Assessing Aggressiveness via Reaction Times Online
Vol.6,No.1(2012)
Aggressive tendencies can be assessed either commonly by explicit measures (self-report questionnaires), or by implicit measures that require the speeded classification of quickly presented stimuli and the recording and analysis of the reaction-times. We explored the psychometric properties of implicit measures assessing aggressiveness objectively: the Implicit Association Test (IAT) and its derivate, the Single-Target IAT. While the IAT focused on the automatic attitude towards aggressiveness, the ST-IAT focused on the self-concept. This feasibility study describes in methodological detail how a diversity of game players can be recruited to take these measures with common web- browser technology, even though reaction-time measurement in the range of a few hundred milliseconds is at stake. Self-reported and objective characteristics of users of violent, less violent, and no games differed. The results are partly in line with what can be expected on the basis of psychological theorizing, but structural-equation modelling shows that implicit measures on attitudes and self-concept differ in quality. Pitfalls and challenges for internet studies on computer players involving reaction-time measures are pointed out.
computer games; implicit association test; single-target IAT; aggressiveness; internet
Matthias Bluemke
Psychological Institute, University of Heidelberg, Germany
Dr. Matthias Bluemke is an assistant professor of social psychology at the Psychological Institute, University of Heidelberg, D-69117 Heidelberg, Germany. After completing his undergraduate studies at the University of Trier, he obtained his diploma in psychology and his doctorate in psychology at the University of Heidelberg. As a member of the social psychology department, his interests lie in group dynamics and cognitive factors of social phenomena with a focus on methods and psychometrics of explicit and implicit measures. He contributed several book chapters and conference papers. He also has published articles in journals of interest to social psychologists and researchers on interindividual differences, among them Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, European Review of Social Psychology, Memory and Cognition, Cognition and Emotion, Aggressive Behavior, and other journals. He served as a peer reviewer to most of these journals. In 2003 he received the Best German Diploma Thesis
Award in Social Psychology (in collaboration with Malte Friese) by the Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Psychologie (DGPs). Later he received the prestigious Hengstberger Award to hold a fruitful and stimulating conference on the future of implicit measures at the University of Heidelberg, and two Postdoctoral Fellowships by the German Research Foundation for further research on the validity of implicit measures at the University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand.
Joerg Zumbach
Department of Science Education and Teacher Training, University of Salzburg, Austria
Prof. Dr. Joerg Zumbach is a full professor and, since 2007, Head of the Department of Science Education and Teacher Training, University of Salzburg, A-5020 Salzburg, Austria. He obtained his diploma in psychology and doctorate from the University of Heidelberg, Germany. His main interests are educational and instructional psychology, media-based learning, and the media- aggression link. He works at the intersection of theory development and applied research in relation to cognitive processing in computer-based learning environments and blended learning approaches. He is author and editor of several books on web based teaching and problem-based learning. His articles have been published, among others, in Computers in Human Behavior, Journal of Educational Multimedia and Hypermedia, Journal of Educational Computing Research, Aggressive Behavior, and Journal of Nonverbal Behavior.
Anderson, C. A. (2002). Aggression. In E. Borgatta (Ed.), The Encyclopedia of Sociology. New York: MacMillan.
Anderson, C. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: A meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychological Science, 12, 353-359.
Anderson, C. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2002). Human aggression. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 27-51.
Anderson, C. A., & Carnagey, N. L. (2009). Causal effects of violent sports video games on aggression: Is it competitiveness or violent content? Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 45, 731-739.
Anderson, C. A., & Murphy, C. R. (2003). Violent video games and aggressive behavior in young women. Aggressive Behavior, 29, 423-429.
Anderson, C. A., Shibuya, A., Ihori, N., Swing, E. L., Bushman, B. J., Sakamoto, A., Rothstein, H. R., & Saleem, M. (2010). Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in Eastern and Western countries: A meta- analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 136, 151-173.
Bandura, A. (1973). Aggression: A social learning analysis. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall.
Banse, R., Clarbour, J., & Fischer, I. (2005). Implicit and explicit aggressiveness, social desirability, and the prediction of aggressive behaviour. Unpublished research.
Banse, R., & Fischer, I. (2002, July). Implicit and explicit aggressiveness and the prediction of aggressive behavior. Poster presented at the 11th European Conference on Personality, European Society for Personality Psychology, Jena, Germany.
Bartholow, B. D., & Anderson, C. A. (2002). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior: Potential sex differences. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 38, 283-290.
Bensley, L., & Van Eenwyk, J. (2001). Video games and real-life aggression: Review of the literature. Journal of Adolescent Health, 29, 244-257.
Björkqvist, K., Österman, K., & Lagerspetz, K. M. J. (1994). Sex differences in covert aggression among adults. Aggressive Behavior, 20, 27-33.
Bluemke, M., Friedrich, M., & Zumbach, J. (2010). The influence of violent and nonviolent computer games on implicit measures of aggressiveness. Aggressive Behavior, 36, 1-13.
Bluemke, M., & Friese, M. (2006). Do features of stimuli influence IAT effects? Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 42, 163-176.
Bluemke, M., & Friese, M. (2008). Reliability and validity of the Single-Target IAT (ST-IAT): Assessing automatic affect towards multiple attitude objects. European Journal of Social Psychology, 38, 977-997.
Bluemke, M., & Zumbach, J. (2007). Implicit and explicit measures for analyzing the aggression of computer gamers. InSteffgen & M. Gollwitzer (Eds.), Emotions and aggressive behavior (pp. 38-57). Göttingen: Hogrefe & Huber Publishers.
Bösche, W. (2010). Violent video games prime both aggressive and positive cognitions. Journal of Media Psychology: Theories, Methods, and Applications, 22, 139-146.
Bosnjak, M. & Tuten, T. L. (2001). Classifying response behaviors in web-based surveys. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 6(3).
Bushman, B. J., & Anderson, C. A. (2002). Violent video games and hostile expectations: A test of the general aggression model. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 28, 1679-1686.
Bushman, B. J., Baumeister, R. F., Stack, A. D. (1999). Catharsis, aggression, and persuasive influence: Self-fulfilling or self-defeating prophecies? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76, 367-376.
Bushman, B. J., Rothstein, H. R., & Anderson, C. A. (2010). Much ado about something: Violent video game effects and a school of red herring: Reply to Ferguson and Kilburn (2010). Psychological Bulletin, 136, 182-187.
Buss, A. H., & Perry, M. (1992). The aggression questionnaire. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63, 452-459.
Carnagey, N. L., & Anderson, C. A. (2004). Violent video game exposure and aggression: A literature review. Minerva Psychiatrica, 45, 1-18.
Ceranoglu, T. A. (2010). Video games in psychotherapy. Review of General Psychology, 14, 141-146.
Christopherson, K. M. (2007). The positive and negative implications of anonymity in Internet social interactions: 'On the Internet, Nobody Knows You're a Dog.' Computers in Human Behavior, 23, 3038-3056.
Cohen, J. (1973). Eta-squared and partical eta-squared in fixed factor ANOVA designs. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 33, 107-112.
Colwell, J., & Kato, M. (2003). An investigation of the relationship between social isolation, aggression, and computer game play in Japanese adolescents. Asian Journal of Social Psychology, 6, 149-158.
Durkin, K., & Barber, D. E. (2002). Not so doomed: Computer game play and positive adolescent development. Applied Developmental Psychology, 23, 373-392.
Durkin, K. (2010). Video games and young people with developmental disorders. Review of General Psychology, 14, 122- 140.
Eichstaedt, J. (2001). An inaccurate-timing filter for reaction-time measurement by JAVA-applets implementing internet- based experiments. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, and Computers, 33, 179-186.
Fazio, R. H. (2001). On the automatic activation of associated evaluations: An overview. Cognition and Emotion, 15, 115- 141.
Fazio, R. H., & Olson, M. A. (2003). Implicit measures in social cognition: Their meaning and use. Annual Review of Psychology, 54, 297-327.
Ferguson, C. J. (2010). Blazing angels or resident evil? Can violent video games be a force for good? Review of General Psychology, 14, 68-81.
Ferguson, C. J. (2007a). Evidence for publication bias in video game violence effects literature: A meta-analytic review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 12, 470-482.
Ferguson, C. J. (2007b). The good, the bad and the ugly: A meta-analytic review of positive and negative effects of violent video games. Psychiatric Quarterly, 78, 309-316.
Ferguson, C. J., Cruz, A. M., Martinez, D., Rueda, S. M., Ferguson, D. E., & Negy, C. (2008). Personality, parental, and media influences on aggressive personality and violent crime in young adults. Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment and Trauma, 17, 395-414.
Ferguson, C. J., & Rueda, S. M. (2010). The Hitman study: Violent video game exposure effects on aggressive behavior, hostile feelings, and depression. European Psychologist, 15, 99-108.
Ferguson, C .J., Rueda, S., Cruz, A., Ferguson, D., Fritz, S., & Smith, S. (2008). Violent video games and aggression: Causal relationship or byproduct of family violence and intrinsic violence motivation? Criminal Justice and Behavior, 35, 311-332.
Ferguson, C. J., & Kilburn, J. (2009). The Public health risks of media violence: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Pediatrics 154, 759-763.
Ferguson, C. J., & Kilburn, J. (2010). Much ado about nothing: The misestimation and overinterpretation of violent video game effects in Eastern and Western nations: Comment on Anderson et al. (2010). Psychological Bulletin, 136, 174-178.
Ferguson, C. J., San Miguel, C., & Hartley, R. D. (2009). A multivariate analysis of youth violence and aggression: The influence of family, peers, depression and media violence. Journal of Pediatrics, 155, 904-908.
Feshbach, S. (1961). The stimulating versus cathartic effect of vicarious aggressive activity. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63, 381-385.
Fiedler, K., & Bluemke, M. (2005). Faking the IAT: Aided and unaided response control on the Implicit Association Test. Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 27, 307-316.
Fiedler, K., Messner, C., & Bluemke, M. (2006). Unresolved problems with the "I", the "A" and the "T": Logical and psychometric critique of the Implicit Association Test (IAT). European Review of Social Psychology, 17, 74-147.
Frindte, W., & Obwexer, I. (2003). Ego-Shooter – Gewalthaltige Computerspiele und aggressive Neigungen. Zeitschrift fur Medienpsychologie, 15, 140-148.
Furr, F. M. (2004). Interpreting effect sizes in contrast analysis. Understanding Statistics, 3, 1-25.
Gentile, D. A., & Anderson, C. A. (2003). Violent video games: The newest media violence hazard. In D. Gentile (Ed.), Media Violence and Children (pp. 131-152). Westport, CT: Praeger.
Gawronski, B., & Bodenhausen, G. V. (2006). Associative and propositional processes in evaluation: An integrative review of implicit and explicit attitude change. Psychological Bulletin, 132, 692-731.
Green, C. S., & Bavelier, D. (2006). Effects of video game playing on the spatial distribution of visual selective attention. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 32, 465-478.
