Social networking’s peril: Cognitive absorption, social networking usage, and depression
Vol.9,No.4(2015)
Social networking has become commonplace in today’s always-connected world. Due to this ubiquity, researchers have sought to explore the positive and negative effects that can result from usage of social networking. This research has shown many effects on an individual's psychological well-being, with one of the most concerning being mixed results of how usage relates to depression. In this study, we further examine the relationship between usage and depression for social networking users. In addition, we posit that aspects of cognitive absorption, namely temporal dissonance, focused immersion, and heightened enjoyment, have a direct effect on the amount of usage. A survey of 251 social networking users reveals that temporal dissociation and heightened enjoyment are associated with increased usage, and usage was found to be associated with greater levels of depression. Further, prior research has shown a significant difference between genders in Internet usage and social networking. Therefore, we report our findings as an overall analysis and as a gender-based between- groups analysis. This analysis shows that more variance is explained for females than males in most relationships. Implications for research and society are discussed along with future research directions.
Social networking; depression; cognitive absorption; gender differences; PLS
Stoney Brooks
Middle Tennessee State University, Murfreesboro, Tennessee, United States
Stoney Brooks is an Assistant Professor in the Jones College of Business at Middle Tennessee State University. Stoney received his Ph.D. in Management Information Systems from Washington State University. Stoney’s research is published in Communications of the AIS, Computers in Human Behavior, at the prestigious Americas Conference on Information Systems, and in Green Business Process Management: Towards the Sustainable Enterprise from Springer. Stoney is actively researching negative effects of technology usage, social media, and green IS.
Phil Longstreet
University of Michigan-Flint, Flint, Michigan, United States
Phil Longstreet is an Assistant Professor at University of Michigan-Flint, School of Management. Phil received his Ph.D. in Management Information Systems from Washington State University. Phil’s notable industry experience includes working as a Director of Technology for Cagnor Homes Inc., and Manager of Quality Assurance at Workscape Inc. Phil’s research has been published in Technology and Society and at prestigious conferences including Americas Conference on Information Systems and the Hawaii International Conference for System Sciences. Phil is actively researching in e-commerce visual appeal, computer self-efficacy, social media and technostress.
Agarwal, R., & Karahanna, E. (2000). Time flies when you’re having fun: Cognitive absorption and beliefs about information technology usage. MIS Quarterly, 24, 665–694. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3250951
Andreassen, C. S. (2015). Online social network site addiction: A comprehensive review. Current Addiction Reports, 2, 175–184. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40429-015-0056-9
Baron, R. S. (1986). Distraction-conflict theory: Progress and problems. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 19, 1–40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60211-7
Bech, P., Rasmussen, N.-A., Olsen, L. R., Noerholm, V., & Abildgaard, W. (2001). The sensitivity and specificity of the Major Depression Inventory, using the Present State Examination as the index of diagnostic validity. Journal of Affective Disorders, 66, 159–164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0165- 0327(00)00309-8
Broderick, R. (2013, September 11). 9 teenage suicides in the last year were linked to cyber-bullying on social network ask.fm. BuzzFeedNews. Retrieved from http://www.buzzfeed.com/ryanhatesthis/a-ninth- teenager-since-last-september-has-committed-suicide
Brooks, S. (2015). Does personal social media usage affect efficiency and well-being? Computers in Human Behavior, 46, 26–37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.053
Ceyhan, A. A., & Ceyhan, E. (2008). Loneliness, depression, and computer self-efficacy as predictors of problematic internet use. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 11, 699–701. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2007.0255
Chou, H.-T. G., & Edge, N. (2012). “They are happier and having better lives than I am”: The impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15, 117–121. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2011.0324
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The psychology of optimal experience. New York: Harper & Row.
Davila, J., Hershenberg, R., Feinstein, B. A., Gorman, K., Bhatia, V., & Starr, L. R. (2012). Frequency and quality of social networking among young adults: Associations with depressive symptoms, rumination, and corumination. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 1, 72–86. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0027512
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35, 982–1003. http://dx.doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.35.8.982
Davis, R. A. (2001). A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internet use. Computers in Human Behavior, 17, 187–195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0747-5632(00)00041-8
Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., & Lampe, C. (2007). The benefits of Facebook “friends:” Social capital and college students’ use of online social network sites. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 12, 1143–1168. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2007.00367.x
Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., & Lampe, C. (2011). Connection strategies: Social capital implications of Facebook-enabled communication practices. New Media & Society, 13, 873–892. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1461444810385389
Facebook. (2015). Company Info. Facebook Newsroom. Retrieved from http://newsroom.fb.com/company-info/
Fee, R. L., & Tangney, J. P. (2000). Procrastination: A means of avoiding shame or guilt? Journal of Social Behavior & Personality, 15, 167–184.
Fiske, S. T. (1980). Attention and weight in person perception: The impact of negative and extreme behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 38, 889–906. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022- 3514.38.6.889
Fox, J., & Moreland, J. J. (2015). The dark side of social networking sites: An exploration of the relational and psychological stressors associated with Facebook use and affordances. Computers in Human Behavior, 45, 168–176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.083
Gefen, D., & Straub, D. W. (1997). Gender differences in the perception and use of e-mail: An extension to the Technology Acceptance Model. MIS Quarterly, 21, 389–400. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/249720
Gilroy, F. D., & Desai, H. B. (1986). Computer anxiety: Sex, race and age. International Journal of Man- Machine Studies, 25, 711 – 719. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7373(86)80084-0
Giota, K. G., & Kleftaras, G. (2013). The role of personality and depression in problematic use of social networking sites in Greece. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 7(3), article 6. http://dx.doi.org/10.5817/CP2013-3-6
Gore, P. A., Leuwerke, W. C., & Krumboltz, J. D. (2002). Technologically enriched and boundaryless lives: Time for a paradigm upgrade. Counseling Psychologist, 30, 847–857. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/001100002237758
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). SAGE Publications.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2011). PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. The Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 19, 139–152. http://dx.doi.org/10.2753/MTP1069-6679190202
Hargittai, E. (2007). Whose space? Differences among users and non-users of social network sites. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 13, 276–297. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1083- 6101.2007.00396.x
Hughes, D. J., Rowe, M., Batey, M., & Lee, A. (2012). A tale of two sites: Twitter vs. Facebook and the personality predictors of social media usage. Computers in Human Behavior, 28, 561–569. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2011.11.001
Jia, R., Hartke, H., & Pearson, J. (2007). Can computer playfulness and cognitive absorption lead to problematic technology usage? In ICIS 2007 Proceedings (paper 22).
Kahneman, D. (1973). Attention and effort. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of social media. Business Horizons, 53, 59–68. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2009.09.003
Kardes, F. R. (1996). In defense of experimental consumer psychology. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 5, 279–296. http://dx.doi.org/10.1207/s15327663jcp0503_04
Katz, E., Blumler, J. G., & Gurevitch, M. (1973). Uses and gratifications research. The Public Opinion Quarterly, 37, 509–523. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/268109
Keil, M., Tan, B. C., Wei, K.-K., Saarinen, T., Tuunainen, V., & Wassenaar, A. (2000). A cross-cultural study on escalation of commitment behavior in software projects. Management Information Systems Quarterly, 24, 299–326. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3250940
Kormas, G., Critselis, E., Janikian, M., Kafetzis, D., & Tsitsika, A. (2011). Risk factors and psychosocial characteristics of potential problematic and problematic internet use among adolescents: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health, 11, article 595. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-11-595
Kramer, A. D. I. (2012). The spread of emotion via Facebook. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 767–770). New York, NY, USA: ACM. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2207676.2207787
Kramer, A. D. I., Guillory, J. E., & Hancock, J. T. (2014). Experimental evidence of massive-scale emotional contagion through social networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111, 8788–8790. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1320040111
Kraut, R., Patterson, M., Lundmark, V., Kiesler, S., Mukophadhyay, T., & Scherlis, W. (1998). Internet paradox: A social technology that reduces social involvement and psychological well-being? American Psychologist, 53, 1017–1031. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.53.9.1017
Kross, E., Verduyn, P., Demiralp, E., Park, J., Lee, D. S., Lin, N., … Ybarra, O. (2013). Facebook use predicts declines in subjective well-being in young adults. PLoS ONE, 8(8), e69841. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069841
Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2011). Online social networking and addiction—A review of the psychological literature. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 8, 3528– 3552.
