Investigating markers of behavioural addiction in excessive massively multiplayer online role-playing gamers
Vol.6,No.3(2012)
MMORPG; addiction; attentional bias; impulsivity; high engagement
Olivia Metcalf
Department of Psychology, The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia
Olivia Metcalf is a PhD candidate at the Research School of Psychology, Australian National University, Canberra. For her thesis project she has investigated the psychopathology of excessive video gaming and related behavioural, cognitive and physiological markers. She has previously conducted research on the human visual system using psychophysical techniques.
Kristen Pammer
Department of Psychology, The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia
Dr. Kristen Pammer is an associate professor and undergraduate advisor at the Research School of Psychology, Australian National University, Canberra. Her interests involve the attentional and cognitive processes engaged in various activities, including video gaming. Her research largely involves neurological and psychophysiological methods.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
Armstrong, L., Phillips, J. G., & Saling, L. L. (2000). Potential determinants of heavier internet usage. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 53, 537-550. doi:10.1006/ijhc.2000.0400
Balota, D. A., Yap, M. J., Cortese, M. J., Hutchison, K. A., Kessler, B., Loftis, B., Neely, J. H., Nelson, D. L., Simpson, G. B., & Treiman, R. (2007). The English Lexicon Project. Behavior Research Methods, 39, 445-459. Retrieved from http://elexicon.wustl.edu/
Bardo, M. T., Donohew, R. L., & Harrington, N. G. (1996). Psychobiology of novelty seeking and drug seeking behaviour. Behavioural Brain Research, 77, 23-43. doi:10.1016/0166-4328(95)00203-0
Barratt, E. S., & Patton, J. H. (1983). Impulsivity: Cognitive, behavioural and psychophysiological correlates. In M. Zuckerman (Ed.), Biological bases of sensation seeking, impulsivity, and anxiety (pp. 77-122). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Beard, K. W., & Wolf, E. M. (2001). Modification in the proposed diagnostic criteria for Internet addiction. CyberPsychology and Behavior, 4, 377-383. doi:10.1089/109493101300210286
Blaszczynski, A., & Nower, L. (2002). A pathways model of problem and pathological gambling. Addiction, 97, 487-499. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00015.x
Brevers, D., Cleeremans, A., Tibboel, H., Bechara, A., Kornreich, C., Verbanck, P., & Noël, X. (2011). Reduced attentional blink for gambling-related stimuli in problem gamblers. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 42, 265-269. doi:10.1016/j/jbtep.2011.01.005
Cao, F., Su, L., Liu, T., & Gao, X. (2007). The relationship between impulsivity and Internet addiction in a sample of Chinese adolescents. European Psychiatry, 22, 466-471. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.05.004
Carter, B. L., & Tiffany, S. T. (1999). Meta-analysis of cue-reactivity in addiction research. Addiction, 94, 327-340. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.1999.9433273.x
Castel, A. D., Pratt, J., & Drummond, E. (2005). The effects of action video game experience on the time course of inhibition of return and the efficiency of visual search. Acta Psychologica, 119, 217-230. doi:10.1016/j.actpsy.2005.02.004
Chappell, D., Eatough, V., Davies, M. N. O., & Griffiths, M. D. (2006). EverQuest—It’s just a computer game right? An interpretative phenomenological analysis of online gaming addiction. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 4, 205–216. doi:10.1007/s11469-006-9028-6.
Charlton, J. P., & Danforth, I. D. W. (2007). Distinguishing addiction and high engagement in the context of online game playing. Computers in Human Behavior, 23, 1531-1548. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2005.07.002
Charlton, J. P., & Danforth, I. D. W. (2010). Validating the distinction between computer addiction and engagement: online game playing and personality. Behaviour & Information Technology, 29, 601-613. doi:10.1080/01449290903401978
Collins, E., Freeman, J., & Chamarro-Premuzic, T. (2012). Personality traits associated with problematic and non-problematic massively multiplayer online role playing game use. Personality and Individual Differences, 52, 133-138. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2011.09.015
Decker, S. A., & Gay, J. N. (2011). Cognitive-bias toward gaming-related words and disinhibition in World of Warcraft gamers. Computers in Human Behavior, 27, 798-810. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2010.11.005
Elliott, L., Golub, A., Ream, G., & Dunlap, E. (2012). Video game genre as a predictor of problem use. CyberPsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 15, 155-161. doi:10.1089/cyber.2011.0387
Field, M., & Cox, W. M. (2008). Attentional bias in addictive behaviors: A review of its development, causes and consequences. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 97, 1-20. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.03.030
Fuentes, D., Tavares, H., Artes, R., & Gorenstein, C. (2006). Self-reported and neuropsychological measures of impulsivity in pathological gambling. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12, 907-912. doi:10.1017/S1355617706061091
Griffiths, M. D. (2010). The role of context in online gaming excess and addiction: Some case study evidence. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 8, 119-125. doi:10.1007/s11469-009-9229-x
Grüsser, S. M., Thalemann, R., & Griffiths, M. D. (2007). Excessive computer game playing: Evidence for addiction and aggression? CyberPsychology & Behavior, 10, 290-292. doi:10.1089/cpb.2006.9956.
