The Effect of Computer Gaming on Subsequent Time Perception
Vol.3,No.1(2009)
time perception; computer game; LAN party
Stefanie Luthman
University of Cambridge, United Kingdom
Stefanie Luthman is a Research Associate at the Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom. She has undertaken her PhD studies in psychology where she examined the transfer processes experienced by computer gamers. She is currently working on a project that aims to redesign key aspects of the teaching and learning of physical science and mathematics during the early stages of secondary education. Her research interests are media effects and student engagement and learning.
Thomas Bliesener
University of Kiel, Germany
Thomas Bliesener is chair in developmental psychology, educational psychology and psychology and law at the Institute of Psychology at University of Kiel, Germany. His main research topics are: The development of deviant social behavior, aggression, violence and delinquency from early childhood to adulthood as well as evaluation research on programs on its prevention and intervention.
Frithjof Staude-Müller
University of Kiel, Germany
Frithjof Staude-Müller is a researcher at the Institute of Psychology of the Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel. His research interests are media effects, deviant online behavior and parental mediation of children´s and adolescents´ media use. He is currently working on his PhD thesis on the effects of computer game violence on social information processing.
Angrilli, A., Cherubini, P., Pavese, A., & Manfredini, S. (1997). The influence of affective factors on time perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 59(6), 972-982.
APA (2007). Statement of the American Psychiatric Association on “Video Game Addiction” Retrieved March 3, 2009, from http://www.psych.org/...
Bindra, D., & Waksberg, H. (1956). Methods and terminology in studies of time estimation. Psychological Bulletin, 53(2), 155-159.
Block, R. A. (1990). Models of psychological time. In R. A. Block (Ed.), Cognitive models of psychological time (pp. 1–35). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Block, R. A. (1992). Prospective and retrospective duration judgment: The role of information processing and memory. In F. Macar, V. Pouthas & W. J. Friedman (Eds.), Time, Action and Cognition: Towards bridging the gap (pp. 141–152). Dordrecht, Netherlands: Kluwer Academic.
Block, R. A., & Zakay, D. (1996). Models of psychological time revisited. In H. Helfrich (Ed.), Time and Mind (pp. 171-195). Seattle: Hogrefe & Huber.
Block, R. A., & Zakay, D. (1997). Prospective and retrospective duration judgments: A meta-analytic review. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 4(2), 184-197.
Bobko, D. J., Bobko, P., & Davis, M. A. (1986). Effect of visual display scale on duration estimates. Human Factors, 28(2), 153-158.
Brown, S. W. (1997). Attentional resources in timing: Interference effects in concurrent temporal and nontemporal working memory tasks. Perception & Psychophysics, 59, 1118-1140.
Chou, T. J., & Ting, C. C. (2003). The role of flow experience in cyber-game addiction. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 6, 663-675.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: the Psychology of Optimal Experience. New York: Harper & Row.
Esser, H., & Witting, T. (1997). Transferprozesse beim Computerspiel. Was aus der Welt des Computerspiels übertragen wird [Transfer processes with computer games: What is transferred from the computer-game world]. In J. Fritz & W. Fehr (Eds.), Handbuch Medien: Computerspiele (pp. 247-261). Bonn: Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung.
Fritz, J. (1997). Zwischen Transfer und Transformation. Überlegungen zu einem Wirkungsmodell der virtuellen Welt [Between transfer and transformation: Assumptions of an effect model of the virtual world]. In J. Fritz & W. Fehr (Eds.), Handbuch Medien: Computerspiele (pp. 229-246). Bonn: Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung.
Griffiths, M. D. (2008). Videogame addiction: Fact or fiction? In W. Willoughby & E. Wood (Eds.), Children’s Learning in a Digital World (pp. 85–103). Maldan, Mass.: Blackwell.
Gruber, R. P., & Block, R. A. (2003). Effect of caffeine on prospective and retrospective duration judgements. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 18(5), 351-359.
Gruber, R. P., & Block, R. A. (2005). Effects of caffeine on prospective duration judgements of various intervals depend on task difficulty. Human Psychopharmacology, Clinical and Experimental, 20(4), 275-285.
Lapp, W. M., Collins, R. L., Zywiak, W. H., & Izzo, C. V. (1994). Psychopharmacological effects of alcohol on time perception: The extended balanced placebo design. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 55(1), 96-112.
Myers, D. (1992). Time, symbol transformation, and computer games. Play and Culture, 5, 441-457.