Laudon, K. C., & Traver, C. G. (2014). E-commerce 2015: Business, Technology, Society. Pearson Education.
Mahajan, P. (2009). Use of social networking in a linguistically and culturally rich India. International Information & Library Review, 41, 129–136. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10572317.2009.10762807
Marder, B. (2012). More Facebook friends means more stress, says Business School report. University of Edinburgh Business School . Retrieved from http://www.business-school.ed.ac.uk/about/news-and-press- office/?a=51582&heading_id=2&path=
McQuail, D. (2010). McQuail’s mass communication theory. Sage Publications.
Morrison, C. M., & Gore, H. (2010). The relationship between excessive internet use and depression: A questionnaire-based study of 1,319 young people and adults. Psychopathology, 43, 121–126. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000277001
Moss, G. A., & Gunn, R. W. (2009). Gender differences in website production and preference aesthetics: Preliminary implications for ICT in education and beyond. Behaviour & Information Technology, 28, 447–460 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01449290802332662
Müller, K. W., Dreier, M., Beutel, M. E., Duven, E., Giralt, S., & Wölfling, K. (2016). A hidden type of internet addiction? Intense and addictive use of social networking sites in adolescents. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, Part A, 172–177. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.09.007
Nie, N. H. (2001). Sociability, interpersonal relations, and the internet reconciling conflicting findings. American Behavioral Scientist, 45, 420–435. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/00027640121957277 Nunnally, J., & Bernstein, I. (1994). Psychometric theory. New York: McGraw-Hill.
O’Dell, J. (2011, April 27). For students, what is the “Facebook effect” on grades? Retrieved from http://mashable.com/2011/04/27/facebook-effect-students/
Palmgreen, P., Wenner, L. A., & Rosengren, K. E. (1985). Uses and gratifications research: The past ten years. In K. E. Rosengren, L. A. Wenner, & P. Palmgreen (Eds.), Media gratifications research (pp. 11– 37). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Pempek, T. A., Yermolayeva, Y. A., & Calvert, S. L. (2009). College students’ social networking experiences on Facebook. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 30, 227–238. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2008.12.010
Pollet, T. V., Roberts, S. G. B., & Dunbar, R. I. M. (2011). Use of social network sites and instant messaging does not lead to increased offline social network size, or to emotionally closer relationships with offline network members. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 14, 253–258. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2010.0161
Pratarelli, M. E., Browne, B. L., & Johnson, K. (1999). The bits and bytes of computer/internet addiction: A factor analytic approach. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 31, 305–314. http://dx.doi.org/10.3758/BF03207725
Qualman, E. (2012). 39 social media statistics to start 2012. Retrieved from < href="http://www.socialnomics.net/2012/01/04/39-social-media-statistics-to-start-2012/" target="_blank">http://www.socialnomics.net/2012/01/04/39-social-media-statistics-to-start-2012/
Quan-Haase, A., & Young, A. L. (2010). Uses and gratifications of social media: A comparison of Facebook and instant messaging. Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society, 30, 350–361. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0270467610380009
Raacke, J., & Bonds-Raacke, J. (2008). MySpace and Facebook: Applying the uses and gratifications theory to exploring friend-networking sites. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 11, 169–174. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2007.0056
Rauch, S. M., Strobel, C., Bella, M., Odachowski, Z., & Bloom, C. (2013). Face to face versus Facebook: Does exposure to social networking web sites augment or attenuate physiological arousal among the socially anxious? Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17, 187–190. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2012.0498
Ringle, C. M., Wende, S., & Will, A. (2005). SmartPLS (Version 2.0). Hamburg, Germany: SmartPLS.
Rosen, L. D., Whaling, K., Rab, S., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Is Facebook creating “iDisorders”? The link between clinical symptoms of psychiatric disorders and technology use, attitudes and anxiety. Computers in Human Behavior, 29, 1243–1254. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.11.012
Ruggiero, T. E. (2000). Uses and gratifications theory in the 21st century. Mass Communication and Society, 3, 3–37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1207/S15327825MCS0301_02
Saadé, R., & Bahli, B. (2005). The impact of cognitive absorption on perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use in on-line learning: An extension of the technology acceptance model. Information & Management, 42, 317–327. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2003.12.013
Sanders, G. S., Baron, R. S., & Moore, D. L. (1978). Distraction and social comparison as mediators of social facilitation effects. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 14, 291–303. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-1031(78)90017-3
Sears, D. O. (1986). College sophomores in the laboratory: Influences of a narrow data base on social psychology’s view of human nature. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 515–530. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.51.3.515
Severin, W. J., & Tankard, J. W. (2010). Communication theories: Origins, methods, and uses in the mass media. Longman.
Shaw, L. H., & Gant, L. M. (2002). In defense of the Internet: The relationship between internet communication and depression, loneliness, self-esteem, and perceived social support. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 5, 157–171. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/109493102753770552
Solomon, L. J., & Rothblum, E. D. (1984). Academic procrastination: Frequency and cognitive-behavioral correlates. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 31, 503–509. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022- 0167.31.4.503
Speier, C., Valacich, J. S., & Vessey, I. (1999). The influence of task interruption on individual decision making: An information overload perspective. Decision Sciences, 30, 337–360. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5915.1999.tb01613.x
Steers, M.-L. N., Wickham, R. E., & Acitelli, L. K. (2014). Seeing everyone else’s highlight reels: How Facebook usage is linked to depressive symptoms. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 33, 701–731. http://dx.doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2014.33.8.701
Tandoc E. C., Jr., Ferrucci, P., & Duffy, M. (2015). Facebook use, envy, and depression among college students: Is facebooking depressing? Computers in Human Behavior, 43, 139–146. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.10.053
Tellegen, A., & Atkinson, G. (1974). Openness to absorbing and self-altering experiences (“absorption”), a trait related to hypnotic susceptibility. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 83, 268–277. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/h0036681
Tsitsika, A., Janikian, M., Schoenmakers, T. M., Tzavela, E. C., Ólafsson, K., Wójcik, S., … Richardson, C. (2014). Internet addictive behavior in adolescence: A cross-sectional study in seven European countries. Cyberpsychology, Behavior & Social Networking, 17, 528–535. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2013.0382
van der Heijden, H. (2004). User acceptance of hedonic information systems. MIS Quarterly, 28, 695– 704.