Halperin, J. M., Wolf, L., Greenblatt, E. R., & Young, G. (1991). Subtype analysis of commission errors on the continuous performance test in children. Developmental Neuropsychology, 7, 207-217. doi:10.1080/87565649109540488
Hussain, Z., & Griffiths, M. D. (2009). Excessive use of massively multi-player online role-playing games: A pilot study. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 7, 563-571. doi:10.1007/s11469-009-9202-8
Inquisit 3.0.1.1 [Computer software]. (2008). Seattle, WA: Millisecond Software LLC.
Kim, E., Namkoong, K., Ku, T., & Kim, S. (2008). The relationship between online game addiction and aggression, self-control and narcissistic personality traits. European Psychiatry, 23, 212-218. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.10.010
Kim, J. W., Han, D. H., Park, D. B., Min, K. J., Na, C., Won, S. K., & Park, G. N. (2010). The relationships between online game player biogenetic traits, playing time, and the genre of game being played. Psychiatry Investigation, 7, 17-23. doi:10.4306/pi.2010.7.17
Ko, C. H., Liu, G. C., Hsiao, S., Yen, J. Y., Yang, M. J., Lin, W. C., Yen C. F., & Chen, C. S. (2009). Brain activities associated with gaming urge of online gaming addiction. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 43, 739-747. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.09.012
Liau, A. K., Neo, E. C., Gentile, D. A., Choo, H., Sim, T., Li, D., & Khoo, A. (2011). Impulsivity, self-regulation, and pathological video gaming among youth: Testing a mediation model. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health. Advance online publication. doi:10.1177/1010539511429369
Liu, N., Li, B., Sun, N., & Ma, Y. (2008). Effects of addiction-associated and affective stimuli on the attentional blink in a sample of abstinent opiate dependent patients. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 22, 64-70. doi:10.1177/0269881107077804
Metcalf, O., & Pammer, K. (2011). Attentional bias in excessive massively multiplayer online role-playing gamers using a modified Stroop task. Computers in Human Behavior, 27, 1942-1947. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2011.05.001
Myrserth, H., Pallesen, S., Molde, H., Johnsen, B. H., & Lorvik, I. M. (2009). Personality factors as predictors of pathological gambling. Personality and Individual Differences, 47, 933-937. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2009.07.018
Ng, B. D., & Wiemer-Hastings, P. (2005). Addiction to the internet and online gaming. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 8, 110–113. doi:10.1089/cpb.2005.8.110
Nije Bijvank, M., Konijn, E. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2012). “We don’t need no education”: Video game preferences, video game motivations, and aggressiveness among adolescent boys of different educational ability levels. Journal of Adolescence, 35, 153-162. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2011.04.001
Patton, J. H., Stanford, M. S., & Barratt, E. S. (1995). Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 51, 768-774. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(199511)51:6<768::AID-JCLP2270510607>3.0.CO;2-1
Ray Li, C. S., Chen, S. H., Lin, W. H., & Yang, Y. Y. (2005). Attentional blink in adolescents with varying levels of impulsivity. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 39, 197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2004.06.003
Raymond, J. E., Shapiro, K. L., & Arnell, K. M. (1992). Temporary suppression of visual processing in an RSVP task: An attentional blink? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Performance, 18, 849-860. Retrieved from http://www.dc.uba.ar/materias/incc/practicas/p1/raymond-1992.pdf
Ryan, F. (2002). Detected, selected, and sometimes neglected: cognitive processing of cues in addiction. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 10, 67-76. doi:10.1037/1064-1297.10.2.67
Seay, A. F., & Kraut, R. E. (2007). Projective massive: Self-regulation and problematic use of online gaming. CHI Proceedings: San Jose, CA, USA. Retrieved from http://nguyendangbinh.org/Proceedings/CHI/2007/docs/p829.pdf
Stanford, M. S., Mathias, C. W., Dougherty, D. M., Lake, S. L., Anderson, N. E., & Patton, J. H. (2009). Fifty years of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale: An update and review. Personality and Individual Differences, 47, 385-395. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2009.04.008
Stetina, B. U., Kothgassner, O. D., Lehenbauer, M., & Kryspin-Exner, I. (2011). Beyond the fascination of online-games: Probing addictive behaviour and depression in the world of online-gaming. Computers in Human Behavior, 27, 473-479. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2010.09.015
Thalemann, R., Wölfling, K., & Grüsser, S. M. (2007). Specific cue reactivity on computer game-related cues in excessive gamers. Behavioral Neuroscience, 121, 614-618. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.121.3.614
Tibboel, H., De Houwer, J., & Field, M. (2010). Reduced attentional blink for alcohol-related stimuli in heavy social drinkers. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 24, 1349-1356. doi: 10.1177/0269881109106977
Tiffany, S. T. (1990). A cognitive model of drug urges and drug-use behaviour: Role of automatic and nonautomatic processes. Psychological Review, 97, 147-168. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.97.2.147
van Holst, R. J., Lemmens, J. S., Valkenburg, P. M., Peter, J., Veltman, D. J., & Goudriaan, A. E. (2011). Attentional bias and disinhibition toward gaming cues are related to problem gaming in male adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 50, 541-546. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2011.07.006
Ventura, M., Shute, V., & Kim, Y. J. (2012). Video gameplay, personality and academic performance. Computers & Education, 58, 1260-1266. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2011.11.022
Verdejo-García, A., Lawrence, A. J., & Clark, L. (2008). Impulsivity as a vulnerability marker for substance-use disorders: Review of findings from high-risk research, problem gamblers and genetic association studies. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 32, 777-810. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.11.003
Waters, A. J., Heishman S. J., Lerman, C., & Pickworth, W. (2007). Enhanced identification of smoking-related words during the attentional blink in smokers. Addictive Behaviors, 32, 3077-3082. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2007.05.016
Yee, N. (2006). The demographics, motivations and derived experiences of users of massively multi-user online graphical environments. Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, 15, 309–329. doi:10.1162/pres.15.3.309
Zuckerman, M., & Kuhlman, M. D. (2000). Personality and risk-taking: Common biosocial factor. Journal of Personality, 68, 999-1029. doi:10.1111/1467-6494.00124
Introduction
One of the most popular genres of online games worldwide is Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (MMORPG), in which the gameplay primarily involves the development of an avatar and socialisation within a large-scale game world. Researchers have speculated that the social nature of the persistent worlds and the potential for avatar development are among the features that make MMORPGs so popular, but also create potential for the games to become addictive (Elliott, Golub, Ream, & Dunlap, 2012; Stetina, Kothgassner, Lehenbauer, & Kryspin-Exner, 2011). For example, research has shown that MMORPG users are more likely to play for longer periods of time and are more likely to report health and relationship-related problems as a consequence of their gaming behaviour than gamers of other genres (Kim et al., 2010; Stetina et al., 2011). Thus, the majority of the cyberpsychology literature has focused investigation on the nature of excessive MMORPG use rather than other genres.