Goldberg, L. R. (2001). International Personality Item Pool. A scientific collaboratory for the development of advanced measures of personality traits and other individual differences [WWW document]. Retrieved from: http://ipip.ori.org
Greenwald, A. G., & Farnham, S. D. (2000). Using the implicit association test to measure self-esteem and self-concept. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 1022-1038.
Greenwald, A. G., McGhee, D. E., & Schwartz, J. K. L. (1998). Measuring individual differences in implicit cognition: The Implicit Association Test. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74, 1464-1480.
Greenwald, A. G., Nosek, B. A., & Banaji, M. R. (2003). Understanding and using the Implicit Association Test: I. An improved scoring algorithm. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85, 197-216.
Greenwald, A. G., Poehlman, T. A., Uhlmann, E. L., & Banaji, M. R. (2009). Understanding and using the Implicit Association Test: III. Meta-analysis of predictive validity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 97, 17-41.
Griffiths, M. (1999). Violent video games and aggression: A review of the literature. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 4, 203-212.
Hartig, J., Jude, N., & Rauch, W. (2003). Entwicklung und Erprobung eines deutschen Big-Five-Fragebogens auf Basis des International Personality Item Pools (IPIP40). (Arbeiten aus dem Institut fur Psychologie der Johann Wolfgang Goethe- Universitat, Heft 1, 2003). Frankfurt: Institut fur Psychologie an der Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universitat.
Henrich, J., Heine, S. J., & Norenzayan, A. (2010). The weirdest people in the world? Brain and Behavioral Sciences, 33, 61-135.
Hofmann, W., Friese, M., & Strack, F. (2009). Impulse and self-control from a dual-systems perspective. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 4, 162-176.
Im, E.-O., & Chee, W. (2006). An online forum as a qualitative research method: practical issues. Nursing Research, 55, 267-273.
Jackson, L. A., Witt, E. A., Games, A. I., Fitzgerald, H. E., van Eye, A., & Zhao, Y. (2011). Information technology use and creativity: Findings from the Children and Technology Project. Computers in Human Behavior, 28, 370-376. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2011.10.006
Jin, S.-A. A. (2011). “I feel present. Therefore, I experience flow:” A structural equation modeling approach to flow and presence in video games. Journal of Broadcasting and Electronic Media, 55, 114-136.
Karpinski, A. (2004). Measuring self-esteem using the Implicit Association Test: The role of the other. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 30, 22-34.
Kato, P. M. (2010). Video games in health care: Closing the gap. Review of General Psychology,14, 113-121.
Keller, F., Gunasekharan, S., & Mayo, N. (2009). Timing accuracy of web experiments: A case study using the WebExp software package. Behavior Research Methods, 41, 1-12.
Kestenbaum, G. I., & Weinstein, L. (1985). Personality, psychopathology and developmental issues in male adolescent video game use. Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry, 24, 329-337.
Krahé, B., & Möller, I. (2004). Playing violent electronic games, hostile attribution bias, and aggression-related norms in German adolescents. Journal of Adolescence, 27, 53-69.
Krantz, J. H., & Dalal, R. S. (2000). Validity of Web-based psychological research. In M. H. Birnbaum (Ed.), Psychological experiments on the Internet (pp. 35-60). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
LeBel, E. P., & Paunonen, S. V. (2011). Sexy but often unreliable: Impact of unreliability on the replicability of experimental findings involving implicit measures. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 37, 570-583.
Lee, K. M., & Peng, W. (2006). What do we know about social and psychological effects of computer games? In P. Vorderer, & J. Bryant (Eds.) Playing video games: Motives, responses, and consequences (pp. 325-345). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Lemmens, J. S. & Bushman, B. J. (2006). The appeal of violent video games to lower educated aggressive adolescent boys from two countries. CyberPsychology and Behavior, 9, 638-641.
Levine, T. R., & Hullett, C. R. (2002). Eta squared, partial eta squared, and misreporting of effect size in communication research. Human Communication Research, 28, 612-625.
Lindsay, L. L., & Anderson, C. A. (2000). From antecedent conditions to violent actions: A general affective aggression model. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 26, 533-547.
Nosek, B. A. (2007). Implicit-explicit relations. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16, 65-69.
Nosek, B. A., & Smyth, F. L. (2007). A multitrait-multimethod validation of the Implicit Association Test: Implicit and explicit attitudes are related but distinct constructs. Experimental Psychology, 54, 14-29.
Olson, C. K., Kutner, L. A., Warner, D. E., Almerigi, J. B., Baer, L., Nicholi, A. M. II, & Beresin, E. V. (2007). Factors correlated with violent video game use by adolescent boys and girls. Journal of Adolescent Health, 41, 77-83.
Reips, U.-D. (2000). The Web Experiment Method: Advantages, disadvantages, and solutions. In M. H. Birnbaum (Ed.), Psychological experiments on the Internet (pp. 89-118). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Reips, U.-D. (2002). Internet-based psychological experimenting: Five dos and five don’ts. Social Science Computer Review, 20, 241-249.
Reips, U.-D. (2007). The methodology of Internet-based experiments. In A. Joinson, K. McKenna, T. Postmes, & U.-D. Reips (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Internet Psychology (pp. 373-390). Oxford University Press.
Rosnow, R. L., & Rosenthal, R. (2002). Contrasts and correlations in theory assessment. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 27, 59-66.
Rothermund, K., & Wentura, D. (2004). Underlying processes in the Implicit Association Test: Dissociating salience from associations. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 133, 139-165.
Schmidt, W. C. (2000). The server-side of psychology Web experiments. In M. H. Birnbaum (Ed.), Psychological experiments on the Internet (pp. 285-310). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Sherry, J. (2007). Violent video games and aggression: Why can’t we find links? In R. Preiss, B. Gayle, N. Burrell, M. Allen, & J. Bryant (Eds.), Mass Media effects research: Advances through meta-analysis (pp. 231-248). Mahwah, NJ: L. Erlbaum.
Sparks, G. G., Sparks, C. W., & Sparks, E. A. (2009). Media Violence. In J. Bryant & M. B. Oliver (Eds.), Media Effects: Advances in Theory and Research (3rd ed., pp. 269-286). New York: Routledge.
Strack, F., & Deutsch, R. (2004). Reflective and impulsive determinants of social behavior. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 8, 220-247.
Teubel, T., Banse, R., Asendorpf, J. B., & Schnabel, K. (2011). Implicit but not explicit aggressiveness predicts performance outcome in basketball players. International Journal of Sport Psychology, 42, 390-400.
Uhlmann, E., & Swanson, J. (2004). Exposure to violent video games increases automatic aggressiveness. Journal of Adolescence, 27, 41-52.
Unsworth, G., Devilly, G., & Ward, T. (2007). The effect of playing violent videogames on adolescents: Should parents be quaking in their boots? Psychology, Crime and Law, 13, 383-394.
von Collani, G., & Werner, R. (2005). Self-related and motivational constructs as determinants of aggression: An analysis and validation of a German version of the Buss-Perry aggression questionnaire. Personality and Individual Differences, 38, 1631-1643.
Wells, G. L., & Windschitl, P. D. (1999). Stimulus sampling and social psychological experimentation. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 25, 1115-1125.
Wiegman, O., & van Schie, E.G.M. (1998). Video game playing and its relations with aggressive and prosocial behavior. British Journal of Social Psychology, 37, 367-378.
Wigboldus, D. H. J., Holland, R. W., & van Knippenberg, A. (2004). Single target implicit associations. Unpublished manuscript.
Williams, D., & Skoric, M. (2005). Internet fantasy violence: A test of aggression in an online game. Communication Monographs, 72, 217-233.
Winkel, M., Novak, D. M., & Hopson, H. (1987). Personality factors, subject gender, and the effects of aggressive video games on aggression in adolescents. Journal of Research in Personality, 21, 211-223.
Ybarra, M., Diener-West, M., Markow, D., Leaf, P., Hamburger, M., & Boxer, P. (2008). Linkages between internet and other media violence with seriously violent behavior by youth. Pediatrics, 122, 929–937.
Introduction
This study describes how commonly available Internet technology can be used to assess aggressiveness of computer game players in ecologically-valid settings. Frequent exposure to violent content in media such as television, movies, and computer games is often held responsible for increases in aggressive cognition, affect, and behaviour (Carnagey & Anderson, 2004). This position, though well-established in empirical research, is also still highly debated. Internet studies might be able to disambiguate the empirical research by recruiting unsuspecting gamers, rather than self-selected lab participants (Henrich, Heine, & Norenzayan, 2010), and we will give a full technical account of how to achieve this. Furthermore, implicit measures might help assess aggressiveness objectively, and we will explain how these measures work. We demonstrate that implicit measures, based on response latencies in the range of just a few hundred milliseconds are suitable for Internet assessment of aggressiveness. We also show, via rigorous psychometric analyses, that there are discernible quality differences across different measures.
Psychological Theorizing on Computer Games and Methodological Caveats
From a psychological perspective, one has to differentiate between aggressiveness and aggression. Whereas aggression refers to the actually performed behaviour as observable acts, aggressiveness refers to the inner disposition that might predict aggressive behaviour, the potential for aggression. Several psychological theories seek to explain increased aggressiveness and aggressive behaviour as a consequence of media violence exposure, though others point out that family violence and innate aggression are more likely to cause trait aggression and real-life violence (e.g., Anderson, 2002; Ferguson, Cruz, Martinez, Rueda, Ferguson, & Negy, 2008; Ferguson, Rueda, Cruz, Ferguson, Fritz, & Smith, 2008). Theories that emphasize the role of human cognition in behaviour generation explain increases in aggressiveness and aggression by human information processing (e.g., priming weapons activates aggressive cognitive structures). One model that suggests a causal link between media violence exposure and both short-term and long-term changes in aggressive dispositions is the General Aggression Model (GAM; Bushman & Anderson, 2002; Lindsay & Anderson, 2000). The GAM combines several theories to provide a common theoretical framework. Based on the acquisition, activation, and application of aggressive knowledge structures as represented by cognitive schemata or scripts, the model predicts negative effects following from exposure to violent media. The acquisition of aggressive behavioural scripts starts with the observation of violence, which enables the learning experience of an observer. Once the behavioural script is stored in memory, it awaits activation upon social stimulation (Bandura, 1973). According to this view, violent computer games allow learning experiences and encourage the virtual execution of aggressive behaviour. Not only do games involve the person (and through identification their self-concept) more actively than does passive observation, but it is often the main objective of violent computer games to harm or kill others. This behaviour is repeated frequently among regular players, and it is often reinforced by games (by supportive sounds, appreciative comments, bonus points etc.). We will take the GAM as a starting point to developing our hypotheses. Its prominence is partly based on the fact that not a single psychological theory on aggression predicts positive psychological effects following from exposure to media
violence, except for the catharsis-hypothesis, which to date lacks sufficient empirical justification (e.g., Feshbach, 1961; Bushman, Baumeister, & Stack, 1999). This is not to deny that video games also lead to positive outcomes in other domains; indeed, positive effects of video game play are generally overlooked, such as higher visuospatial cognition (Ferguson, 2007b; Green & Bavelier, 2006), greater creativity (Jackson et al., 2011), and beneficial effects in health- related areas and use for treating psychological disorders (Ceranoglu, 2010; Durkin, 2010; Kato, 2010). Furthermore, there are alternate accounts to the GAM that deny a causal path from violence-exposure to aggressiveness, which posit other pathways. For instance, the Catalyst Model explains aggressive behaviour―and serious aggression and violence in particular―by genetic and proximal environmental influences such as family and peers (Ferguson, Rueda et al., 2008). According to this view, increased consumption of violent video games appears as a distal and negligible influence, or as a by-product, rather than as a causal factor in the ontogeny of aggressive dispositions. In support of this account, a prospective study across one year failed to find a link between media violence exposure and anti-social behaviour (Ferguson, 2011).