van Rooij, A. J., Schoenmakers, T. M., van de Eijnden, R. J. J. M., & van de Mheen, D. (2010). Compulsive internet use: The role of online gaming and other internet applications. Journal of Adolescent Health, 47, 51–57. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.12.021
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., & Ackerman, P. L. (2000). A Longitudinal field investigation of gender differences in individual technology adoption decision-making processes. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 83, 33 – 60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/obhd.2000.2896
Wang, J.-L., Jackson, L. A., Gaskin, J., & Wang, H.-Z. (2014). The effects of social networking site (SNS) use on college students’ friendship and well-being. Computers in Human Behavior, 37, 229–236. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.04.051
Webster, J., & Ho, H. (1997). Audience engagement in multimedia presentations. SIGMIS Database, 28(2), 63–77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/264701.264706
Xu, C., Ryan, S., Prybutok, V., & Wen, C. (2012). It is not for fun: An examination of social network site usage. Information & Management, 49, 210–217. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2012.05.001
Young, K. S., & Rogers, R. C. (1998). The relationship between depression and internet addiction. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 1, 25–28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cpb.1998.1.25
Introduction
Social media has become a way of life for many individuals; in fact, over a billion people are active social media users (Laudon & Traver, 2014). The popularity of social media for social interaction has led many individuals to decrease other social activities such as talking on the phone, sending email, and face-to- face interaction (Nie, 2001; Pollet, Roberts, & Dunbar, 2011). This is not to say that people do not interact with one another, merely that the venue for this interaction has taken a dramatic shift in type and scope. Yet social media, though easy to participate in, may not be in an individual’s best interest when they are seeking to maintain their well-being. This may be partially attributed to the level of cognitive absorption that an individual feels when engaging in social networking sites (SNS). As they feel more cognitively absorbed in the medium, they tend to forgo other activities and instead continue to engage in the medium (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000; Saadé & Bahli, 2005). Further, prior research has shown that hedonic technologies like social networking tend to promote prolonged engagement due to the pleasure that one receives through participation (van der Heijden, 2004). This increased engagement may coincide with a decrease in an individual’s overall well-being by increasing negative life outcomes such as depression (Chou & Edge, 2012; Davila et al., 2012).
Social networking, as the most commonly used social media technology, is at the forefront of the social media research on users. This research first started as an examination of the influences of internet usage on well-being (Morrison & Gore, 2010). This research subsequently branched out to include SNS by seeking to explore the linkages between negative outcomes and SNS usage, sometimes referred to as the dark side of social networking (Fox & Moreland, 2015). The dark side of social networking is associated with numerous negative outcomes, including addiction. Though not a specific focus of this study, recognizing the potential negative effects that can result from excessive SNS usage (i.e. addiction), such as emotional, relational, health-related, and performance problems (Andreassen, 2015), can be an important step in prevention.
In addition to academic research, many practitioner articles and popular news stories focus on the link between SNS usage and depression. For example, in an article posted on BuzzFeed.com in 2013, nine teenagers were identified to have committed suicide in response to cyberbullying on a social media site, Ask.fm (Broderick, 2013). Other reports have indicated that social networking may lead to elevated levels of depression, anxiety, and addiction (Kross et al., 2013). This increasing level of public awareness of the potential negative effects of SNS usage has provided the additional impetus for recent research into harmful outcomes of SNS usage, including how it relates to an individual’s personal well-being (e.g. Kormas, Critselis, Janikian, Kafetzis, & Tsitsika, 2011). This study is a continuation of this research stream.
In this research study, we provide findings concerning the possible negative influences of social networking that support and extend prior research. First, we posit that cognitive absorption leads to higher SNS usage. This is based around the three indicators of focused immersion, heightened enjoyment and temporal dissociation. Next, based on previous research, we posit that this increase in SNS usage will be associated with significant elevated levels of depression. Finally, based on prior literature results showing differences in how the genders interact with technology, we posit that significant differences between the genders will be shown. To test these hypotheses, we conducted a survey where we gathered self-reported measures of cognitive absorption, depression, and SNS usage from participants. This data was then examined for both the full population and partial population subsets divided into gender-defined groups, in relation to our research agenda. Finally, we conclude this article with a discussion of the findings and limitations of this research.
Background
Research conducted before the recent popularity of social media found mixed results for the relationship between Internet use and depression (Kraut et al., 1998; Shaw & Gant, 2002). In the years since this research, SNS usage has become the most popular activity on the Web (Qualman, 2012); this change in usage prompts taking another look at this relationship. Research into this relationship between social networking usage, a subset of Internet usage, and depression, has shown researchers that they share a significant relationship: increased usage is related to increases in depression (Chou & Edge, 2012; Davila et al., 2012). As stated previously, SNS has become a ubiquitous technology with a massive number of people involved on a daily basis. To explain this level of usage, we employ cognitive absorption, as introduced into the Information Systems literature by Agarwal and Karahanna (2000).
Cognitive Absorption
The theoretical basis for Cognitive Absorption is derived from past literature on flow (Csikszentmihalyi, 1990), cognitive engagement (Webster & Ho, 1997), and the personality trait dimension of absorption (Tellegen & Atkinson, 1974). As introduced, cognitive absorption serves as an antecedent to behaviors such as an individual’s perception of the usefulness or ease-of-use of a technology. This in turn influences the individual’s intention to use a given technology (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000). As part of understanding individuals’ intention to use technology, cognitive absorption shows how technological interaction can become more engaging and riveting for an individual. The first aspect of this construct shows that at the extreme, this engagement may lead to a state where the individual may lose awareness of outside events because they are so deeply engrossed with the software; this is known as temporal dissociation. Temporal dissociation is defined as “…the inability to register the passage of time while engaged in interaction” (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000, p. 673). The next aspect shows that when the individual is engaged in the activity, they may have a tendency to ignore other concerns, and instead focus solely on the technological interaction. This is known as focused immersion, which is defined as “… the experience of total engagement where other attentional demands are, in essence, ignored” (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000, p. 673). The third aspect explains that when an individual is engaged in a technological activity, there is a level of pleasure involved that can be measured; this is heightened enjoyment. Heightened enjoyment is defined as “… capturing the pleasurable aspects of the interaction” (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000, p. 673). The fourth aspect seeks to understand the individual’s feeling of control of their use of the technology , and is formally defined as “… representing the user’s perception of being in charge of the interaction” (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000, p. 673). The fifth and final aspect represents the individuals curiosity and is defined as “… tapping into the extent the experience arouses an individual’s sensory and cognitive curiosity.” (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000, p. 673).
Social Networking
Social networking is arguably the most popular of the six classifications of social media (Kaplan & Haenlein, 2010; Wang, Jackson, Gaskin, & Wang, 2014). A SNS is a member-based online community where users often begin by posting basic information about themselves and then communicate with other members in a variety of ways and on a variety of topics (Mahajan, 2009; Pempek, Yermolayeva, & Calvert, 2009). The social networking site Facebook, the largest social medium, has over 1.35 billion users as of September, 2014 (Facebook, 2015).
Uses and Gratifications Theory (UGT) is useful in examining the reasons why a user chooses a technology, such as SNS. UGT assumes that people are active (rather than passive) users and select media based on the gratifications that they seek (Katz, Blumler, & Gurevitch, 1973; Palmgreen, Wenner, & Rosengren, 1985; Ruggiero, 2000). As usage of SNS is primarily for voluntary amusement, users seek to satisfy a variety of needs, including knowledge, relaxation, social interactions, companionship, diversion, and/or escape (McQuail, 2010; Severin & Tankard, 2010). When using SNS, users often feel the need to stay connected with their friends and/or keep up with the news about topics of interest (Quan-Haase & Young, 2010). This usage can be to seek the gratification of relationship maintenance, which can lead to increased social capital (Ellison, Steinfield, & Lampe, 2007, 2011). However, seeking relationship maintenance can have significant negative outcomes as well. For example, the more friends a person has on Facebook, the greater stress they will feel (Marder, 2012). This stress arises in part when people present a version of themselves on Facebook that is unacceptable to some of their online friends; for example, posts displaying swearing, recklessness, drinking, and/or smoking.