While research has established that a significant number of gamers appear to use MMORPGs excessively and report suffering negative consequences as a result (e.g. Chappell, Eatough, Davies, & Griffiths, 2006; Charlton & Danforth, 2007, 2010; Hussain & Griffiths, 2009; Yee, 2006) there remains debate as to whether or not this behaviour constitutes an addiction (Griffiths, 2010; Ng & Weimer-Hastings, 2005). One major limitation is the lack of experimental evidence investigating key features of behavioural addiction in excessive MMORPG users. A few studies have investigated the presence of physiological markers of addiction in excessive MMORPG users by employing cue-reactivity paradigms (Grüsser, Thalemann, & Griffiths, 2007; Ko et al., 2009; Thalemann, Wöfling, & Grüsser, 2007). Cue-reactivity is the phenomenon found in addiction whereby, during the development of the disorder, addicts automatically respond physiologically and behaviourally to addiction-related cues (Carter & Tiffany, 1999). Cue-reactivity has been investigated in all substance abuse disorders and pathological gambling with robust findings and the process is thought to be fundamental in the development and maintenance of addiction (Carter & Tiffany, 1999). In a cue-reactivity paradigm, addicts and non-addicts are presented with addiction-related and non-addiction related cues. Typically, addicts respond significantly differently to addiction-related cues compared to non-addiction cues, whereas non-addicts show no differences. One such response to addiction-related cues is the subjective experience of craving, or strong feelings of desire to engage in the addiction-related behaviour or substance, typically measured by self-report (Tiffany, 1990). Studies investigating both physiological responding and craving in excessive MMORPG users have found that they show greater physiological arousal and report higher levels of craving to MMORPG-related cues compared to non-MMORPG related cues (Grüsser et al., 2007; Ko et al., 2009; Thalemann et al., 2007). Importantly, this difference in responding is not found in regular MMORPG users, and these findings replicate those from studies investigating substance addiction and pathological gambling (see Carter & Tiffany, 1999, for review).
In addition to eliciting subjective feelings of craving and altering physiological arousal, cue-reactivity also simultaneously elicits a cognitive response that manifests implicitly, or beyond the addict’s awareness (Ryan, 2002). The most studied type of implicit cognitive response in addiction is the attentional bias, or the bias found in an addict’s attention system that prioritises the processing of addiction-related cues over non-addiction related cues (see Field & Cox, 2008, for review). Attentional bias is measured in paradigms that tap into automatic cognitive processes and thus is not subject to the same limitations as self-report measures. There is recent evidence indicating that excessive MMORPG users are exhibiting signs of attentional bias (Decker & Gay, 2011; Metcalf & Pammer, 2011). Both studies reported faster reaction times from excessive MMORPG users for gaming-related stimuli compared to performance on non-gaming related stimuli, whereas regular or non-gamers showed no such bias in performance (Decker & Gay, 2011; Metcalf & Pammer, 2011). However, both studies investigating attentional bias in excessive MMORPG users employed reaction-time dependent paradigms. Given that regular video gamers have improved reaction times due to game training effects (e.g., Castel, Pratt, & Drummond, 2005) attentional bias results that reported differences in responses to MMORPG-related stimuli may have been the result of enhanced reaction times in MMORPG users instead of cue-reactivity. Moreover, a recent study that employed an attentional bias paradigm failed to find a relationship between degree of gaming addiction and attentional bias (van Holst et al., 2011).