Despite k = 136 studies (based on more than 130,000 participants) showing negative side-effects of violent computer games, the issue remains debated within the field (e.g., Anderson et al., 2010; Ferguson & Kilburn, 2010; Bushman, Rothstein, & Anderson, 2010). Aggregating across these studies, several meta-analyses have revealed substantial increases in aggressive behaviour, aggressive cognitions, and physiological arousal; they also pointed to a decrease in prosocial behaviour (Anderson, 2004; Anderson et al., 2010; though see Ferguson & Kilburn, 2009). Other meta-analyses have arrived at smaller effects or concluded to the contrary, often pointing out weaknesses and methodological flaws in existing research (Ferguson, 2007a; Ferguson & Kilburn, 2009, 2010; Sherry, 2007). Researchers who are sceptical of the causal role of violence-exposure in aggressiveness stress publication bias and evidence for null- and reverse findings regarding the presumed relationship (e.g., Bösche, 2010; Colwell & Kato, 2003; Durkin & Barber, 2002; Ferguson & Rueda, 2010; Ferguson, San Miguel, & Hartley, 2009; Unsworth, Devilly, & Ward, 2007; Williams & Skoric, 2005). Indeed, some would argue that studies showing negative effects―upon closer inspection―may actually appear to show the opposite from what has been concluded (Anderson & Dill, 2000; Ybarra, Diener-West, Markow, Leaf, Hamburger, & Boxer, 2008). Within this multitude of voices, scientific warnings (Frindte & Obwexer, 2003; Gentile & Anderson, 2003) and considerable concern by the broader public have emerged after violent first-person shooters became popular. There is however a notable gap between research evidence and the more melodramatic outcry of teachers and parents on the one hand, and the trenchant denial of increased aggressiveness among typical consumers of violent game content on the other. While it is possible that consumers might simply be dishonest about the effects of violent games on aggression, it is also possible that the extant empirical research suffers significant methodological limitations.
Rather than focusing on methodological questions surrounding the quality of meta-analyses, we address three potential shortcomings of aggression research that might limit the external validity of primary research underlying meta-analyses. First, to the degree that researchers employ self-report measures, they presuppose that participants provide true and informative responses to questions on behaviour, attitudes, and self-concept. While some argue that self-reports in research supporting the exposure-aggression link should not be trusted, the same argument might be made against research that denies such a link. Second, the characteristics of typical samples might preclude generalizing the empirical findings to real-world gamers. Third, on a related note, how treatments (i.e., games) are determined and how participants are recruited (e.g., advertising strategies, students) may be prone to certain kind of biases. All three problems are likely to interact with each other in unpredictable ways; both over- and underestimation of gaming-effects might occur.
Self-report measures still form the most common class of measures of aggressiveness, though hidden observation and objective tasks have occasionally been used to assess aggressive behaviour (e.g., noise-blast tasks; Bartholow & Anderson, 2002). (1) Self-reports may be limited to what respondents believe to be true about themselves; (2) they merely include aspects that can be introspectively identified; and (3) given their blatant nature, they might be affected by social desirability (e.g., under-reporting of socially undesirable aggressiveness) and self-presentation (e.g., malicious intentional exaggeration). Reporting tendencies can bias any outcomes and conclusions on gamers who might feel under attack when answering questions on socially sanctioned behaviour. Not surprisingly, aggression research has been criticized for often using non-standardized and ad-hoc measures (Lee & Peng, 2006; Ferguson, 2007a). Studies on game effects should incorporate objective measures of aggressive dispositions, not only aggressive behaviour. We will propose such measures that do not depend on participants’ explicit beliefs, but assess impulsive aspects that cannot be introspectively identified easily and whose measurement is not strongly affected by social desirability and self- presentational concerns.
With regard to sample characteristics, few studies actually focus on the effects of violent game exposure on regular computer game players; they focus on testing psychological theories instead, often relying on ad-hoc convenience samples. In consequence, the effect sizes observed in lab studies on theory-testing cannot easily be generalized to real- world effects of average and heavy gamers. Effect sizes represent the strength of a treatment as a function of the variability of aggressiveness in the recruited samples. Therefore, to the extent that lab treatments do not reflect the potency or harmfulness of real-world treatments, effect sizes will not represent effects in the real world. Moreover, if participants are sampled that do not show aggressiveness variability and responses to games like real-world players do, then any obtained effect sizes do not correspond to the situation outside the lab. The following aspects are problematic for aggression research carried out in the lab then: (1) Increases in aggressiveness might only be observed in heavy consumers of violent media, once they have overcome their natural disgust reaction to violence (Sparks, Sparks, & Sparks, 2009); (2) typical lab participants might not be used to violent game content, and hence might be the most vulnerable at least in the short term, whereas long-term players may eventually habituate (Winkel, Novak, & Hopson, 1987; Ferguson & Rueda, 2010); (3) what appears to be increases in aggressiveness on average (a statistical main effect) may actually be due to a few vulnerable players with particular dispositions (a statistical interaction of type of viewer with violent content), but investigations on vulnerable players are hardly ever carried out (Bensley & van Eenwyk, 2001; Griffiths, 1999); and (4) long-term effects are less frequently studied than short-term effects among lab samples (Lee & Peng, 2006). In sum, many study samples may differ from typical gamers or potentially gamers most at risk. Experimental research might overly rely on participants who are less at risk to playing huge amounts of games, but when these participants are playing violent games, they might be even more prone to transitory negative consequences (Anderson & Murphy, 2003). We suggest increasing efforts to examine typical gamers.
With regard to selectivity effects, the typical recruitment procedure restricts the quality of the research and the type of research questions that can be asked. As such, (1) advertising a study on gamers gives away the research idea from the beginning and risks sampling-biases due to self-selection as much as it risks response-biases among participants who may want to protect themselves or the status of their peers (e.g., Williams & Skoric, 2005); (2) though developmental aspects might put particular individuals more at risk than others (Kestenbaum & Weinstein, 1985), a variety of age groups is difficult to recruit; (3) supposedly non-violent games (e.g., sports and racing games, simulations, adventures) have been catching up in realism as well as in graphic/gory elements (Anderson & Carnagey, 2009), yet a comparison of different types of gamers is still rare; often it is merely one particular violent game that is compared to one particular non-violent game as a control condition (‘N=1’–problem; Wells & Windshitl, 1999), leaving the possibility of confounding variables such as physiological arousal (cf. Bluemke, Friedrich, & Zumbach, 2010; Frindte & Obwexer, 2003); and (4) positive factors that may counteract any negative consequences of violent games (such as social networks, self- confidence, peaceful games, and relaxation/flow) are hardly represented in typical research (Durkin & Barber, 2002; Bluemke et al., 2010; Jin, 2011). We suggest that selectivity issues be addressed and more attention be paid to various game types and typical players in the natural environment.
To approach any consequences of computer games not with regard to theory, but with regard to real-world effects, one needs to access a sample of players that (a) shows signs of heavy use or a variety of game play, (b) includes a meaningful number of high-risk players so that they might be singled-out or their psychological characteristics be identified, and (c) incorporates users’ natural environment (including protective factors). Participants should be unsuspecting and blind to the study topic, so that self-selection can be ruled out. Finally, objective measures of aggressiveness that cannot be easily distorted need to be applied. While it should be clear by now that Internet sampling is a viable option to invite players who might be most at risk, it is yet to be shown that aggressiveness can be measured objectively in online research.
Reaction-Time Based Measurement of Aggressive Dispositions
A recent twist in psychological theorizing, which can partly explain the discrepancy between users’ and researchers’ evaluations of video games, is the suggestion that the crucial dispositions responsible for changes in aggressiveness might not be cognitively accessible at all. Dual-process/dual-system theories entail that human behaviour is often governed by impulses that cannot be predicted on the basis of questionnaires (Strack & Deutsch, 2004). Spontaneous categorization processes enable us to arrive at quick decisions with a reasonable degree of accuracy upon encountering objects in our world (e.g., people, things, words). Automatic associations are triggered upon perceiving objects, supplying category-based information which is accompanied by automatic evaluations (Fazio, 2001). Reflecting on explicit measures (questionnaires) not only invokes a different mode of operation of the mind, but the crucial components governing behaviour within fractions of a second may actually remain inaccessible―despite our best attempts at answering adequately. Rather than relying on introspection, relevant measures have to tap into spontaneous cognitive and affective processes in the range of a few hundred milliseconds. Relatively unobtrusive measures, or implicit measures, such as the Implicit Association Test (IAT; Greenwald, McGhee, & Schwartz, 1998) and its derivate, the Single- Target IAT (ST-IAT; Wigboldus, Holland, & van Knippenberg, 2004), provide an alternative way of measurement based on objective reaction times in computer-based sorting-tasks (a detailed description of the methodology follows below). They tap into associative cognitive structures and automatic evaluations, they overcome participants’ introspective limits and response styles, and they qualify for the prediction of impulsive behaviour (Fazio & Olson, 2003). Implicit measures provide a complementary look into the associative basis of attitudes, beliefs, and personality traits. Implicit and explicit measures are only weakly correlated, speaking to distinct concepts, yet both are useful predictors of behaviour (Nosek, 2007; Greenwald, Poehlman, Uhlmann, & Banaji, 2009). Implicit measures have added value in domains of impulsive behaviour and low self-control (Hofmann, Friese, & Strack, 2009).
An IAT can assess whether aggression is more positively or negatively connoted; alternatively, the closeness of one’s self-concept to aggression might be observed. For instance, previous research has shown that an aggressive self- concept IAT can predict penalty time-outs of rough ice hockey players (“poor” outcomes of aggression), though explicit measures were not predictive (Banse and Fischer, 2002; Banse, Clarbour, & Fischer, 2005). This finding has recently been corroborated by Teubel, Banse, Asendorpf, and Schnabel (2011) who showed that basketball scoring performance (“good” outcomes) can likewise be predicted by aggressiveness-IATs over and beyond explicit measures. With regard to exposure to violence in computer games, the IAT was mostly related to participants’ long-term play of violent computer games outside of the lab and―in contrast to explicit questionnaires―it detected the effect of playing a violent computer game after a mere 10 minutes (Uhlmann & Swanson, 2004). These findings have been replicated under stricter control of potentially confounding variables (Bluemke et al., 2010), but they leave open the question whether attitudinal IATs and aggressive self-concept ST-IATs measure something meaningful when applied to “heavy users” of computer games over the Internet.