Additionally, as the amount of time users spend with social networking increases, they have less time for other endeavors, which can result in negative life outcomes. Distraction-Conflict Theory provides one possible explanation for why time may cause negative outcomes to occur. It postulates that the presence of others distracts an individual, causing an attentional conflict (Sanders, Baron, & Moore, 1978). Attentional conflict refers to the situation where the individual feels the tendency, desire or obligation to allocate attention to these two (or more) exclusive inputs (Baron, 1986; Sanders et al., 1978). This type of conflict leads to a cognitive overload, which in turn can elevate stress, arousal and drive in the individual (Baron, 1986). When someone is exposed to an interruption or distraction, they may forget some of the information needed for processing their primary task and, therefore, some cues are lost or never enter working memory (Speier, Valacich, & Vessey, 1999). As they complete the interruption task and return to the primary task, a recovery period is needed to reprocess information that was forgotten while attending to the interruption or lost from working memory due to capacity (incoming cues being greater than a decision maker can process) and structural interferences (decision maker has to attend to two inputs with the same physiological mechanisms) (Kahneman, 1973). Concerning Facebook, distractions can be initialized by sound (when a user receives a chat message) and by sight (when the web browser blinks colors or changes page titles for receiving a new chat message or relevant posting). Even simply knowing that one’s friends and family may be available through the site at any given moment can be a distractor (Brooks, 2015), and thus lead towards negative outcomes.
As another potential avenue towards these negative life outcomes, R.A. Davis (2001) proposed the theory of the cognitive-behavioral model of pathological internet use (CBM-PIU). As Davis (2001) notes, this theory is different from other PIU models and theories (Pratarelli, Browne, & Johnson, 1999) in that it emphasizes the person’s cognitions or thoughts as the reason for the problematic behavior rather than other sources. This theory shows that though usage may not be pathological in the traditional definition, the compulsive thoughts and action surrounding the activity may nonetheless become problematic for the individual. Further, this theory proposes that there exist two types of problematic behaviors for internet use: specific and generalized. “Specific pathological Internet use includes those people that are dependent on a specific function of the Internet. Clinical and media accounts of this include overuse (abuse) of online sexual material/services, online auction services, online stock trading, and online gambling. Specific PIU is related to only one aspect of the Internet, and exists entirely independent of multiple Internet functions.”
(R. A. Davis, 2001). On the other end of the spectrum, there is generalized: “Generalized pathological Internet use involves a general, multidimensional overuse of the Internet. It might also include wasting time online without a clear objective. Often, generalized PIU can be associated with the ‘chat’ found online and dependence on e-mail” (R. A. Davis, 2001). Both of these use situations may exist for an individual that uses SNS on an ongoing or pathological basis. For example, to avoid withdrawal symptoms, pathological users feel a need to frequently check their social networks (Kuss & Griffiths, 2011). For the more casual user, SNS can be a distraction from their daily activities or something to do while procrastinating.
It should be noted that not all problematic usage need be labeled as pathological. Several studies have addressed motives and health-related correlations of nonpathological use of SNS (Müller et al., 2016). A recent survey of European adolescents found that 70% of the participants were using SNS on a regular basis with 40% using it on average at least 2 hours a day (Tsitsika et al., 2014). Heavier SNS usage was predictive for heightened internalized problems, lower academic achievement, and retreating from alternative activities. In one online survey, the number of Facebook friends a user has was associated with symptoms related to narcissism and histrionic personality disorders (Rosen, Whaling, Rab, Carrier, & Cheever, 2013). Additionally, using social media in a classroom setting may be associated with lower happiness and decreased task performance (Brooks, 2015).
Gender Differences in SNS Usage
The genders experience differences in how they relate to technology and their motivations for using technology. For example, a key differentiation factor in the perception of websites is gender. Members of each gender have been found to prefer websites designed by the same gender (Moss & Gunn, 2009). This difference may affect the use of social networking sites as well. Other technology-related differences have been found as well. Decisions made by males are more strongly influenced by their attitude toward using a new technology, whereas women are more strongly influenced by the subjective norm and perceived behavioral control (Venkatesh, Morris, & Ackerman, 2000). These findings are robust across income, organization position, education, and computer self-efficacy levels. In a study of over 300 students, approximately half women and half men, it was found that females had significantly higher computer anxiety than males (Gilroy & Desai, 1986). Women and men also differ in their perceptions of e-mail (Gefen & Straub, 1997). Concerning SNS specifically, the genders can differ on the percentage of users of a SNS (Hargittai, 2007), women are more likely to use SNS in general (Hargittai, 2007), and it has been suggested that women are at greater risk than men for developing addiction (Kuss & Griffiths, 2011).
Hypotheses Development
As noted in the background section, previous research has been able to establish a link between excessive usage and negative life outcomes such as depression. As with Internet usage, it is important to understand this link. Additionally, determining some of the multitude of potential factors that can influence the usage of the world’s most popular websites will aid in shaping our understanding of the phenomenon.
When the Internet was introduced, many people were enthusiastic about the technology and quickly immersed themselves in the medium. Scholars have proposed cognitive absorption as one way to explain the immersion experienced by many technology users. Cognitive absorption has been shown to have a significant positive relationship with the behavioral intention to use a technology (i.e. World Wide Web) (Agarwal & Karahanna, 2000). This intention to use a technology has been widely accepted as a key determinant of actual usage of a technology (F. D. Davis, Bagozzi, & Warshaw, 1989). As a subset of the Internet and World Wide Web, SNS produced a similar immersive response, shown by the rise of MySpace, Facebook, Orkut, Pinterest, and other SNS platforms. These similarities in an individual’s response to the different technologies shows that though cognitive absorption was originally intended to demonstrate a relationship with technology usage in general, it is likely that the construct is robust enough to also demonstrate a relationship with a specific technology, such as SNS.
In particular, three of the aspects of cognitive absorption, namely focused immersion, heightened enjoyment, and temporal dissociation, are the most likely to demonstrate this relationship as they are the most closely tied to SNS usage. Focused immersion is a goal of SNS platform owners since they seek to capture the attention of the users for as long as possible. To achieve this level of immersion, they seek to provide the user fun and entertainment to influence a state of heightened enjoyment and keep them engaged and using the site. Additionally, when a user is concentrating on a specific task, especially if the task is enjoyable, time can seem to fly by. This temporal dissociation can influence the overall amount of time spent with a technology since the user is not conscientious of the actual amount of time invested. Believing that a shorted amount of time spent then actually has passed should directly correlate with this greater amount of time spent.
Given the nature of these three aspects of cognitive absorption, it is likely that as these aspects increase, there will be an associated increase in SNS usage. Therefore, we hypothesize that:
H1: Focused immersion will have a positive relationship1 with SNS usage
H2: Heightened enjoyment will have a positive relationship with SNS usage
H3: Temporal dissociation will have a positive relationship with SNS usage
There is a growing body of work suggesting that SNS usage is associated with a multitude of negative outcomes. Given that 96% of college students use Facebook (O’Dell, 2011), SNS usage’s association with decreased happiness in college students is a sign of the potential negative impacts of use (Brooks, 2015). Consistent with the associated decrease in happiness, increases in depression associated with SNS usage have been found for both compulsive/dysfunctional users (Tsitsika et al., 2014; Young & Rogers, 1998) and general users (e.g. Ceyhan & Ceyhan, 2008; Davila et al., 2012). Even the amount of time spent with these technologies is associated with increased depression (Rosen et al., 2013).