One explanation for the discrepancy in attentional bias studies may be the methods by which researchers identify MMORPG addiction. A significant limitation facing MMORPG addiction research is the lack of consistency across identification measures. Most scales currently in use have been adapted from pathological gambling scales which comprise items that tap into withdrawal, euphoria, conflict, behavioural and/or cognitive salience, relapse, and tolerance. However, there is a lack of experimental evidence investigating whether all pathological gambling criteria are suitable to identify MMORPG addiction. There is some debate as to whether cognitive salience, meaning thinking a great deal about gaming; tolerance, meaning engaging in the activity more frequently; and euphoria, meaning feelings of excitement from engaging in an activity genuinely constitute MMORPG addiction (Beard & Wolf, 2001; Charlton & Danforth, 2007, 2010). Charlton and Danforth suggest that cognitive salience, tolerance and euphoria are not essential criteria for MMORPG addiction. Rather, these criteria represent gamers who frequently play, but do not necessarily suffer any significant negative consequences as a result. This class of gamer has been termed highly engaged and research suggests that addicted and highly engaged gamers differ significantly (Charlton & Danforth, 2007, 2010). Thus, differences in methods of identifying addiction could account for previous non-significant findings (van Holst et al., 2012).
Debate surrounding whether excessive MMORPG use constitutes an addiction continues and there remains significant scope for investigating cue-reactivity in excessive MMORPG users. The current study aims to investigate attentional bias employing a paradigm that does not require reaction time-dependent processing. In addition, performance for gamers who endorse only peripheral criteria compared to those who endorse core criteria will be compared. The Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP) paradigm involves the presentation of a rapid and sequential stream of visual stimuli such as letters, words or pictures. When observers are required to detect two targets within the stream, they typically have poorer detection of the second target if presented within 200-500ms relative to the presentation of the first target. The failure to detect the second target is known as the attentional blink (Raymond, Shapiro, & Arnell, 1992), and while there remains debate as to the exact nature of the phenomenon, the attentional blink is thought to be due to an attentional bottleneck occurring at the encoding stage of the attention system. Attentional resources are tied up in the processing of the first target when the second target is presented too temporally close, leaving insufficient resources to devote to the processing of the second target (Raymond et al., 1992).
The attentional blink paradigm can be used to investigate attentional bias: addicts and controls are presented with either addiction-related or neutral words as the second target. For non-addicts, there is no difference in detection rates of the second target, irrespective of which word condition (Brevers et al., 2011; Liu, Li, Sun, & Ma, 2008). However, addicts show a more attenuated attentional blink for addiction stimuli, in that they have better recall of second targets that are addiction-related compared to neutral. This effect is thought to be due to the attentional bias, or the prioritizing of the processing of addiction-related stimuli. Given the finite resources of the attention system, the attentional bias enables the addict to overcome the attentional bottleneck by diverting resources to the processing of the addiction-related words, whereas this same effort is not spent on non-addiction related stimuli (Waters, Heishman, Lerman, & Pickworth, 2007).
Furthermore, overall performance on an RSVP task is also thought to vary with levels of impulsivity. Ray Li, Chen, Lin, and Yang (2005) found that individuals with higher levels of impulsivity had poorer performance on an RSVP task than low impulsivity individuals. Studies investigating attentional bias in opiate addiction found in addition to an attenuated blink for opiate-related words, opiate addicts overall showed poorer performance compared to non-addicts on neutral word recall (Liu et al., 2008). Therefore, in addition to measuring attentional bias, the RSVP may also be an indicator of impulsivity. Impulse-control is thought to be particularly central to pathological gambling, as the addiction relies on dependence on the activity or an inability to resist engaging in the activity, rather than physical dependence on a psychoactive substance seen in substance abuse addictions (Blaszczynski & Nower, 2002). Pathological gambling is currently classified in the DSM-IV-TR as an impulse-control disorder (APA, 2000) indicative of how central the role of abnormal levels of impulsivity is to the disorder. Research has shown that impulsivity is a significant risk factor for pathological gambling (Verdejo-García, Lawrence, & Clark, 2008) and that performance in tasks designed to measure behavioural aspects of impulsivity are impaired (Fuentes, Tavares, Artes, & Gorenstein, 2006).
Despite the importance of impulsivity to pathological gambling, and the general expectation in the literature that impulsivity must play a major role in the aetiology of MMORPG addiction, there remains very little experimental research. Two studies have experimentally investigated impulsivity in excessive MMORPG users with conflicting findings. Decker and Gay (2011) found that excessive MMORPG users exhibited behavioural signs of impulsivity in a computerised task designed to measure disinhibition, or the inability to withhold an inappropriate response to stimuli. In comparison, van Holst et al. (2011) found no relationship between measures of disinhibition and game addiction. Neither study took a psychometric measure of impulsivity, and as previously discussed, differences may in part be due to methods of identifying game addiction. Research investigating impulsivity in excessive Internet users has also been conducted with mixed results. For example, Armstrong, Phillips, and Saling (2000) found no relationship between excessive Internet use and impulsivity. In comparison, a more recent study found a sample of Internet addicts were significantly higher in impulsivity compared to non-addicts (Cao, Su, Liu, & Gao, 2007). Therefore, while impulsivity plays an important role in the development of addiction, the relationship between impulsivity and MMORPG use remains unclear.