We suggest that aggression research would profit if online studies were used to recruit heavy gamers that are otherwise difficult to access, and if study designs would incorporate implicit measures. Though attitudinal IATs are common, they have rarely―if ever―been applied to measure the spontaneous evaluation of aggression, and to our knowledge self- concept ST-IATs have rarely―if ever―been applied to measure the automatic aggressive self-concept. Both measures are psychometrically untested, calling for an in-depth inspection of their reliability and convergent validity. While previous work focused on theoretical aspects what the affective underpinnings of explicit and implicit measures are and how both relate to aggressiveness (Bluemke & Zumbach, 2007), this article delves into the methodological and technical details how externally valid groups of gamers can be recruited to compare subjectively measured explicit aggressiveness with objectively measured implicit aggressiveness. Using an aggressive attitude IAT and an aggressive self-concept ST-IAT, this study (a) demonstrates that the Internet can be used to implicitly measure aggressiveness, (b) describes in technical detail how to arrive at a comparison of types of gamers in online studies, and (c) provides evidence from correlation analyses and structural equation models on the implicit–explicit relationships.
Experiment
The World Wide Web (WWW) provides an excellent tool to access skilled computer users and active gamers in particular (note that several games can be played online). We were interested in recruiting heavily engaged participants who use forums to discuss computer game play (e.g., cheats and solutions). Overcoming the limitations of university samples (e.g., lack of variability in regional background, age group, study majors), the WWW provides access to a diversity of gamers who play a broad range of games (cf. Reips, 2000, 2002). Insofar social desirability considerations biases outcomes of lab studies, perceived higher anonymity on the Internet should minimize this (Christopherson, 2007). Additionally, both IAT and ST-IAT make use of objective reaction times, making systematic distortions less likely (but see Fiedler, Messner, & Bluemke, 2006, for a discussion of this “implicitness assumption”, and Fiedler & Bluemke, 2005, for a test of fakeability).
Hypotheses
Suppose three groups were of major interest: (a) gamers who are regularly exposed to unavoidable, outstanding violent content in arousing first- and third person shooters (SHOOT); (b) users of computer games that have main objectives other than killing but sometimes involve violent elements and arousal (PLAY; e.g., simulations, adventure games, racing games); and (c) other experienced computer users who do not play computer games at all (CONTROL; e.g., internet and office users). Following from the General Aggression Model (GAM) and recent findings (Anderson et al., 2010), aggressiveness should be highest among players that are most frequently primed with violent content: SHOOT > PLAY > CONTROL. More specifically,
Hypothesis 1: Following Wiegman and van Schie (1998), explicitly measured Agreeableness should differ significantly among players and non-players. Agreeableness is a psychological construct that relates to aggression and prosocial behaviour. Due to the long-term influence of violent games, regular players of violent shooters (SHOOT) should have lower agreeableness scores than non-playing control participants (CONTROL), Hypothesis 1a: SHOOT < CONTROL. The same holds true to a lesser degree to players of other computer games that are exposed to less, but occasional violent elements (PLAY), Hypothesis 1b: PLAY < CONTROL. With regard to other broad personality characteristics, participant groups should rather be comparable, Hypothesis 1c: SHOOT = PLAY = CONTROL.
Hypothesis 2: With regard to aggressiveness, players of violent shooters should have higher explicit aggressiveness than non-playing computer users, if not the highest aggressiveness in the sample (Anderson et al., 2010), Hypothesis 2a: SHOOT > CONTROL. Players of other computer games that have less violence exposure should have higher aggressiveness than other non-playing computer users, Hypothesis 2b: PLAY > CONTROL. At the same time, players of violent shooters should be more at risk than players of non-violent games to develop aggressive dispositions, Hypothesis 2c: SHOOT > PLAY.
Hypothesis 3: Playing violent computer games should have a similar impact on implicit measures (Uhlmann & Swanson, 2004; Bluemke et al., 2010), but because of the direction of the measures, for both the spontaneous evaluation of aggression (IAT) as well as the automatic aggressive self-concept (ST-IAT), the hypothesis is reversed. Less negative associations and a less peaceful self-concept should result among players of violent computer, Hypothesis 3a: SHOOT < CONTROL. Likewise, players of less violent computer games should have lower scores on implicit measures, Hypothesis 3b: PLAY < CONTROL; finally, following GAM, Hypothesis 3c: SHOOT < PLAY.
Hypothesis 4: To the extent that implicit and explicit measures are rooted in the same cognitive basis of aggressiveness, they should be correlated (Nosek, 2007; Nosek & Smyth, 2007). According to previous research, implicit and explicit measures are only weakly correlated, but if implicit–explicit correlations were non-negligible, this would speak to the validity of an implicit measure in terms of a partially shared cognitive basis underlying the implicit and explicit measures. In the absence of relevant literature, we did not hypothesize on the relationship between the two implicit measures on automatic self-concept and automatic attitude.
Method
Participants, Recruitment Strategy, and Attrition
Recruiting depended on the availability of German-speaking participants; unlike being in a laboratory setting, no experimenter was present to answer questions or settle problems of comprehension. In all likelihood, our total sample was predominantly Caucasian with 95% reporting to be native speakers of Germans. Some participants might have had a non-German background (e.g., Austrian, Swiss), though their proportions would be negligible in the light of the recruiting strategy (i.e., predominantly German websites with “.de”-suffixes) and not differ across the compared groups. For a diversified sample of players and non-players we invited active members of Internet forums, mailing lists, and newsgroups available in German language (cf. Table 1). Newsgroups and discussion boards that appeared inactive were not considered. Starting with the most important game genres, some of which are better known than others, publicly available game descriptions and bestseller lists were inspected for prototypical games (e.g., Top 100 PC games, www.pcgames.de/Spiele/Top-100; Entertainment Software Rating Board, www.esrb.org). We checked whether a corresponding forum could be identified via Internet search engines. Whereas many newsgroups and mailing lists are accessible by anyone, recruitment via forums depended not only on the availability of a game-specific forum, but also on its member activity and experimenters’ access to it, alternatively on support by the forum moderators. If we could not advertise the study ourselves, selection of a board depended on whether the administrators could be contacted and convinced to promote the study.
With regard to violent and non-violent computer gamers, we focused on forums that discussed relevant target games. Of the available German newsgroups some had a (mostly non-violent) focus on broad game genres (strategy, adventure, simulation, miscellaneous). Given the popularity of violent games among relatively young players (Lemmens & Bushman, 2006; Olson et al., 2007), efforts were taken to recruit non-playing computer users from the student population. As a minimal common denominator for different types of computer users, we deemed general software issues and the most frequently used office software to be viable options. Consequently, forums with a broad computer-related focus were targeted, as long as games were not specifically in the spotlight. A social networking site that was popular among students at the time was the Unicum-platform. Invitations were also spread via the German newsgroup for general software issues (miscellaneous software), via the newsgroup for the office suite most frequently used in Germany (Microsoft), and via a platform bringing together hardware and software problems of different platforms and operating systems (PC-Hilfe). We did not consider more specific software due to the negligible user proportions we anticipated in the adolescent and young adult population. We further sampled among young people via lists that were available to us and required computer access, without having specific references to computers or game use (Unicum’s main forum, Psychological Institute). None of these study entry points is qualitatively sufficient to identify type of computer users and type of computer games. Further filtering was required to sort participants into quasi-experimental groups (see Independent Variable section below).
Table 1. Internet newsgroups, forums, and mailing-lists used for recruitment of participants.
|
Forum / Newsgroup |
Address |
Focused Type of User |
Target Group |
|
Counterstrike |
counterstrike.4pforen.4players.de |
Shooter |
SHOOT |
|
Quake |
www.quake.de/index.php?q=d3 |
Shooter |
SHOOT |
|
Medal of Honour |
www.medalofhonour.de |
Shooter |
SHOOT |
|
Strategy Newsgroup |
de.rec.spiele.computer.strategie |
Strategy games |
PLAY |
|
World of Warcraft |
wow-europe.com/de |
Online-Gaming |
PLAY |
|
Myst |
www.myst-community.de |
Adventure & Role Play |
PLAY |
|
Adventure Newsgroup |
de.rec.spiele.computer.adventure |
Adventure & Role Play |
PLAY |
|
Sims |
www.diesims.de/pages.view_frontpage.asp |
Simulation |
PLAY |
|
Settlers |
www.siedler.de/home.php |
Simulation |
PLAY |
|
Simulation Newsgroup |
de.rec.spiele.computer.simulation |
Simulation |
PLAY |
|
Fifa (Football) |
forumfifa.ea.com/viewforum.php?f=9 |
Sports |
PLAY |
|
Spielen.com |
spielen.com |
All game genres |
PLAY |
|
Oxybrain – Web/PC/Games |
www.oxybrain.de/forumdisplay.php?&f=48 |
All game genres |
PLAY |
|
[RPG]-Board |
www.rpgboard.org/subboard.php4?id=22 |
All game genres |
PLAY |
|
Computer Games Newsgroup |
de.rec.spiele.computer.misc |
All game genres |
PLAY |
|
Computer Support |
www.pchilfe.org/Linki0.html |
Hardware/Software |
CONTROL |
|
Unicum – Leisure & Fun – Computer |
www1.unicum.de/forum/upload/forumdisplay.php?f=16 |
Students/Computer |
CONTROL |
|
Unicum – Interpersonal – Main Forum |
www1.unicum.de/forum/upload/forumdisplay.php?f=6 |
Students/General |
CONTROL |
|
Members Psychological Institute |
<intern e-mail list> |
Students |
CONTROL |
|
Software Newsgroup |
de.comp.software.misc |
Software |
CONTROL |
|
Office-Software Newsgroup |
microsoft.public.de.german.office |
Office |
CONTROL |
We advertised an anonymous scientific study on the relationship between personality and computer use, which was not suspicious given the common denominator of most forums. We avoided highlighting “gaming” or “aggression” to reduce topic-related self-selection. We did not offer monetary incentives to reduce the likelihood of multiple participation, and to stimulate the curiosity of computer users instead, we offered “feedback about personality traits as measured by reaction times”. In accordance with ethical requirements, we automatically debriefed participants at the end of the study and automatically generated feedback on participants’ reaction times (e.g., how quickly they associated themselves with aggressive in comparison to peaceful in the ST-IAT). In the absence of representative norms for general and aggression specific personality scores, no feedback was provided on explicit measures. We stressed the experimental nature of implicit measures and provided email addresses for correspondence.