There are many potential factors that can help explain why SNS use and depression are associated. Earlier studies have shown that SNS is a strong predictor of Internet addiction behavior (Kormas et al., 2011; van Rooij, Schoenmakers, van de Eijnden, & van de Mheen, 2010), and this addictive or pathological usage is associated with depression (Tsitsika et al., 2014). Often, SNS users are accessing the medium while realizing that they are wasting time or procrastinating a task that they should be engaged in (Hughes, Rowe, Batey, & Lee, 2012). As the user continues this engagement with SNS, they may experience feelings of shame about procrastinating, a sense of hopelessness towards being able to get tasks accomplished, and other negative life outcomes such as depression (Fee & Tangney, 2000; Solomon & Rothblum, 1984). Envy stemming from SNS usage can lead to depression, especially for heavier users (Tandoc, Ferrucci, & Duffy, 2015). The more an individual uses SNS, the more likely they are to engage in certain behaviors that lead them to consume others’ personal information. In doing so, they are confronted with more instances when they are prone to comparing themselves with others (Chou & Edge, 2012; Tandoc et al., 2015). These social comparisons have a significant associated with Facebook-related depression (Steers, Wickham, & Acitelli, 2014). Also, the degree of social anxiety has been discussed as a mediator of the effects of SNS use (Rauch, Strobel, Bella, Odachowski, & Bloom, 2013).
Based on this foundation set forth by previous research, we hypothesize that:
H4: Greater SNS usage will be associated with an elevated level of depression The research model is shown in Figure 1.
Additionally, the plethora of research on gender differences in the technology realm suggests that there are differences in how the genders use social networking. Research has found differences between the genders on factors that influence SNS usage (Hargittai, 2007), and the effects of this usage (e.g. Tsitsika et al., 2014). For example, social comparisons have been found to mediate a relationship between Facebook usage and depression for men only (Steers et al., 2014). Additionally, one study found that females experience higher levels of psychosocial symptoms then males across all levels of SNS usage (Müller et al., 2016). Based on these previous findings, and since technology adoption and usage can differ between genders, it is likely that the relationship between SNS usage and depression will be different between the genders as well. As such, we propose that these differences will be found here as well.
H5: There will be significant differences in the hypothesized relationships between men and women.
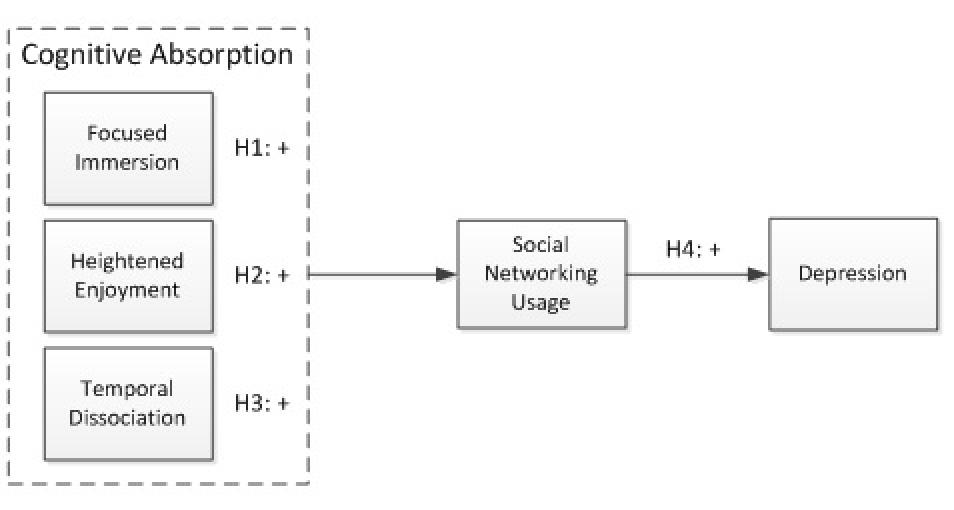
Figure 1. Research model.
Methods
Subjects and Procedure
This research was conducted at a large university in the northwestern United States. Participants were recruited through undergraduate business college courses, both face-to-face and online sections, and were given course credit for their participation. Student participants were deemed applicable for this study as research has shown that young adults are very accustomed to using new technologies (Gore, Leuwerke, & Krumboltz, 2002) and students in particular (Kuss & Griffiths, 2011) use SNS because of the inbuilt features of Web 2.0 (applications that facilitate the creation of user-generated content in a virtual community) (Giota & Kleftaras, 2013). Young adults and students of any age group are more likely than any other groups to have a profile in a SNS (Raacke & Bonds-Raacke, 2008). To be applicable for the study, subjects were required to be SNS users. After removing responses from non-users and those with incomplete data from the full data set (N = 268), the final data set consisted of 251 participants (146 males), 95% of whom were aged between 18 to 24 (M = 20.72, SD = 3.71). Participants ranged between two months and ten years of experience with social networking (M = 74.6 months, SD = 30.02) and used social media platforms between 5 and 84 hours per week (M = 19.8, SD = 18) 85% of which was SNS.
The data collected for these hypotheses is a part of a larger data collection gathered through three online surveys. Participants were asked to complete all three surveys in order to receive course credit. With the exception of SNS usage and a personally identifying measure used to assign course credit, each survey contained different constructs and items of measure. The surveys were offered to the participants in a staggered timeline. Only one survey was available for participation at a given time, and this availability lasted one week. After closing the survey, one week lapsed before the next survey was available for a one-week timespan. Multiple surveys were used due to the large number of constructs gathered in the complete data collection, the subjective nature of cognitive, behavioral, and perceived measures, to prevent response biases (for example, cognitive absorption and depression were measured on different surveys), and to collect multiple SNS usage measures. The collection of multiple usage measures allow for a more accurate picture of actual time spent longitudinally rather than using a single snapshot-in-time measure.
Measures
Cognitive absorption. The scales for focused immersion, heightened enjoyment, and temporal dissonance were adapted from Agarwal and Karahanna (2000). These scales have been previously found to impact Perceived Usefulness and Perceived Ease of Use of a technology (Saadé & Bahli, 2005), and can lead to problematic usage of hedonic technologies (Jia, Hartke, & Pearson, 2007). Items were reworded to fit the SNS nature of this study.
Focused immersion. To assess the level of focused immersion, five Likert-type questions on a 7-point scale ranging from ‘strongly disagree’ to ‘strongly agree’ were used. Sample items include “While using social networking I am able to block out most other distractions” or “While on social networking, I am immersed in the task I am performing.” After testing for internal validity, two items were omitted due to weak indicator loading (β < .5) and a lack of negatively affecting content validity (Hair, Hult, Ringle, & Sarstedt, 2013). After exclusion, the summed scores for the scale could range from 3 to 21, and this sample has M = 10.9 and SD = 2.65. Composite reliability of the scale was .90. Composite reliability is reported instead of Cronbach’s alpha due to alpha’s limitations in the population and since the analysis method of choice, PLS, prioritizes the indicators according to their individual reliability instead of assuming that all indicators are equally reliable (Hair et al., 2013, p. 101). Composite reliability varies between 0 and 1, with values between 0.7 and 0.95 being acceptable (Nunnally & Bernstein, 1994).