We employed an attention-based paradigm that measured cue-reactivity to investigate attentional bias, in addition to differences in performance by gamers who endorsed core and peripheral criteria. We predict that gamers identified as addicted endorsing the core criteria of the Addiction-Engagement Questionnaire (AEQ: Charlton & Danforth, 2007) will exhibit an attenuated attentional blink for gaming-related words. In contrast, should the peripheral criteria of the AEQ not be representative of MMORPG addiction, gamers who endorse only these criteria will show no difference in blink performance irrespective of word type. Finally, as attentional blink performance is a measure of attentional capacity and varies with impulsivity (Liu et al., 2008); we sought to explore differences between addicted and non-addicted gamers in general attentional performance.
Study 1
Method
Participants
Thirty-seven MMORPG users (14 female, 23 male, Mage = 22.2 years, range: 18-29 years) were recruited with flyers located on Australian National University campus and video game stores and online forums. Inclusion criteria stipulated a minimum 5 hours MMORPG use per week in the preceding 6 month period. Twenty non-MMORPG users (9 female, 11 male, Mage = 21.9 years, range: 18-31 years) were recruited using flyers located solely on campus and were required to have never played a MMORPG. Participants were reimbursed AUS$10 for their time. All participants had normal or corrected-to-normal vision, were fluent in English and gave informed written consent. This study was approved by the Australian National University Human Research Ethics Committee.
Materials and Procedure
Addiction-Engagement Questionnaire. Charlton and Danforth (2007, 2010) developed this 24-item, 7-point Likert scale for a specific MMORPG titled Asherson’s Call. Items are positively and negatively worded. Charlton and Danforth propose it is not suitable to use all items previously used to identify behavioural addictions, specifically the cognitive salience, tolerance and euphoria items. Rather, these items tap into degree of engagement. The AEQ has 12 items that tap into high engagement and 12 items that tap into addiction, with seven addiction items considered “core” criteria (Table 1). Comprising the seven core criteria are three items that tap into conflict, two into behavioural salience and one item each for relapse and withdrawal. Charlton and Danforth recommend a cut-off of more than half of the core criteria being endorsed to identify addiction (2007). Thus, in the current study addiction was indicated by four or more of the seven core criteria being endorsed. Participants who endorsed three or less of the core criteria for addiction were classed as highly engaged. We amended the wording of the original AEQ from “Asheron’s Call” to “MMORPG/s” and asked participants to consider their preferred MMORPG when responding. Charlton and Danforth (2010) reported good internal consistency with an addiction scale Cronbach’s alpha of 0.79 and engagement scale alpha of 0.80. The Cronbach’s alpha for the addiction scale in the current study was .90 and the engagement scale was .93.
Table 1. The seven core addiction items contained in the Addiction-Engagement Questionnaire.
|
1. |
I often fail to get enough sleep because of playing MMORPGs. |
|
2. |
My social life has sometimes suffered because of my playing MMORPGs. |
|
3. |
Arguments have sometimes arisen at home because of the time I spend playing MMORPGs. |
|
4. |
Playing MMORPGs has sometimes interfered with my work. |
|
5. |
I have made unsuccessful attempts to reduce the time I spend playing MMORPGs. |
|
6. |
I never miss meals because of playing MMORPGs.a |
|
7. |
When I am not playing MMORPGs I often feel agitated. |
|
Note. aReversed. |
|
Rapid Serial Visual Presentation Task. Fifteen MMORPG-related words were sourced from popular gaming sites and rated by regular MMORPG users not used in the current experiment for relevance to MMORPG gameplay. Fifteen neutral, household-related words served as the other half of the second target (T2) word pool. The two word lists did not differ on word length (M = 4.93 and M = 5.07 letters, respectively, p > 0.05) or HAL frequency of use (M = 9.49 and M = 9.47, respectively, p > 0.05; Balota et al., 2007).
A list of 60 neutral first target (T1) words was compiled and deemed unrelated to gaming or household items, ranging from 4-8 letters in length (M = 6.5) and frequency of use was M = 9.1. Two-hundred distracter words were also compiled, ranging from 10-13 letters in length to ensure adequate masking and were also deemed non-related to household items or gaming.
Procedure
Stimuli were generated and responses recorded using the Inquisit software package (Millisecond Software, 2008). Tasks were displayed on a Sony Trinitron 22-in. monitor operating at a refresh rate of 100 Hz with a spatial resolution of 1024 x 768 pixels. The monitor was presented at eye level and participants were seated approximately 50cm away. Responses were recorded using a keyboard.
Each trial began with a white fixation cross presented for 1000ms, followed by the 16-item RSVP stream, with 14 distracter words in white and both targets in red. All stimuli were presented for 100ms consecutively in Arial font, size 30, on a black background. For each block, T1 was always selected without replacement from the neutral list of 60 T1 words. T2 was selected randomly from the MMORPG list for half the trials and the household related items for the remainder of the trials. Distracter words were selected at random for each trial with no distracter word repeated on a single trial. Trials were presented in random order.
T1 could be presented at position 3, 4 or 5 in the RSVP stream and T2 could be presented immediately after T1 (Lag 1, 100ms), Lags 2-4 and Lag 8 (800ms). There was one for every combination of T1 starting position (3) and the 5 lag positions, for two T2 types, resulting in 30 trials per block. Participants completed two blocks, resulting in 60 trials for the experiment, meaning each T2 word was presented twice. At the end of each trial participants were prompted to manually report the two targets. Participants were given 10 practice trials. Practice trials contained T1 and T2 words that were deemed neutral, non-household or gaming related and were not used in the experiment proper. After completing the RSVP, participants were given the AEQ and provided demographic information.