Within one month of sampling, potentially interested participants started the online-study, if only out of curiosity (N = 673). Characteristic for longer Internet studies, participants dropped out on later web pages. After socio-demographic variables (552), explicit personality variables (450), implicit measures (246), and explicit aggressiveness questions, there were 238 complete responders. The retention-rate was 35.4%, which is in line with what can be expected for a 20-minute study without monetary incentives (Bosnjak & Tuten, 2001; Im & Chee, 2006). In an unsupervised setting high motivation and sufficient attention should not be taken for granted, so we quality-filtered data sets when participants indicated multiple participation, low motivation, insufficient German language skills, or missing informed consent (207). Eleven participants were excluded due to extremely high error rates (more than 20% per critical block in IAT and ST-IAT; cf. Greenwald et al., 1998) indicating random responding. The remaining total sample size (N = 196) outnumbered each single adult sample in Anderson and Bushman’s (2001) seminal meta-analysis.
Independent Variable
For a comparison of the three focal groups some further filtering was required. To represent the focal groups adequately, control questions and filters will narrow the sample down. The following combined procedure leads to conservative assignment for the group comparisons and a smaller filtered sample (N = 109); the rest of the participants cannot be categorized unambiguously. For instance, participants may report not using computers regularly for gaming despite being members of a game forum, and members of non-violent boards may report playing shooters.
In a publicly accessible web study several screening steps can and should be taken to ensure that only appropriate participants are selected into focal groups: (1) The multiple site entry technique (Reips, 2000, 2007) requires the posting of specific hyperlinks (URLs) in the anticipated SHOOT-, PLAY-, and CONTROL-forums (cf. Table 1), so that the game focus of users who entered the study can be traced back. (2) As the posted link might have been reposted or emailed to other, non-targeted participants, the HTTP-referrer (i.e., the web page that linked to the web study) should be documented. For technical reasons it may not always be transferred (depending on the browser configuration, or when entered manually into the browser), so we additionally asked how a participant received the study invitation, thereby filtering for uncontrolled spreading to non-targeted participants. Most importantly, (3) further questions on the use of computers and game genres precluded that the presumed CONTROL participants were in fact players, and ensured that the presumed forum members were actually playing the respective target games. All participants used check-boxes to indicate the main categories of their computer use (some examples provided): office (e.g., Word, PowerPoint, ...), communication (email, newsgroups, chat), internet (web browsing, Google), passive multi-media use (listening to music, watching videos/movies), active multi-media use (music/video/movie editing), computer games, server administration, and other (cf. Table 2; less important categories omitted from the table). Furthermore, participants reported on the total hours of their daily computer use, which game categories they played, if any, and how many weekly hours they spent on any of the game categories (cf. Table 2). The minimum value that needed to be entered was one hour, so that participants who did not report at least this almost negligible amount of game play received a zero score. In our case the independent group factor of real-world players and non-players encompassed (cf. Table 2):
- Players of violent computer games (SHOOT): All participants who were recruited via sites pertaining to different violent computer games (i.e., shooters; cf. Table 1), and who indicated via check-boxes regular computer use for playing games (cf. Table 2), and who—as expected due to their recruitment path—played violent shooters for at least one hour (cf. Table 2; n = 37);
- Players of computer games containing less or no violence (PLAY): All participants who were recruited via sites related to other (less or non-violent) computer games (cf. Table 1), who indicated via check-boxes regular computer use for playing games (cf. Table 2), and who—as expected due to their recruitment path—played any game genre for at least one hour, apart from shooters (cf. Table 2; n = 49);
- Non-playing computer users (CONTROL): All participants who were recruited via student sites, forums on computer issues, or general email-lists (cf. Table 1), who indicated via check-boxes regular computer use either for office work, communication, or internet (cf. Table 2), but who did not so for the purpose of playing computer The filtering ensures a total game play of zero hours as a consequence of not reporting at least a single hour of game play for any game category (cf. Table 2; n = 23).
Table 2. Socio-demographics, computer and game use of total sample, filtered sample, and groups (summary statistics; SD in parentheses)
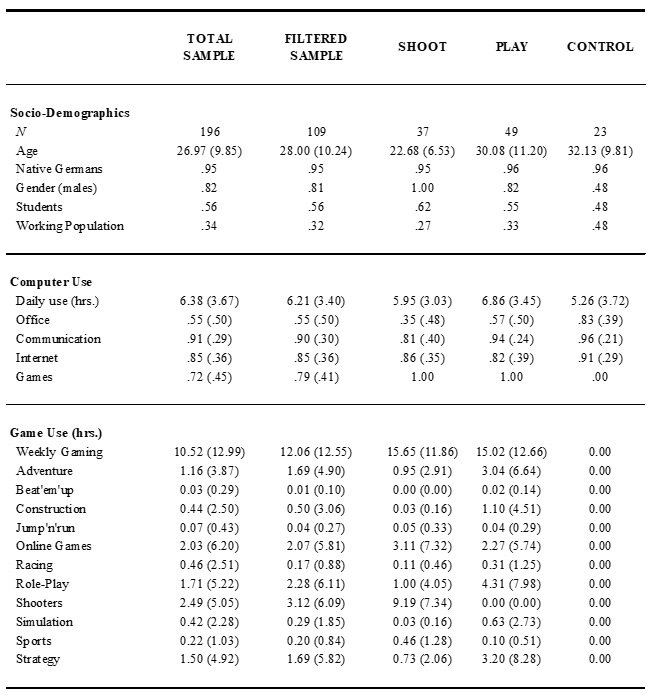
The filtered sample maintains the most important characteristics of the initial sample in terms of socio-demographics and computer use. Participants were notably older than many lab samples in psychological research. Only half of the sample reported to be students, whereas a third reported to be employed (employees, appointees, workers, freelancers); the rest were unemployed, homemakers, or other. Distinct from many convenience samples from psychology departments and our control group in particular, active players were mostly male, χ2 = 24.87, p < .001, reflecting the attraction of male players to games, and violent games specifically―a finding that replicates a known trend (Lemmens & Bushman, 2006; Olson et al., 2007). Another significant trend across the three groups emerged for the age distribution, F(2, 106) = 9.06, p < .001, reflecting once more that it was mostly young men who were attracted to shooters. Apart from these differences, all participants had sufficient computer experience and used computers regularly either for office work, communication, Internet, or games. The groups were defined by what they spent their time on, while the daily amount of computer use was similar across groups, F(2, 106) = 1.92, n.s.. Whereas CONTROL did not play computer games, SHOOT and PLAY reported playing more than 15 hrs. a week, while the gamers did not differ, t < 1, n.s.. PLAY participants did not play violent shooters, whereas shooters dominated among SHOOT participants, who spent two-thirds of their time on these games (> 9 hrs.). Of minor importance here, the popularity of other games differed slightly among the players. Given the computer experience we sought, the groups did not differ in average reaction times in the implicit measures, M = 987 ms, SD = 186, F(2, 106) = 1.00, n.s.. This is a crucial check, because―unlike passive reception of violent media―actively playing computer games might help participants to responding fast to various stimuli (e.g., Ferguson, 2007b), which in turn might differentially affect the meaning of the reaction-times of gamers and control participants.
Dependent Variables
Explicit Measures. One questionnaire assessed five fundamental personality traits: Extraversion, Neuroticism, Conscientiousness, Openness to Experiences, and Agreeableness. We used a 40-item questionnaire on these “Big Five”, based on the free International Personality Item Pool (IPIP40; Hartig, Jude & Rauch, 2003; Goldberg, 2001). Personality traits allow to characterise the sample and compare the groups with regard to traits that should not differ. A thorough assessment of explicit aggressiveness was done with Buss and Perry’s (1992) 29-item aggression questionnaire (BPAQ; von Collani & Werner, 2005), which serves as a quasi-standard in aggression research. It contains the subscales Physical Aggression, Verbal Aggression, Anger, and Hostility.
Implicit Measures. As reaction-time measures we used the Implicit Association Test (IAT; Greenwald et al., 1998) and its derivate, the Single-Target IAT (ST-IAT; Wigboldus et al., 2004). Both instruments are computer-based, speeded classification tasks that require double discrimination of stimuli. The IAT assessed the time required for categorising aggressive and peaceful target words (e.g., REVENGE, COMPROMISE) interspersed with positive and negative attribute stimuli (e.g., JOY, PAIN) in a double-discrimination task (details follow below). The ST-IAT measured the response times when categorizing self-related stimuli (e.g., ME, MINE) coupled with aggressive and peaceful stimuli. In other words, the IAT measured the spontaneous evaluation of aggressive and peaceful behaviour, whereas the ST-IAT assessed the automatic aggressive self-concept.
In experimental laboratories specialized software or hardware is available to achieve millisecond accuracy. To time the presentation of stimuli precisely and to record users’ reaction times accurately in an online study, implicit tasks had to be programmed in a way so that they could be run independently from network latency, computer architecture, and operating system (cf. Keller, Gunasekharan, & Mayo, 2009). We used a JAVA applet that could be run locally in users’ web browsers. Initial script checks ascertained that JAVA was enabled on a user’s machine. If not, participants were made aware of the technical limitations and encouraged to adjust system settings or change the browser.1 Though the absolute accuracy of the computer architecture and operating system in terms of stimulus presentation and reaction- time measurement may differ (e.g., for Linux, Mac OS, and Windows-based systems), the (ST-)IAT outcomes are based on the comparison of reaction times in two different tasks on the same system, so that participants’ scores (averaged across a series of trials) are not systematically biased by the computer architecture.2
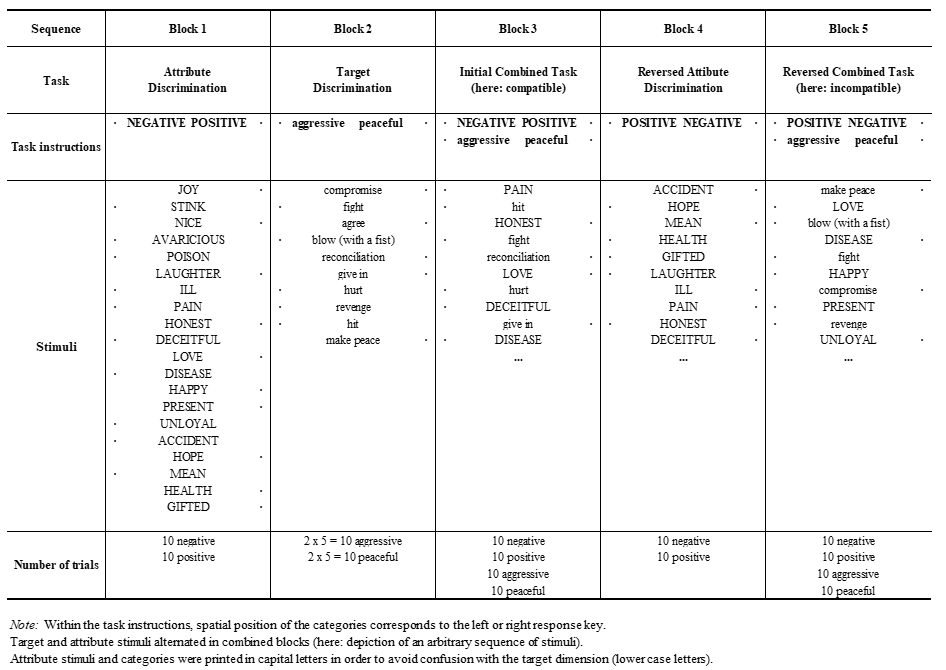
Aggressive Attitude IAT. Participants categorize a random sequence of stimuli presented sequentially in the middle of the screen on the basis of the category from which they are drawn. Category labels at the top of the screen are used as task instructions and inform participants about the left and right response key (S + L) for each category, for instance, positive and negative, or aggressive and peaceful. Initially, participants are familiarized with categorising positive and negative attribute words. Next, they are familiarized with aggressive and peaceful target words. In the subsequent critical block, participants categorise both target and attribute stimuli simultaneously, still using only two response keys. This allows for two possible category-to-response-key assignments: One critical block couples aggressive + negative on the same response key and peaceful + positive on the other response key, which is compatible with the negative attitude towards aggression of most people. Another critical block—presented after additional training trials for the reversed target categories—reverses the target category assignment, yielding aggressive + positive and peaceful + negative (which is attitudinally incompatible). The reaction time until a stimulus word is identified by a key-stroke is recorded. Practice blocks contained 20 trials and critical blocks contained 40 trials each. Table 3 illustrates procedure and stimuli (English translations of German stimuli that were taken from Bluemke and Friese, 2006, and Banse et al., 2005).