Heightened enjoyment. To assess the level of heightened enjoyment, four Likert-type questions on a 7- point scale ranging from ‘strongly disagree’ to ‘strongly agree’ were used. Sample items include “I have fun interacting with social networking” or “Using social networking provides me with a lot of enjoyment.” After testing for internal validity, one item was omitted due to weak indicator loading (β < .5) and a lack of negatively affecting content validity (Hair et al., 2013). After exclusion, the summed scores for the scale could range from 4 to 28, and this sample has M = 19.2 and SD = 3.60. Composite reliability of the scale was .90.
Temporal dissonance. To assess the level of temporal dissonance, five Likert-type questions on a 7- point scale ranging from ‘strongly disagree’ to ‘strongly agree’ were used. Sample items include “Sometimes I lose track of time when I am using social networking” or “I often spend more time on social networking than I had intended.” The summed scores for the scale could range from 5 to 35, and this sample has M = 24.6 and SD = 6.65. Composite reliability for the scale was .94.
Depression. To measure the participants’ levels of depression, the Major Depression Inventory (MDI) was used (Bech, Rasmussen, Olsen, Noerholm, & Abildgaard, 2001). This measure has been referenced in hundreds of studies and has been rigorously validated and tested. Twelve Likert-type items, prefaced with “How much of the time in the last 2 weeks…”, were asked on a six-point scale ranging from ‘all of the time’ to ‘at no time’. Sample items include “Have you felt lacking in energy and strength?” or “Have you felt less self-confident?”. The MDI includes two pairs of questions that are inverses of each other; the item with the greater value (higher depression) for each individual is used and the other item is dropped from the scale. Some examples of this are the items “Have you felt very restless?” and “Have you felt subdued?”. This process reduces the number of items in the scale from twelve to ten. The scale is formatted such that higher values show a greater level of depression. An EFA conducted on the items using SPSS v20 showed that all items loaded onto a single factor. The sample ranges from 10 to 49, and has M = 22.38, SD = 8.07. Composite reliability for the items was .88.
Social networking usage. Participants were asked to indicate how many hours per day and how many days per week they use social networking on average. These questions were asked on all three surveys. The hours per day were multiplied by the days per week to create an hours per week measure for each survey. This measure was then averaged across the three surveys to create a single, more accurate measure of usage. The data was examined for extreme outliers before averaging (i.e. 15 hours on surveys 1 and 2, then 90 hours on survey 3); none of the responses were removed for this issue. Small average standard deviation per respondent (SD = 3.51) was observed across the three individual surveys. After aggregating the data, the combined sample had a range of 1 to 140 hours per week, with M = 19.8 hours and SD = 18.06.
Analysis and Results
The structural model was assessed using SmartPLS 2.0 (Ringle, Wende, & Will, 2005). PLS was selected for analysis given its applicability for predicting key constructs and key “driver” constructs, rather than OLS, which is ideal for theory testing, theory confirmation, or comparison of alternative theories (Hair, Ringle, & Sarstedt, 2011). Additionally, PLS does not make assumptions about the normality of data, allowing for non-normal data to be analyzed. PLS is appropriate when the research is interested in determining the existence and strength of relationships, rather than examining alternative models to determine the best fit. As such, PLS does not provide fit indices for the model. Additionally, unlike the cognitive absorption scales, which used the individual items, depression was analyzed as a single summed composite value, following the method used by Bech et al. (2001).
Table 1 provides correlations and reliability statistics on the sample. Composite reliability for each construct is showing appropriate internal validity and the Fornell-Larcker criterion, where the square root of AVE of each construct is larger than the correlation with any other construct, is found, supporting discriminant validity (Hair et al., 2013). The statistical model for our hypotheses is shown in Figure 2.
Table 1. Reliability and Correlation Matrix.
|
|
CR |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1. Depression |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
2. Focused Immersion |
.902 |
.113* |
.869 |
|
|
|
|
3. Heightened Enjoyment |
.902 |
.001 |
.237** |
.835 |
|
|
|
4. Social Networking Usage |
N/A |
.173* |
.047* |
.208** |
N/A |
|
|
5. Temporal Dissociation |
.941 |
.163* |
.513** |
.322** |
.306** |
.873 |
| Note: Square Root of AVE bold in diagonal; CR – Composite Reliability. * p < .05; ** p < .01. N/A: These values are not applicable to single-item constructs (Hair et al., 2013, p. 99). | ||||||
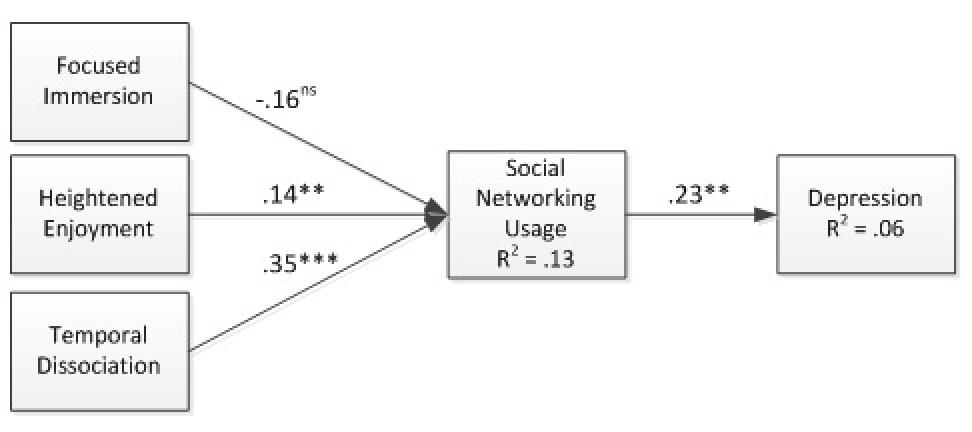
Figure 2. Structural Model (** p < .01; *** p < .001).
Both heightened enjoyment and temporal dissociation show significant positive relationships with SNS usage, supporting H2 and H3. This means that in our sample, those users that enjoy their SNS usage and lose track of time when using it have greater amounts of overall SNS usage. Focused immersion was found to have a negative, non-significant relationship with usage, lending no support for H1.
Finally, usage has a significant positive relationship with depression. In line with a number of practitioner outlets and academic research (e.g. Ceyhan & Ceyhan, 2008; Davila et al., 2012; Young & Rogers, 1998), greater SNS usage is associated with higher levels of depression.
Gender Analysis
After analyzing the structural model for the full dataset, ANOVAs were used to determine if differences in SNS usage exist between the genders. The ANOVA shows that there are significant differences in SNS usage between men and women (p < .001). Based on this significant difference, our structural model was analyzed separately for the two genders. Table 2 shows the reliability and discriminant validity of the two separate models. Like the analysis of the full dataset, composite reliability values are above accepted thresholds and discriminant validity is supported. As with Table 1, the composite reliability and square- root of AVE for depression and SNS usage are 1 since the constructs are represented with a single item each. All correlations are significant at p < .05.