Results
Demographics and scales. Eighteen gamers (6 female, 12 male, Mage = 21.4 years, range: 18-26 years) endorsed four or more of the core criteria of the AEQ and were classified as addicted, whereas the remaining 19 gamers (8 female, 11 male, Mage = 23 years, range: 20-29 years) endorsed less than three of the core criteria and both of the engaged criteria and were thus classified as highly engaged. Non-MMORPG users endorsed none of the criteria. Chi-square revealed no significant differences between groups for sex ratio, χ2 (2, n = 57) = .572, p = .751. A one-way ANOVA revealed no significant differences between groups for age, F (2, 54) = 1.428, p = .249. Addicted and highly engaged participants played similar amounts of MMORPGs per week (M = 10-15 hours) and had been playing for the same length of time (M = 2.3 years) with no significant differences between the two groups (both p’s > 0.05).
Rapid serial visual presentation task. Percentage of correct T2 responses was calculated for each condition in trials for which T1 was identified correctly. Independent calculation of T1 indicated no significant differences in recall across groups or conditions (p’s < 0.05). The dependent variable of correct T2 responses given correct T1 recall was subjected to a mixed measures 3 (group: addicted, engaged, non-gamer) x 2 (word type: neutral, gaming) x 5 (Lag: 1, 2, 3, 4, 8) ANOVA. There was a significant main effect for Lag, Wilks’ Lambda = .263, F (4, 51) =35.73, p < .0005, η2= .427, indicating that the attentional blink effect was found with poorer recall for all words at the early lags compared to the later lags. The 3-way interaction was non-significant, Wilks’ Lambda = .881, F (3, 102) = .830, p = .578. The important word by group interaction was significant, Wilks’ Lambda = .870, F (2, 54) = 4.046, p = .023, η2= .130.
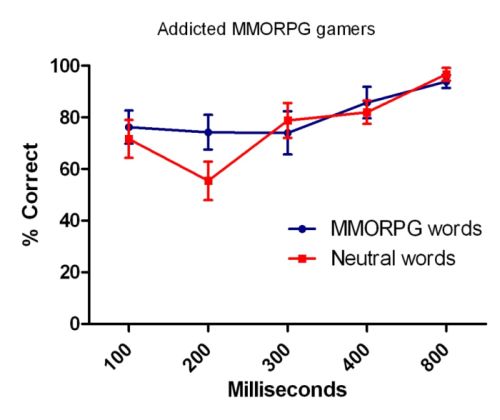
Planned post-hoc comparisons revealed at Lag 2 there was significantly better performance for addicted MMORPG users on MMORPG words than neutral words, t(18)= -2.776, p = .013 but not for non-MMORPG users (p = .330) or highly engaged (p = .912). Performance by word type over lag for addicted and engaged MMORPG users is presented in Figure 1-2. Finally, the lag by group interaction was non-significant, Wilks’ Lambda = .800, F (2, 54) = 1.504, p = .165, indicating that the three groups did not differ in overall attentional blink performance, irrespective of word condition.

Discussion
All participants exhibited an attentional blink, with poorer performance at early lags, specifically Lag 2 (200ms). In addition, the results indicated there was significantly better recall for MMORPG words compared to neutral words in addicted gamers at Lag 2, consistent with an attentional bias. Importantly, this difference in performance was not found in highly engaged or non-MMORPG users. Our findings are consistent with previous research using the RSVP to measure attentional bias in opiate addiction (Liu et al., 2008) excessive alcohol use (Tibboel, De Houwer, & Field, 2010), smoking (Waters et al., 2007) and pathological gambling (Brevers et al., 2011). Furthermore, previous excessive MMORPG use studies reported differences in addiction-related stimuli processing by addicted and non-addicted gamers using reaction-time dependent paradigms (Decker & Gay, 2011; Metcalf & Pammer, 2011). The current findings confirm these results are due to attentional-bias related processing changes in the encoding stage of attention, not potential confounds of altered reaction-time processing in gamers. Additionally, as all highly engaged gamers endorsed the tolerance and salience criteria of the AEQ, yet endorsed three or less of the core criteria, and did not show an attenuated attentional blink for MMORPG words, this is behavioural evidence that relying on endorsement of criteria that tap into cognitive salience or tolerance may falsely identify gaming addiction. This may account for why at least one study failed to find a relationship between a measure of attentional bias and gaming addiction (van Holst et al., 2011). With multiple recent studies indicating that excessive MMORPG users display cue-reactivity physiologically, through reports of craving and signs of attentional bias, comparable to those from established addictions, there is accumulating evidence that excessive MMORPG use constitutes an addiction (Decker & Gay, 2011; Grüsser et al., 2007; Ko et al., 2009; Metcalf & Pammer, 2011; Thalemann et al., 2007).