The difference between the critical blocks (IAT effect) served as the relevant outcome. Apart from the category arrangement, there are no differences between the critical blocks. Any resulting speed differences in classifying stimuli are attributed to the association between target and attribute categories. From shorter reaction times in the aggressive + positive block than in the aggressive + negative block one would infer a stronger associative link between the concept aggressiveness and positivity. The IAT effect is defined as the difference of the latency in the longer incompatible minus the latency in the shorter compatible block:
IAT effect = M(RTaggres s ive+pos itive & peaceful+negative) − M(RTpeaceful+pos itive & aggress ive+negative) [Eq.1]
Hence, the higher the IAT effect, the more negative the spontaneous evaluation of aggressive behaviour. Within the class of implicit measures (e.g., affective priming, go/no-go association task, extrinsic affective Simon task) the IAT is one of the most reliable measures (Cronbach’s Alpha = .60–.90; LeBel & Paunonen, 2011).
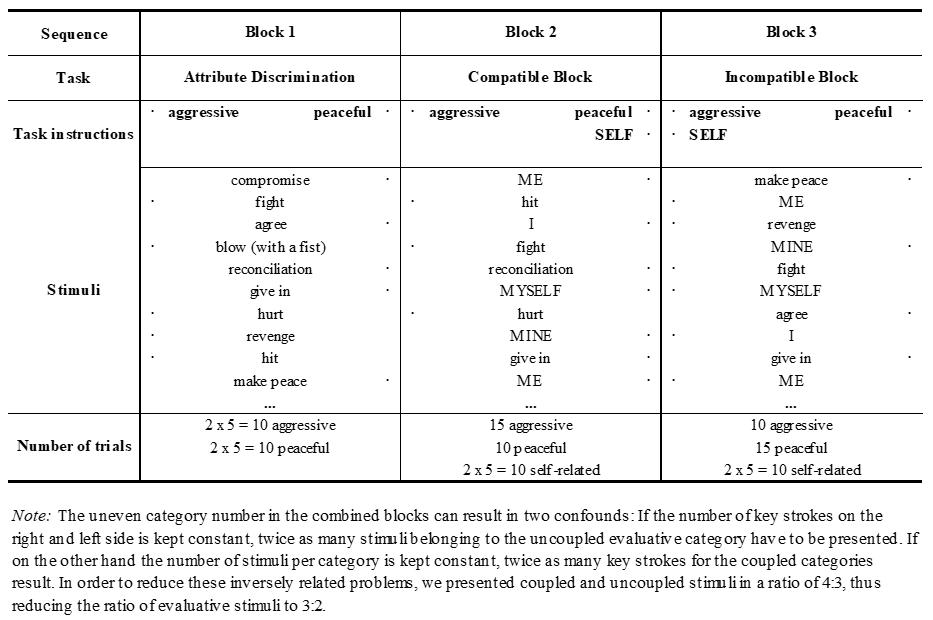
Aggressive Self-Concept ST-IAT The ST-IAT generally follows the IAT-logic, but the ST-IAT gives up one of the target categories and focuses on one target category exclusively, hence Single-Target IAT (Wigboldus et al., 2004; cf. Table 4). Moreover, by exchanging the evaluative categories with self-related concepts, and by using ME, I, MINE as stimuli representing the category self, automatic attitude measures can be turned into measures of automatic self-concept (Greenwald & Farnham, 2000). We were interested in how easily a person associates her self spontaneously with peaceful o r aggressive; thus we dropped the category other altogether, resulting in a self-concept Single-Target IAT. While Uhlmann and Swanson (2004) used the typical (comparative) IAT that involved the comparison of the category self to an unspecific other category, we preferred a non-comparative assessment of the self-concept. The typical IAT procedure is mainly adequate for those situations where natural dichotomies are compared (e.g., men and women), however the measurement outcome can strongly depend on the chosen counter-category (Karpinski, 2004).
Aggressive and peaceful ST-IAT stimuli were the same as in the IAT. The uneven number of ST-IAT categories in the critical blocks requires a compromise between keeping the balance of the number of right and left key strokes and the balance of the number of positive and negative stimuli. We drew 35 stimuli for each critical block in a relation of 10:10:15 from the categories so that each coupled category had 10 stimuli and the uncoupled category had 15 stimuli. Latency differences between the two critical blocks result in ST-IAT effects:
ST-IAT effect = M(RTself+aggres s ive) − M(RTself+peaceful) [Eq.2]
Table 3. Structure and Stimuli of Aggressive-Attitude IAT.
The higher the ST-IAT effect, the stronger the automatic link of the self-concept to peaceful behaviour. Although the ST- IAT is newer than the IAT, evidence shows that it reaches sufficiently good reliabilities (for further details cf. Bluemke & Friese, 2008).
Table 4. Structure and Stimuli of Aggressive Self-Concept IAT.
Procedure
Participants initially reported on socio-demographic variables and their specific computer use. To prevent carry-over effects from the more blatant aggressiveness measures, a fixed sequence of the following measures (IPIP40, ST-IAT, IAT, BPAQ) measures was applied, with measures being ordered according to increasing conspicuousness. We additionally counterbalanced the order of the critical blocks in both IAT and ST-IAT to control for order effects and speed gains within each procedure, which could otherwise affect the interpretation of latency differences (cf. Bluemke & Friese, 2008). Differing from Table 3, in the light of sufficient practice trials on aggressive and peaceful words in the preceding ST-IAT, we left out the second IAT block (aggressive/peaceful discrimination) to keep the web study as short as possible. Using a client-server technology, HTML/PHP web pages were delivered by an Apache web server (Schmidt, 2000). A JAVA applet provided the implicit measures and collected all reaction times within a user’s JAVA environment, before they were transferred back to the server and stored in a MySQL database. Data were analyzed by using statistical software (SPSS).
Data preparation
The scale means of the five IPIP40-scales, the four BPAQ scales, and the overall-BPAQ mean served as explicit measures (reversely scored items were recoded prior to aggregation). IAT and ST-IAT effects were computed as difference scores of mean reaction times in the two critical blocks. Prior to computation, the reaction times had to be prepared in the following manner in line with common practices and recommendations in the literature (Greenwald et al., 1998). Implausibly short and long latencies (due to reflexive responding or momentary inattention) were recoded to 300 and 3000 ms. If participants made a categorisation error, the response time was treated as missing data. Finally, participants’ (ST-)IAT effects were analysed as individualized effect sizes in units of individual standard deviations: A participant’s mean latency difference was divided by the individual’s standard deviation of latencies, yielding a so-called D-measure (cf. the improved scoring algorithm by Greenwald, Nosek, & Banaji, 2003). No error penalties were applied, because errors do not reflect the cognitive processes proper (violation of following task instructions) and because the reasons for the errors may differ between gamers and non-gamers. Note that the difference scores eliminate any influences due to speed differences between participants, but only individual standardization allows a meaningful comparison of the individual difference scores. For a better grasp, we report untransformed latencies in the text.
Results
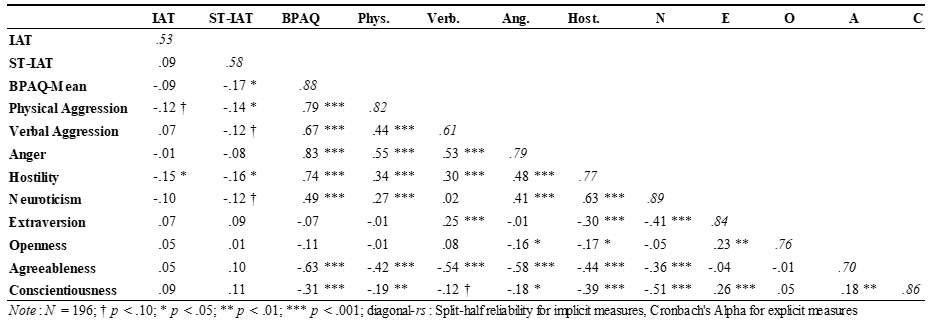
Reliabilities
Reliability of implicit measures is usually lower than that of explicit measures as reaction-times are highly volatile; often error variance can only be averaged out across a larger number of trials, which makes the sorting procedure quite repetitive. In Internet studies the researcher faces a trade-off: either to risk drop-out due to the length of the procedure or low reliability due to an insufficient number or trials. The reliability as estimated by internal consistency of item responses should reach values higher than .70. Reliabilities in the current sample were mostly satisfying for explicit measures (see reliabilities, Table 6). The split-half reliabilities of the implicit measures (odd- and even-numbered items; scale-length corrected by the Spearman-Brown prophecy formula) were rST-IAT = .53 and rIAT = .58―lower than what is typically found in lab studies. Some online participants may have “playfully” explored the unfamiliar test procedure (cf. participants excluded due to high error rates). As reliability poses a bound on validity correlations, future online studies may improve on reliability when employing 50–60 trials per block while keeping the overall procedure at reasonable length.