Table 2. Reliability and Correlation Matrix.
|
Males (Females) |
CR |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1. Depression |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
2. Focused Immersion |
.89 (.85) |
.015 (.183) |
.850 (.950) |
|
|
|
|
3. Heightened Enjoyment |
.91 (.87) |
-.088 (.063) |
.240 (.232) |
.841 (.797) |
|
|
|
4. Social Networking Usage |
N/A |
.151 (.245) |
.120 (-.048) |
.269 (.188) |
N/A |
|
|
5. Temporal Dissociation |
.95 (.92) |
.080 .(266) |
.542 (.428) |
.329 (.341) |
.316 (.279) |
.887 (.832) |
| Note: Square Root of AVE bold in diagonal CR – Composite Reliability. N/A: These values are not applicable to single-item constructs (Hair et al., 2013, p. 99). | ||||||
Statistical Model
The results of analyzing the model for the two genders separately show interesting findings (see Figure 3). Focused immersion has a significant negative relationship with SNS usage for women, but not for men. Greater levels of focus for women into their SNS tasks results in a lesser amount of time spent on those tasks. This is contrary to H1 that posits a positive relationship. Both heightened enjoyment and temporal dissociation significantly influence usage for both men and women, continuing to support H2 and H3. Perhaps most interesting, though the relationship between SNS Usage and Depression is significant for both genders, it is stronger for women than men, and usage explains more than double the amount of depression for women than men (R2 = .07 for females, .03 for males).
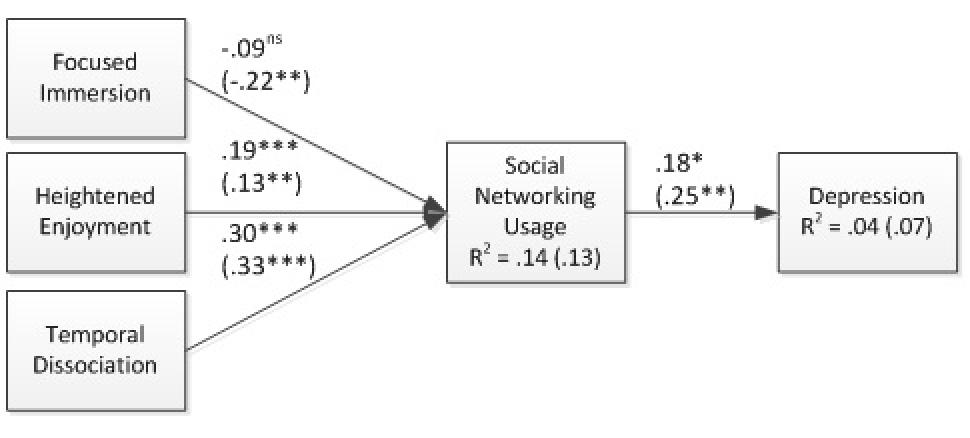
Figure 3. Structural Model – Females in Parentheses (p < .05; ** p < .01; *** p < .001).
Multigroup Analysis
To gain additional insight into the differences between the two genders in our model, multigroup analysis was performed. Using the formula in Keil et al. (2000), we can determine if the differences in the relationships are statistically significant. Table 3 shows the results.
For all four relationships analyzed in this model, the differences between the two genders are significant at the p < .001 level. When computing the multigroup analysis formula, males were considered group 1, and females were considered group 2. This is why the significant negative-values mean that the relationship is stronger for females (group 2). With the exception of the relationship between heightened enjoyment and SNS usage, the relationships are significantly stronger for females.
Table 3. Results of the Multigroup Analysis.
| Path | T-Value | P-Value | Stronger For? |
|
FI --> USAGE |
-133.827 |
< .001 |
Females |
|
HE --> USAGE |
246.515 |
< .001 |
Males |
|
TD --> USAGE |
-150.266 |
< .001 |
Females |
|
USAGE --> DEP |
-112.427 |
< .001 |
Females |
Discussion
Results from this study suggest a statistically significant relationship between the amount of time a person spends using SNS and their associated depression level. From the results, we see that an increased level of SNS usage corresponds with an elevated level of depression, thus providing support for H4. These results support previous research that found a link between SNS addiction and emotional problems (Andreassen, 2015). Though addiction was not addressed here, the relationship with depression was found across all amounts of SNS usage time in our sample. One large-scale survey of European adolescents found the prevalence of dysfunction Internet behavior, which can include SNS addiction, at 13.9% (Tsitsika et al., 2014). The significant relationship between SNS usage and depression found here lends support for the effect occurring in a more generalized population subset than just individuals exhibiting addiction symptoms.
Further, this relationship may explain up to 6% of an individual’s depression level, which, when considering the multitude of factors that affect depression and the limitations inherent in survey-based research, is important to note. Moreover, this minimal degree of variance explained is an interesting result because of the implied implications. On one hand, if the degree of variance explained is truly only 6%, then it may be fairly safe to disregard SNS usage as a specific factor affecting depression, and instead only account for it when looking at a more holistic view of problematic usage of technology. On the other hand, it is also possible that that the low degree of variance explained was an artifact of the nature of the study, and as such, the variance explained was greatly reduced because of the self-reported nature of the data.
Interestingly, this result is in contrast with Wang et al.’s (2014) finding that SNS usage can be positively associated with users’ well-being. The positive association was found concerning “social” SNS usage, not general usage as was examined here. Since our sample was comprised of college students, who have been found to use Facebook most often for social interaction (Pempek et al., 2009), a positive association with depression could have occurred. Given our contrasting findings, it is possible that the subjects were primarily using SNS for non-social purposes, such as entertainment, which may not have a significant relationship with well-being (Wang et al., 2014), or for utilitarian gratifications, such as coordination (Xu, Ryan, Prybutok, & Wen, 2012).
Another possible explanation for the contrasting result is emotional contagion. On Facebook, people frequently express emotions, which are later seen by their friends (Kramer, 2012). These emotions can run the gamut of human experiences, from positive to negative. Adults spend more time looking at negative than positive stimuli (Fiske, 1980). This majority of time spent looking at negative expression can lead Facebook users to feel similar negative emotions (Kramer, Guillory, & Hancock, 2014). If the majority of the expressions the subjects encountered were negative, the emotional contagion could have influenced their depression.
Further, support was shown for using at least two of the aspects of cognitive absorption for explaining variance in SNS usage. The results show increasing levels of heightened enjoyment and temporal dissociation correspond with increasing levels of SNS usage, thus providing support for H2 & H3. Focused immersion was presented with a non-significant path, so H1 was not supported from these results. This provides an addition to the cognitive absorption literature as it supports expanding the reach of the construct beyond the traditional boundaries of technology usage and into the SNS usage literature. Moreover, these findings provide interesting avenues of future research using cognitive absorption to provide further insight into individuals’ usage of SNS platforms. Additionally, cognitive absorption’s increased ability to understand variance in SNS usage could lead to a greater ability to understand increased levels of depression that have been associated with internet and SNS usage in theories such as the CBM-PIU.
As suggested by the theory of CBM-PIU, the increase in depression could be related to dependence on the medium, which would then correspond to overuse of the technology. It may also stem from a more generalized over use of the SNS technology, which may be rooted in wasting time using SNS technologies without a clear objective. This dependence on the technology could cause the corresponding increase in depression as the individual realizes how much time they are wasting on the SNS technology, and their powerlessness to unplug themselves from it. Examining these findings at a more granular level, it also becomes apparent that there are significant differences between the genders in relation to SNS usage and depression.