Rau, P. L. P., Peng, S. Y., & Yang, C. C. (2006). Time distortion for expert and novice online game players. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 9, 396-403.
Schneider, S. M., Prince-Paul, M., JoAllen, M., Silverman, P., & Talaba, D. (2004). Virtual reality as a distraction intervention for women receiving chemotherapy. Oncology Nursing Forum, 31(1), 81-88.
Tinklenberg, J. R., Roth, W. T., & Kopell, B. S. (1976). Marijuana and ethanol: Differential effects on time perception, heart rate, and subjective response. Psychopharmacology, 49, 275-279.
Totzke, I., Schoch, S., & Krüger, H. P. (2006). Fehleinschätzung von Zeit als Ursache für Ablenkungseffekte beim Fahren: Bedeutung von Menüstruktur und visuellen Anforderungen [Misjudgment of time as the cause of distraction effects whilst driving: The importance of task menu structure and visual demands]. MMI-Interaktiv, 11, 58-74.
Witting, T. (2007). Wie Computerspiele uns beeinflussen. Transferprozesse im Erleben der User [How computer games influence us: Transfer processes experienced by users]. München: kopaed.
Wood, R. T. A., & Griffiths, M. D. (2007). Time loss whilst playing video games: Is there a relationship to addictive behaviours? International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 5(2), 141-149.
Wood, R. T. A., Griffiths, M. D., & Parke, A. (2007). Experiences of time loss among videogame players: An empirical study. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 10, 38-44.
Zakay, D. (1990). The evasive art of subjective time measurement: Some methodological dilemmas. In R. A. Block (Ed.), Cognitive models of psychological time (pp. 59-84). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Zakay, D., & Block, R. A. (1996). The role of attention in time estimation processes. In M. A. Pastor & J. Artieda (Eds.), Time, internal clocks and movement (pp. 143–164). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier.
Introduction
Time distortion is a common phenomenon in events of exceptional negative or positive evaluation. In an unpleasant setting such as waiting for a bus when already being late, time might be experienced as passing very slowly. In contrast, pleasant situations often cause the subjective feeling that time passes too quickly. However, time distortion is not only limited to extraordinary events but can also emerge in daily life situations. A person who is completely absorbed in performing an activity might reach a state of flow, a mental condition that is marked among other characteristics by a distorted sense of time (Csikszentmihalyi, 1990). Such flow experiences are often reported by people who play computer and video games (Chou & Ting, 2003; Wood, Griffiths, & Parke, 2007). Despite the pleasure of forgetting time and space in electronic games, time loss can also have negative consequences for the player such as missing appointments (Esser & Witting, 1997; Wood et al., 2007) and has been linked to video game addiction (for a critical review of video game addiction see Griffiths, 2008). However, neither is video game addiction regarded as a mental disorder (APA, 2007), nor does time loss offer much diagnostic value for video game addiction as time loss is reported by high- and low frequency players alike (Wood & Griffiths, 2007; Wood et al., 2007), warranting more research into the nature of video game addiction and the role of time loss in this context.
A question that has not been addressed so far is if, and how, time distortion continues after gaming. It may run out quickly, persist for a while, or even rebound in the absence of the game. In the present study, we test the assumption that computer gamers experience time loss whilst gaming because attentional resources allocated towards the processing of nontemporal (i.e. game) stimuli are subtracted from the attention paid to the processing of temporal stimuli (Zakay & Block, 1996) and that this time distortion persists temporarily after gaming as players transfer time processing schemata activated during the game session to real-life situations (Fritz, 1997). An answer to the question how computer games influence time perception subsequent to gaming is crucial since many activities of daily life such as driving in traffic and operating machinery require precise time perception. While occasional time losses during game sessions might be appreciated by some gamers (Wood et al., 2007), persistent time distortions after gaming could have detrimental effects on real-world performance and the safety of gamers and their surroundings.
Although the study of time perception is a well-established research field, the partially inconsistent terminology across and within publications can lead to confusion. Following the specifications of researchers who have tried to standardize the terminology in time perception studies (Bindra & Waksberg, 1956; Block & Zakay, 1997; Zakay, 1990), a short introduction into the nomenclature of time perception is presented here in order to enhance the comprehension of the present experiment and the studies that are referred to in this article.