Personality traits (IPIP40)
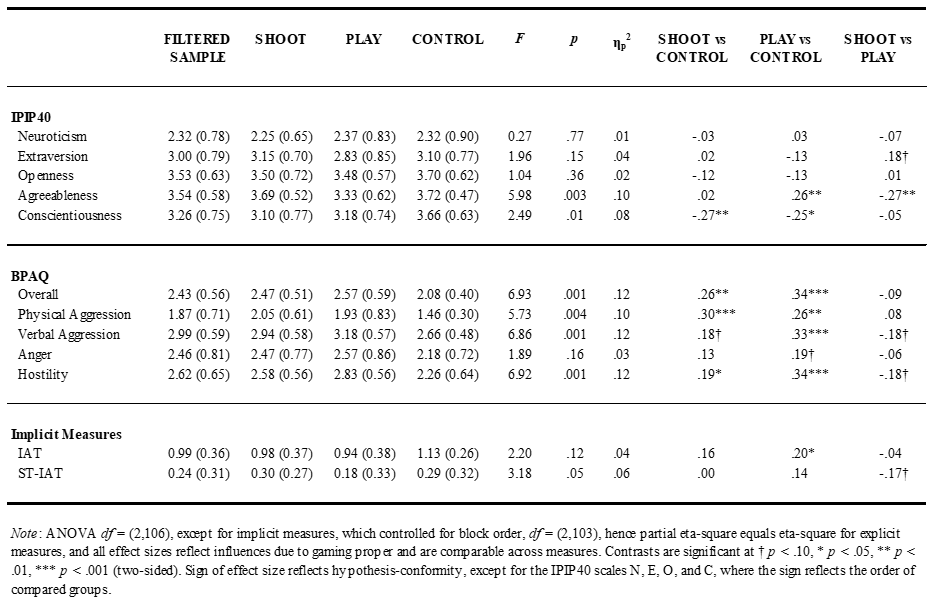
A multivariate analysis (MANOVA) of personality traits showed that, overall, there were significant differences between the groups, FPillai(10, 206) = 3.99, p < .001, partial eta squared ηp2 = .16. Hence, analyses of variance (ANOVAs) on the individual traits were run (see Table 5). Assuming equal group variances, Table 5 reports the effect size, r, for group- specific comparisons, coded as +1 and −1 for the contrasted groups (0 for the non-contrasted group; Rosnow & Rosenthal, 2002). Positive effect sizes indicate conformity with the hypothesized direction of a difference. If no a priori predictions were made (aggression-unrelated personality traits), the sign of the correlation simply reflects the numerical difference depending on the order of the compared groups. Although the use of contrasts inherently justifies the use of directional (one-sided) testing and one-tailed p-values (Furr, 2004; Rosnow & Rosenthal, 2002), we report p-values for two-tailed tests, because some tabulated contrasts do not reflect predictions derived a priori, and sometimes the empirical outcome opposes the hypothesized direction for a planned comparison. Importantly, Agreeableness differed significantly among groups, yet it was not SHOOT participants who diverged from CONTROL (disconfirming Hypothesis 1a), but participants in the less violent PLAY-group (Hypothesis 1b). As expected, no significant differences were found for Extraversion, Neuroticism, and Openness to Experiences (Hypothesis 1c). However, there were significant differences in Conscientiousness; CONTROL had higher values than SHOOT and PLAY. Though unpredicted, increased Conscientiousness among people who use computers predominantly for work, not games, makes intuitive sense.
Explicit Aggressiveness (BPAQ)
A multivariate analysis (MANOVA) of explicit aggressiveness scales revealed that the groups differed significantly, FPillai(8, 208) = 3.66, p < .001, ηp2 = .12. Hence, BPAQ-scales were analysed with ANOVAs (Table 5). As expected, CONTROL had the lowest levels of Physical Aggression, Verbal Aggression, Hostility, and overall BPAQ-aggressiveness; no significant differences were found for Anger though. Confirming Hypothesis 2a for SHOOT and Hypothesis 2b for PLAY, both gaming groups had higher explicit aggressiveness than CONTROL. Except for a non-significant trend in physical aggression, SHOOT did not have higher values than PLAY, as the two player groups themselves overlapped substantially. Contrary to what followed from the GAM, Hypothesis 2c was disconfirmed.
Table 5. Means (SD) of explicit measures (IPIP40, BPAQ) and implicit measures (IAT, ST-IAT), N = 109; ANOVA models for 3 groups of users: F-test, significance level (p), overall effect size (ηp2), and effect sizes (r) from group-specific contrasts.
Aggressive Attitude IAT
As expected, all three groups responded substantially faster in the aggressive + negative (peaceful + positive) block, M = 876 ms, SD = 209, than in the aggressive + positive (peaceful + negative) block, M = 1322, SD = 286. Consequently, a strong IAT effect resulted, M = 446 ms, SD = 201. Both SHOOT (436 ms) and PLAY (425 ms) had IAT effects about 100 ms smaller than those of CONTROL (522 ms). Although 100 ms differences would usually be considered substantial in social-cognitive research, a 3 (group factor: SHOOT, PLAY, CONTROL) x 2 (order of critical IAT blocks: aggressive + positive first or second block) ANOVA with repeated-measurement on the latter factor revealed no significant effects (Table 5), only a tendency for the group factor, disconfirming Hypothesis 3a and 3b. Despite missing the commonly accepted significance level, the pattern mimics the one found for explicit aggressiveness: Both gaming groups tended to deviate from the control group in the expected direction, yet once more PLAY deviated from CONTROL stronger than SHOOT, contradicting Hypothesis 3c that predicted more aggressive dispositions among players of violent shooters. At this stage one might conclude that unreliability prevented to establish this difference with statistical conclusiveness, but we defer the final evaluation of the IAT until further evidence on its validity.
Aggressive Self-Concept ST-IAT
As expected, participants responded faster in the self + peaceful block, M = 780 ms, SD = 167, than in the self + aggressive block, M = 887 ms, SD = 173. Consequently, positive ST-IAT effects were obtained. On average self was associated 107 ms faster with peaceful than with aggressive (SD = 138). Conducting an identical ANOVA on the ST-IAT effect as on the IAT before revealed a significant group main effect as expected (Table 5). However, SHOOT (139 ms) and CONTROL (140 ms) had almost identical ST-IAT effects, disconfirming Hypothesis 3a. Confirming Hypothesis 3b, PLAY had lower ST-IAT effects (71 ms) than CONTROL. In other words, PLAY participants were not able to associate self with peaceful as quickly as CONTROL or SHOOT participants, or they more readily associated self with aggressive. Again, it was not SHOOT, but PLAY participants whose self-concept turned out to be less peaceful when measured objectively, thereby mimicking the pattern found for self-reported agreeableness, but contradicting Hypothesis 3c.3
Implicit–Explicit Correlations
Pearson correlations were run across the complete sample (Table 6). Because lower (ST-)IAT effects mean relatively higher aggressiveness and higher scores in the explicit measures mean higher aggressiveness, negative correlations were expected. The lower the IAT effects, the stronger tended to be Physical Aggression and Hostility. A similar, but clearer pattern emerged for the ST-IAT which weakly, but significantly correlated with Physical Aggression and Hostility. Despite this parallelism, both implicit measures assessed different constructs as IAT and ST-IAT themselves were not related. Importantly, the IAT did not correlate significantly with the overall BPAQ-score, whereas the ST-IAT did. Keep in mind the fact that the implicit–explicit correlations should be rather low—and nevertheless be meaningful, as implicit and explicit constructs tend to be distinct and only weakly related (Nosek, 2007; for a critical note on the value of implicit- explicit correlations, see Fiedler et al., 2006). Although implicit and explicit correlations point to rather dissociated aspects in the aggressive domain, in sum Hypothesis 4 was supported for the aggressive self-concept ST-IAT, but was not supported for the attitudinal IAT (at best in one facet). As mere unreliability of the implicit measures might obscure implicit–explicit relationships, a method that accounts for measurement error is required.
Table 6. Intercorrelations.
Structural Equation Models (SEM)
We used the AMOS software package to model the covariance matrix. Latent variables were used to explain the responses at the manifest level of indicator variables, and maximum likelihood was used to estimate error-free relationships among the variables (Figure 1). Explicit aggressiveness as a latent variable was determined by all BPAQ subscales. Implicit aggressiveness as a latent variable was estimated from four sequential blocks of trials. Based on these 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th block-quarters four mini-(ST-)IAT effects (t1–t4) could be derived. Each indicator was influenced by a uniqueness term that captured specific aspects plus unspecific measurement error. Noticeably, in both ST-IAT (Figure 1, top panel) and IAT (Figure 1, bottom panel) the 2nd block had the strongest standardized regression weights (λ = .71/.80), so the amount of error variance, e2 = (1 – λ2), differed for each indicator and the variance was explained best in the 2nd quarter of each implicit measure (λ2 = .50 and .65).
Simply computing (ST-)IAT effects (across all trials) to correlate them with criteria does not take measurement error across trials into account. Once measurement error is controlled for in SEM, the true relationship between explicit and implicit latent variables can be estimated. The relationship between the automatic aggressive self-concept (ST-IAT) and explicit aggressiveness (AGG) became clearer, r = −.23. By contrast, the relationship between the automatic attitude towards aggression (IAT) and AGG was completely gone, r = .01. Thus, there was no sign of validity for the attitudinal IAT at all, only for the ST-IAT assessing the automatic aggressive self-concept. Lack of model fit cannot explain the absent correlation; the observed data did not differ significantly from the predicted data, neither for the IAT, χ2(19) = 26.69, n.s., SRMR = .051 (ideally < .05), nor for the ST-IAT, χ 2 (19) = 15.37, n.s., SRMR = .038. The tendency for the correlation between attitudinal IAT and BPAQ seems to stem from a methodological artefact (correlated errors), not substantive overlap of the constructs themselves.
Discussion and Conclusion
We examined the applicability of explicit and implicit measures in online studies when reaching out to players who should be of utmost concern to researchers. We showed how different players of computer games can be recruited online and the aggressiveness of their players analyzed. By tuning the recruiting and filtering strategies one can obtain access to relevant populations and increase the external validity of research (cf. Krantz & Dalal, 2000). To select a sufficient number of participants into focal groups, several purification steps―beginning with recruitment and ending with filtering―are necessary though. Moreover, we investigated the usefulness of an IAT assessing the spontaneous evaluation of aggression and a Single-Target IAT assessing the automatic aggressive self-concept. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of measuring aggressiveness objectively in Internet studies.
First of all, independent from block order, all users alike evaluated aggressive stimuli negatively in the IAT and they associated themselves with the peaceful rather than with the aggressive pole in the ST-IAT. The absolute magnitudes should not be overemphasized though, as the average (ST-)IAT effect depends―among other things―on the particular choice of stimuli (Bluemke & Friese, 2006). Note that relatively strong IAT effects in milliseconds resulted. While usually 100-200 ms differences are typical for IATs, the aggressive-attitude IAT effect was more than twice as strong. We suspect that societal norms on attitudes towards aggression are engraved on our minds so that the detection of any meaningful interindividual differences becomes futile. In other words, an IAT assessing automatic aggressive attitudes might mostly capture error variance. The strong IAT effect might be more the outcome of a cognitive short-cut due to figure-ground recoding (Rothermund & Wentura, 2004); different from the self-concept ST-IAT, the attitudinal IAT allows stimuli to be sorted simply by focusing on the valence of the stimuli. As all aggressive (peaceful) stimuli have negative (positive) connotations, it is very easy (or difficult) to sort them with attribute stimuli of corresponding (non-corresponding) valence. Not only gives this rise to substantial IAT effect sizes, it results in a kind of “ceiling effect”. These IAT scores cannot be very informative on participants then, and accordingly the IAT failed to uncover significant differences among groups.
