a predictor.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2016 Gina Roussos, John F. Dovidio