Looking at the differences between the genders, we see a marked differences in the variance explained: males change to 4% while females change to 7%, thus providing support for H5. Further, we see that focused immersion was non-significant for males and had a significant negative relationship for females. Speculatively, this could indicate a number of different things, such as that women tend towards more superficial SNS usage, that women multi-task more while using SNS therefore limiting immersion, or a currently unknown reason. This finding is of interest as it shows that the different genders react differently to SNS and as such, efforts to alleviate negative effect may have to independently target each gender. For both males and females, heightened enjoyment corresponds with an increased level of SNS usage, with males showing a slightly higher level of usage than females. This may indicate that for males, as their enjoyment level increases, they are more willing to increase their SNS usage than females, this is again showing a marked difference in how the genders are influenced by SNS usage. For temporal dissociation, this relationship is reversed: females increase their SNS usage more than males with heightened temporal dissociation. It is possible that males have a greater awareness of their “inner clock” when using SNS than females do; this would allow females to lose track of time during SNS activities more easily than males. Finally, the link between SNS usage and depression shows a noticeable, significant gap between the genders, with females corresponding to greater levels of depression with increased SNS usage than their male counterparts do. These findings were of particular interest to us, as they showed that future research would benefit from between-groups research focusing specifically on the gender differences. This research could be especially useful when examined from an experimental viewpoint in a controlled environment, as this would allow for minimization of extraneous outcomes exhibited in some survey-based research.
Research Contribution
This research contributes to the body of knowledge on the negative effects of technology usage because it shows that something as basic as the amount of time an individual spends using SNS services is associated with differing degrees of depression. With regards to the conflicting findings in previous studies, our results lend support for the existence of the relationship between SNS usage and depression. This is not to say that the relationship exists for the entire population, as is shown by the number of studies without significant results. Rather, for our sample of college students, both males and females, the relationship exists; future research is needed to determine the existence and potential effect of this relationship on other population subsets to establish generalizability. As each member of the sample had prior experience with SNS, this relationship may have manifested over time. When considering the nature of depression and the amount of time it can take to manifest, our results support that usage of SNS technologies might be a contributing factor to any increased levels of depression experienced by the user.
However, the results from this study only explain a small amount of the variance in an individual’s depression level. This may be due to the nature of the subjects and that we were using self-reported data in the survey instrument. Still, being able to shown a significant association with depression under these circumstance, and with this population subset, provides evidence that the association does indeed exist, and that in more ideal circumstances, a more robust association could emerge.
Overall, this research has tied in well with existing literature by showing that in general, SNS usage corresponds with heightened depression levels. This research provides a contribution to the research arena through strengthening prior research findings and through providing additional support for some of the negative outcomes of SNS. Further, we show that differences also exist in relation to the negative outcomes for males and females. At the societal level, the results from this study provide support that the use of SNS should be approached with caution and with the awareness that greater use of SNS may lead to negative outcomes in regards to one’s overall well-being, with the female demographic being at a slightly elevated risk of negative outcomes.
Limitations and Future Directions
A limitation of this research is that it examined three specific periods of system usage. This cross- sectional data does not allow for causal links concerning prolonged SNS usage and well-being. Additionally, this research is limited in that we employed student subjects for the study. This subset of the population has been known to show ambiguous results in the past (Kardes, 1996; Sears, 1986), but for this study, they were deemed appropriate as they represent a substantial portion of SNS users, they are known as frequent users of the technology, and they show high levels of familiarity with SNS platforms. This research is further limited in that it is exploratory by nature, as this type of investigation has not been performed in the past. As such, no broad implication can be formed to explain the phenomenon until further research is conducted, and a theoretical model emerges to explain the results and causalities.
Future research following this study could investigate specific aspects of SNS that influence depression. For example, viewing humorous posts on Facebook could decrease depression, while perhaps reading a post about how an ex-spouse has recently found someone new could increase depression. In line with this reasoning, an examination of usage by SNS type, function, and purpose of use could provide a deeper insight into specifics of SNS that relate to elevated levels of depression. From observation of users, it could be postulated that more public, personal SNS (i.e. Facebook) have the potential to cause greater harm than professional SNS (i.e. LinkedIn). Expanding this stream further, examining effects of usage of the different social media types beyond social networking can provide a larger view of the phenomenon.
Additionally, based on the gender differences found in this study, continued research using between groups analysis for males and females could be beneficial for each of the above noted future directions. Specifically, the unexpected negative relationship between focused immersion and SNS usage for females is worthy of deeper investigation. Finally, once more is known about the cause of the relationship between SNS usage and depression this research stream could be expanded to include other negative outcomes such as loneliness, fear, suicidal thoughts, and cyberbullying.
Conclusion
The results from this research study have shown that increased levels of heightened enjoyment and temporal dissociation may explain an increased level of SNS usage. This in turn corresponds with an elevated level of depression. These findings are in line with previous research in the field and expand upon them by showing the relationship with cognitive absorption. Further, they provide support that further research should be conducted in this area to determine the underlying cause(s) of this association. This may also need to be addressed at a societal level so that the negative outcomes of SNS can be better understood and more readily treated or avoided. At the individual level, these findings become important because they may help to curb the desire to over indulge in SNS usage.
Notes
- Positive in this context is meaning that Focused Immersion will explain a significant increase in Social Networking Usage. The same terminology is used throughout the manuscript for clarity.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the numerous subjects that participated in this study. We would also like to thank the editors and reviewers who provided invaluable advice for improving this manuscript.
Appendix
Table A1. Items and PLS-Based Loadings.
|
Item Loading |
|||
|
Construct |
All |
Males |
Females |
|
Focused Immersion |
|
|
|
|
While using social networking I am able to block out most other distractions. |
.829 |
.744 |
.744 |
|
While using social networking, I am absorbed in what I am doing. |
.913 |
.914 |
.911 |
|
While on social networking, I am immersed in the task I am performing. |
.862 |
.883 |
.988 |
|
Heightened Enjoyment |
|
|
|
|
I have fun interacting with social networking. |
.832 |
.881 |
.660 |
|
Using social networking provides me with a lot of enjoyment. |
.876 |
.893 |
.793 |
|
I enjoy using social networking. |
.892 |
.906 |
.818 |
|
Using social networking bores me. (-) |
.732 |
.662 |
.896 |
|
Temporal Dissociation |
|
|
|
|
Time appears to go by very quickly when I am using social networking. |
.859 |
.875 |
.819 |
|
Sometimes I lose track of time when I am using social networking. |
.904 |
.902 |
.888 |
|
Time flies when I am using social networking. |
.897 |
.902 |
.886 |
|
Most times when I get on to social networking, I end up spending more time that I had planned. |
.851 |
.876 |
.777 |
|
I often spend more time on social networking than I had intended. |
.853 |
.880 |
.783 |
|
Depression |
|
|
|
|
Have you felt low in spirit or sad? |
|
|
|
|
Have you lost interest in your daily activities? |
|
|
|
|
Have you felt lacking in energy and strength? |
|
|
|
|
Have you felt less self-confident? |
|
|
|
|
Have you had a bad conscience or feelings of guilt? |
|
|
|
|
Have you felt that life wasn't worth living? |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Have you had difficulty in concentrating, e.g., when reading the newspaper or watching television? |
|
|
|
|
Have you felt very restless? |
|
|
|
|
Have you felt subdued? |
|
|
|
|
Have you had trouble sleeping at night? |
|
|
|
|
Have you suffered from reduced appetite? |
|
|
|
|
Have you suffered from increased appetite? |
|
|
|
|
Social Networking Usage |
|
|
|
|
The number of hours per week of social networking usage were found by multiplying: |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
On average, how many hours per day do you use social networking? |
|
|
|
|
On average, how many days per week do you use social networking? |
|
|
|

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2015 Stoney Brooks, Phil Longstreet