Figure 1. SEM-based correlations of implicit and explicit aggressiveness for ST-IAT and IAT.
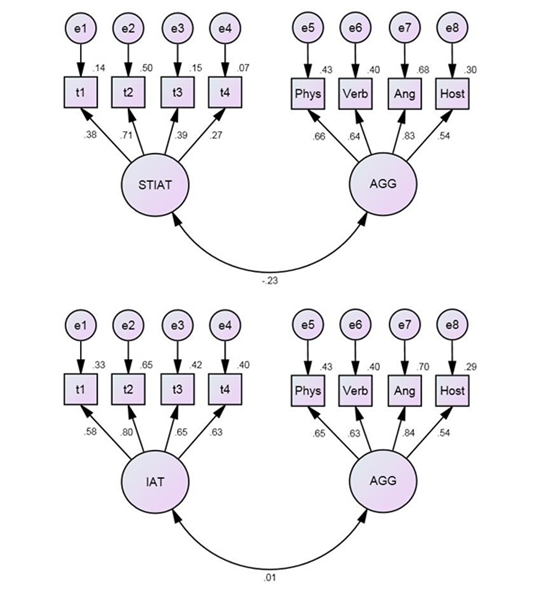
Importantly, a further notable divergence between the implicit measures became evident. While they tapped into distinct constructs and correlated in the expected lower range with facets of self-reported aggressiveness, the evidence for meaningful measurement in terms of implicit–explicit correlations was more compelling for the ST-IAT than for the IAT. There was no sign of validity of automatic aggressive attitudes at the construct level, only for the automatic aggressive self-concept. Low correlations between implicit and explicit measures are partly due to reduced transparency and controllability of the former. Also automatic cognition does not fully coincide with reflective cognition. Whereas explicit self-reports capture propositional aspects that contain acknowledged or attributed truth values, implicit measures are based on associations that can either be acknowledged, negated, or suppressed (Gawronski & Bodenhausen, 2006). Usually both types of constructs should share parts of the cognitive basis, and a full dissociation between IAT and explicit measures is unlikely in the first place (Nosek, 2007). Importantly, ST-IAT effects were not as extreme, but showed signs of convergent validity.
The superior sensitivity of the ST-IAT to detect differences between participants became also evident at the group level. The pattern converged with findings from explicit measures. Notably, it was players of less violent games who had the most aggressive self-concept implicitly, who also scored lowest on Agreeableness, and who had reliably higher aggressiveness scores than the control participants. For the players of shooter games, who should be most at risk according to prominent theories such as the GAM (Bushman & Anderson, 2002), such a clear-cut deviance from the control group could not be established. Though SHOOT also differed from CONTROL in most aggressiveness scales, descriptively they did not have the highest scores―apart from physical aggressiveness―, and according to the ST-IAT, their automatic aggressive self-concept was comparable to that of CONTROL, mirroring the pattern for Agreeableness.
The present study was not intended to test between theories, but the findings can be evaluated against two models. Given that SHOOT and PLAY differed from CONTROL in various aggressive dimensions, these findings may be read as being in line with the GAM. However, given the lack of the crucial difference between SHOOT and PLAY, there is equivocal support for the GAM at best. As the present study cannot rule out that arousal differences obscured existing group differences, our findings may be more in line with the GAM than they reveal on the surface. Though transitory, being excited by game play is one way how the GAM accounts for increased aggressiveness scores; therefore, the PLAY group may show heightened levels (especially if the web study was taken shortly after gaming). Moreover, some PLAY participants may have been exposed to substantial amounts of aggressive elements in ostensibly non-violent games, blurring the difference between both types of players further. Note that our focus was on identifying committed players of violent shooters in real-world settings to see whether their aggressive dispositions deviate substantially from those of others.
From the perspective of the Catalyst Model (Ferguson, Rueda et al., 2008), however, it makes sense that SHOOT did not differ significantly in aggressiveness from PLAY, because aggressiveness is strongly shaped by genetic and proximal societal influences, rather than violence-exposure in video games. Consequently, correlations between the preferred type of game play and aggressiveness would only emerge if individuals with certain kinds of personalities have been drawn to certain kinds of games. According to this view, aggressive dispositions should be consistently related to choice of games. Therefore, the Catalyst Model cannot explain the inconsistency why at times both SHOOT and PLAY deviated from CONTROL (see overall BPAQ, Physical Aggression), why at other times predominantly PLAY, but not SHOOT, differed from CONTROL (see ST-IAT, Verbal Aggression), and why PLAY appeared more aggressive implicitly and less agreeable explicitly than both SHOOT and CONTROL (see ST-IAT, Agreeableness). This inconsistent pattern is unlikely due to a mismatching control group or due to a mismatch of control variables between SHOOT and PLAY. For instance, the unequal gender proportions can hardly account for any group differences in explicit and implicit aggressiveness, with gender effects amounting to |t|s ≤ 1.43, ps ≥ .16, rEffectSize ≤ .10, except for a small, but well-known readiness among men to physically aggress (Björkqvist, Österman, & Lagerspetz, 1994), t(194) = 2.36, p = .02, rEffectSize = .17, which may have boosted physical aggressiveness. The relatively strong deviance of PLAY from CONTROL, and the inconsistent pattern for SHOOT, cannot be easily accommodated by the Catalyst Model either.
In sum, we think there is neither unequivocal support for the GAM nor for the Catalyst Model. Clearly, our findings do not support the idea that players of violent shooters are particularly at risk in applied settings. We therefore stress here the difference between causal effects that can be demonstrated among atypical players under controlled conditions in laboratory studies, but which might be transitory (e.g., cognitive priming), and long-term effects among real players that might reflect causal influences of violence-exposure on dispositions, but are conflated with the inverse relation (personality-driven selection of environments), positive gaming effects, and socializing. Merely pointing the finger at shooter games may be misguided then, because modern sports and racing games can contain lots of competitive and violent elements too (e.g., running over pedestrians; sports fouls). Some game elements might increase aggressive dispositions and diminish differences between different types of players. Alternatively, players of shooters (and non- violent players alike) might be exposed to positive influences (playing in social groups, flow experiences, peaceful content during the remaining 6 hrs of game play), and these may buffer harmful effects of violent content to a certain extent (Bluemke et al., 2010; Ferguson, 2010; Jin, 2011).
Limitations
With regard to the self-selection problem, drop-out might have undermined the detection of any relationship between game genre and aggressiveness if particularly vulnerable gamers stopped after they suspected aggression-related measures. We tried to confine self-selection from the beginning and throughout the procedure by using unobtrusive measures first. Afterwards, we compared drop-out participants to the final sample: Participants who had at least completed the Agreeableness subscale (but not the implicit measures) did not differ from the participants who took the aggression-related instruments; given the relationship between Agreeableness and Explicit Aggressiveness, a systematic bias in the remaining sample due to drop-out seems unlikely. We conclude that Internet studies offer recruitment advantages such as easy access to target groups, but Internet-specific problems require precautionary measures such as a BigFive-inventory at an early position.
As regards the comparison of gamers and non-gamers, a cautious note may be in place, too. Recruitment of different types of gamers appears to be straightforward when game-specific boards are available. However, recruitment of a control group can be more troublesome. Though we successfully recruited non-gaming computer users that did not differ in skills in computer usage, our focus on computer users prevents further generalization to the wider population (who may not use computers at all). The composition of the control group in terms of personality traits and socio-demographic variables will depend on the choice of forums and mailing-lists as well. Still, no discrepancy in fundamental personality traits was evident, apart from the difference in conscientiousness.
To test complex hypotheses on overall violence-exposure in various types of media, or to identify beneficial effects of social gaming or multi-player modes, even more fine-grained filter questions than we used might be appropriate, and additional questions on the time spent on games (and not merely game categories) might be asked (Krahé & Möller, 2004). Though our Internet study was successful at recruiting diverse players, to establish effect sizes at a societal level some aspects need to be addressed in future studies: A specific comparison of the theories such as the GAM and the Catalyst Model requires a proper longitudinal design; different games and game types should be equally and fully represented; the amount of violence exposure should be estimated across all types of games played (while controlling for exposure in other media at the same time); positive counter-influences should be measured too. Furthermore, it would be worthwhile to add behavioural criteria, so that the validity of implicit measures to predict aggression over and beyond explicit measures can be inspected. Finally, online assessment with implicit measures that target at players requires extended measurement procedures to increase their reliability.
Outlook
Our study directs attention to the new ways of measuring aggressiveness objectively. Implicit measures assess spontaneous aggression-related associations in which participants themselves hardly have insights, but that are useful for predicting impulsive aggression. They add benefits when investigating the gaming effects, and in combination with online studies they reach out to samples that matter. At this stage, we conclude that attitudinal IATs are unlikely to work very well in the domain of aggression, whereas self-concept ST-IATs do. It is our hope that this study inspires researchers to look for creative ways how to involve regular players in studies on computer games and to consider unobtrusive measures of aggressive dispositions more frequently.
Notes
- Users of the Mac OS platform may encounter technical difficulties with JAVA applets. The Sun Java implementation officially supports Windows and Linux systems, whereas Apple’s JAVA version is unofficial and not fully compatible with Sun’s JAVA version. As of the end of 2010, JAVA is deprecated on the Mac OS platform, and whether a community-based JAVA fork can achieve compatibility in the future remains to be seen.
- If one is concerned with erroneous data due to sudden high load conditions (virus scans ), “inaccurate timing filters” can be used to single the affected trials out ex post facto (Eichstaedt, 2001).
- A significant order effect emerged Participants who started with the self + peaceful block, had a stronger ST-IAT effect (181 ms) than when they worked on the self + aggressive block first (53 ms), F(2, 106) = 21.92, p < .001, ηp2= .17. This harmless methodological artefact is well-known from the literature and results from initial accommodation to the relative task difficulty. If participants start with the compatible block self + peaceful, they experience the subsequent block as much more difficult than when working on the reversed order. The block order did not interact with the group factor, F < 1. As block order introduces error variance in implicit measures, it renders eta squared as an overall effect size for the group factor less useful (Cohen, 1973; Levine & Hullett, 2002). Therefore, partial eta squared is reported, which effectively controls for the block order influence, whereas in the absence of control factors for the explicit measures partial eta squared equals eta squared.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2012 Matthias Bluemke, Joerg Zumbach