Interestingly, there was no difference in overall performance, irrespective of word type for the different groups. Overall attentional blink performance is an indicator of attentional processing capacity, and we found no evidence that addicted gamers had a different attentional capacity to highly engaged or non-MMORPG users. Furthermore, previous research has found that individuals with higher impulsivity (Ray Li et al., 2005) and opiate addicts compared to controls (Liu et al., 2008) have steeper attentional blinks. A limitation facing the current study is the RSVP is not an explicit measure of impulsivity. The following exploratory study aims to expand on the previous study by employing an attention-based paradigm that taps into a more explicit indicator of impulsivity. Disinhibition is found in individuals higher in impulsivity and is due to a difficulty in inhibiting an inappropriate response (e.g. Halperin, Wolf, Greenblatt, & Young, 1991). Study 2 will also include a trait measure of impulsivity. The aim is to investigate whether a sample of regular MMORPG users differed in both a trait and behavioural measure of impulsivity to non-MMORPG users, and furthermore, investigate the relationship between impulsivity and degree of addiction and engagement.
Study 2
Method
Participants
MMORPG users (8 female, 15 male, Mage = 22.4 years, range: 18-40 years) and non-video gamers (11 female, 10 male, Mage = 23.1 years, range: 20-27 years) were recruited in a similar manner to Experiment 1, except non-video gamers were required to have played no video games in the preceding 6 month period and never have played any genre of video game regularly. None of the participants in Study 1 participated in Study 2. All participants had normal or corrected-to-normal vision, were fluent in English and gave informed written consent. This study was approved by the Australian National University Human Research Ethics Committee. All participants were reimbursed AUS$10 for their time.
Materials and Procedure
Continuous Performance Task. Each trial involved the presentation of capital letters (B, C, D, G, K, O, Q, S, Y and X) in 60pt Arial font for 247ms. After the presentation of a letter, an inter-stimulus interval (ISI) duration of 1000ms, 2000ms or 4000ms occurred before the next letter was presented. All participants started the CPT with a 1000ms ISI block comprising 30 trials, followed by a 2000ms block and a 4000ms block. The set of three blocks with increasing ISI was then repeated twice, meaning participants completed 9 blocks in total, lasting a total of 15 minutes. Participants were required to respond only when an “X” was presented. Each block contained 5 targets (X) and 25 distractors. Accuracy and reaction times were recorded.
Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11. The 11th version of the BIS comprises 30 items in three subscales of factors: attentional (inattention and cognitive instability), motor (motor impulsiveness and lack of perseverance), and non-planning (lack of self-control) (Patton et al., 1995). Positive and reverse-coded statements are presented with participants required to respond on a Likert scale from 1 to 4 with 1 being “Rarely/ Almost Never” and 4 being “Almost Always/Always”.
Procedure
Stimuli were presented using the same equipment as per Study 1. Participants were explicitly told to respond as accurately and rapidly as possible to the target letter and to maintain their performance over the entire 15 minute duration. Participants completed the CPT followed by the BIS-11, the AEQ as per Study 1 and provided demographic information.
Results
Demographics and scales. Chi-square revealed no significant differences between groups for sex ratio, χ2 (1, n = 44) = 1.386, p = .239. One-way ANOVA was run on age and BIS-11 scores. There were no differences in age, F (1, 42) = .384, p = .539 or overall impulsivity scores, F (1, 42) = .061, p = .806. Pearson’s product moment correlations were calculated between degree of addiction and engagement in MMORPG users and impulsivity scores. Addiction and total BIS score were positively correlated r = .467, n = 23, p = .025 as was addiction and non-planning factor r = .435, n = 23, p = .038, but not addiction and the attentional or motor impulsivity factors (both p’s > 0.05). Engagement showed no relationship with any of the impulsivity factors (all p’s > 0.05). There was a positive correlation between amount of hours spent playing MMORPGs per week and engagement r = .540, n = 23, p = .008, but not between hours played and addiction r = .175, n = 23, p = .424.
Continuous performance task. False alarms were recorded when participants responded to any other letter than the target “X.” False alarms are indicative of disinhibition, or the inability to withhold an inappropriate response. Misses were calculated as any occasion when participants failed to respond to the target and are indicative of lapses in attention. Mean reaction times to the three ISI’s were recorded for each participant. A one-way ANOVA was run on errors and misses and overall reaction times. Non-gamers had significantly more false alarms compared to MMORPG users (p = .010), but no differences in misses (p = .262) or reaction times to the different ISI’s (all p’s < 0.05).
General Discussion
The second exploratory study set out to investigate the role of impulsivity in MMORPG use. There were no significant differences in levels of trait impulsivity between the sample of MMORPG users and non-video gamers. Behaviourally, MMORPG users exhibited less impulsivity as indicated by fewer errors on the CPT task compared to non- video gamers. Given that the BIS-11 is a trait measure of impulsivity, the current findings suggest that impulsivity is not related to a preference to play MMORPGs. Recent research indicates that certain personality traits are related to preference to play certain genres of games (Nije Bijvank, Konijn, & Bushman, 2012; Ventura, Shute, & Kim, 2012). Individuals with higher impulsivity were more likely to play action video games, whereas individuals with lower levels of impulsivity were more likely to play socially-orientated MMORPGs (Nije Bijvank et al., 2012). The current findings support the notion that MMORPG users do not have elevated impulsivity. While the fast-paced nature of action video games may attract individuals with higher levels of impulsivity, it may be that the repetitive nature of long periods of MMORPG use (termed “grinding” by MMORPG users) attracts gamers with lower levels of impulsivity. Moreover, Study 2 found no relationship between engagement and any impulsivity factors, and combined with the results from Study 1 confirm that peripheral criteria are indicative of a distinct type of gamer who is not addicted. These findings support Charlton and Danforth’s (2007, 2010) proposal that peripheral criteria such as cognitive salience and tolerance are unsuitable for identifying MMORPG addiction. Furthermore, the results add to growing evidence that video gamers are a heterogeneous group, and research in cyberpsychology employing video gamer populations should consider distinguishing between genres of games and addicted and engaged gamers.
While there was no evidence for individuals higher in impulsivity to prefer to play MMORPGs, there was some evidence for a unique relationship between MMORPG addiction and impulsivity. Total BIS score and the non-planning factor correlated positively with addiction whereas the attentional and motor factors did not. The non-planning factor of the BIS-11 represents the aspect of impulsivity that results in an inability to think about future consequences regarding one’s own actions, and maps onto aspects that concern self-control (see Stanford et al., 2009, for review). These findings are consistent with studies that have found that the strongest predictor of excessive MMORPG use is poor self-regulation (Collins, Freeman, & Chamarro-Premuzic, 2012; Liau et al., 2011; Seay & Kraut, 2009). While the current study provides support for a specific role of deficits in self-control in excessive MMORPG use, there was no relationship between response inhibition or the attention and motor factors of impulsivity and addiction. Comparable findings by van Holst and colleagues (2011) showed no relationship between disinhibition and addiction scores in a sample of excessive male adolescent online gamers. Collins and colleagues (2012) also found that levels of general dysfunctional impulsivity had no relationship with excessive MMORPG use and proposed that impulsivity is not essential to the aetiology of MMORPG addiction. The experimental evidence from the current study and from van Holst and colleagues (2011) supports this proposal.
Limiting the role of impulsivity in MMORPG addiction to deficits in self-control differs markedly from the role impulsivity is thought to play in other addictions, particularly pathological gambling. Research has shown poorer response inhibition in addicted gamblers, attributed to elevated levels of impulsivity (e.g. Fuentes et al., 2006). In addition, pathological gamblers have significantly higher scores on all three sub-factors of the BIS-11 in comparison to controls (Myrserth, Pallesen, Molde, Johnsen, & Lorvik, 2009). Thus, while impulsivity in excessive MMORPG use has not yet been extensively explored, recent research combined with the current findings suggests that beyond self-regulation deficits, the relationship between impulsivity and excessive gaming deviates significantly from other addictions and that the role of impulsivity in pathological gambling is not comparable to its role in MMORPG addiction. It remains unclear as to why this might be the case as the area remains new to research. Impulsivity is a multi-faceted construct (Barratt & Patton, 1983) meaning that multiple behavioural and psychometric measures are required to determine relationships with impulsivity. One factor of impulsivity that plays a major role in addiction is sensation-seeking. It has been postulated that individuals high in sensation-seeking are more likely to seek out stimulating activities such as gambling or risky substance use, predisposing them to develop an addiction (Bardo, Donohew, & Harrington, 1996; Zuckerman & Kuhlman, 2000). As discussed, there is evidence that high sensation-seeking individuals prefer fast-paced action video games, which are very stimulating (Nije Bijvank et al., 2012). Thus, low sensation-seeking individuals who prefer MMORPGs may go on to develop MMORPG addiction but remain low sensation-seekers, which would distinguish MMORPG addiction significantly from other types of addiction. However, this proposal remains speculative given that sensation-seeking was not directly explored in this study. If sensation-seeking and general elevated impulsivity play a limited role in the aetiology and maintenance of MMORPG addiction, it is possible that other predictors of excessive MMORPG use such as poor self-control, loneliness and low self-esteem (Collins et al., 2012; Kim, Namkoong, Ku, & Kim, 2008; Stetina et al., 2011) may play more central roles and thus be more important in the development of treatment. In sum, there is significant scope to develop the MMORPG addiction model.
There are several limitations to the current study. Firstly, the current study is limited by sample size and characteristics. For example, whether these results apply to excessive adolescent MMORPG users is uncertain. We also primarily recruited fantasy style MMORPGs (e.g. World of Warcraft) in which the role-playing element is heavily emphasised. Whether these impulsivity findings apply to MMORPGs that contain more action gameplay is unclear. Secondly, Study 2 employed correlational methodology to investigate the relationships between impulsivity and MMORPG addiction, whereas future studies should employ cross-sectional or longitudinal studies. Furthermore, given that impulsivity is multi-faceted and requires multiple measures, a different measure of impulsivity may not replicate these findings. The exploratory nature of Study 2 means more comprehensive investigation of impulsivity in excessive MMORPG use is required.
Conclusion
The current studies tested the prevailing hypothesis that excessive MMORPG use constitutes a behavioural addiction, similar to pathological gambling. Study 1 found behavioural evidence for cue-reactivity in addicted but not engaged MMORPG users, and Study 2 found a relationship between addiction and impulsivity, specifically the non-planning impulsivity factor. However, both studies failed to find evidence of attentional indicators of impulsivity in excessive MMORPG users. Thus, elevated impulsivity in the development of MMORPG addiction may be limited to deficits in self-control as current evidence suggests. Importantly, both studies support the existence of two types of regular gamers, those who are addicted and those who are highly engaged. Future research measuring MMORPG addiction must tap into core criteria to avoid over estimating the prevalence and further research is needed to elucidate the role of impulsivity in the aetiology of MMORPG addiction.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2012 Olivia Metcalf, Kristen Pammer