In time perception studies with a prospective paradigm, the participant is forewarned about the upcoming task of temporal judgment. In studies with a retrospective paradigm, the subject experiences a time period and will only afterwards be informed about the need of giving an estimate of its duration.
In addition to these study paradigms, there are three different methods for executing the judgment. In the method of verbal estimation, subjects are asked to verbally estimate the duration of a time interval (the standard) that they have experienced. The second method is called production, in which the experimenter instructs the subject to attempt the exact production of a given time interval (e.g. by a stop watch). In the method of reproduction, the experimenter demonstrates a standard (e.g. by sound) that the subject subsequently tries to reproduce.
Inaccurate time judgments can be attributed to deviations of subjective time flow (i.e. the psychological time) from the objective time. A decreased subjective time flow is usually experienced as the feeling that time flies, while an increased subjective time flow is often experienced as a dragging of time. The outcome of such time distortions in time perception studies depends heavily on the applied method. In a verbal estimation task, a decreased subjective time flow will result in an underestimation of the standard time. Using a production task, however, a subject with decreased subjective time flow will produce larger time intervals than the standard. As with the method of production, a decreased subjective time flow during the reproduction of a standard time interval will cause an overreproduction. An increased subjective time flow will cause the opposite effects, meaning an overestimation or under(re)production of the standard, depending on the utilized method.
Theoretical and empirical background of time perception
Theories and studies on time distortion in relation to playing computer games are rare. Myers (1992) theorizes that subjective time during a game session becomes more drawn out when the player’s experience with the game increases. However, his model was derived from reflections on games of the early nineties and has not been tested on contemporary computer games. Another theoretical inquiry on time distortion with regard to video games is the transfer process model by Fritz (1997). He proposes ten types of schema transfers between the real and the virtual world, including the transfer process of time. According to his model, time schemata learned and applied in a game are transferred to post-game experiences. Both models are interesting approaches to explain the underlying processes of time perception whilst and after playing electronic games. However, empirical studies on time distortion among computer game players have rather drawn on models that were developed to explain the phenomenon of time perception in general (for reviews on such models, see Block, 1990; Block & Zakay, 1996).
Since attentional processes play a key role in prospective time judgments (Block, 1992), as measured in the present study, one model focusing on attention in time perception shall now be illustrated in more detail. The attentional-gate model (Block & Zakay, 1996; Zakay & Block, 1996) combines the assumption of an internal clock with that of attentional processes in time perception. Briefly, pulses that are produced by a pacemaker of an internal clock are seen as the raw material of time information. These pulses accumulate in the clock’s cognitive counter and are transferred to working memory. There, time judgment is made by the comparison of the number of accumulated pulses with the average pulse number assembled in similar time periods of the past. In contrast to other internal-clock models, the number of accumulated pulses in the counter depends not only on the clock’s pulse rate, with high arousal increasing the pulse rate and low arousal decreasing it, but also on the transmissibility of the pulse stream into the counter. According to this model, a gate between pacemaker and counter determines the transmission of pulses between both. The gate in turn is influenced by the allocation of attentional resources between the processing of time and nontemporal stimuli. If a person assigns more attention to the passage of time, the gate opens and more pulses from the pacemaker accumulate in the counter, leading to longer duration judgments. Contrary, if an event demands more attention and resources shift from time processing to the more salient task, the gate closes and fewer pulses accumulate, causing a shortening of the subjective duration of a time interval.
In addition to attentional processes, diverse situational variables can influence the perception of time. Angrilli, Cherubini, Pavese, and Manfredini (1997) have found interaction effects between affective states and arousal on time judgments, with underestimations of display times of attention-absorbing stimuli (here aversive low-arousal pictures) and overestimations of display durations of less captivating stimuli (pleasant low-arousal pictures). The reverse was found for highly arousing stimuli. Drugs can also alter the sense of time. As for the more common drugs, two prospective studies have showed reductions in duration estimates due to caffeine intake (Gruber & Block, 2003, 2005). Alcohol seems to have a similar effect on time perception as studies have found overproductions of time following alcohol consumption (Lapp, Collins, Zywiak, & Izzo, 1994; Tinklenberg, Roth, & Kopell, 1976).
In summary, time perception proves to be a complex phenomenon sensitive to personal and situational variables, with the latter apparently exerting their influence by affecting a person’s arousal and/or attention. The following chapter reviews to what extent the use of electronic games as a situational factor can alter the sense of time.
Time distortion among computer game players
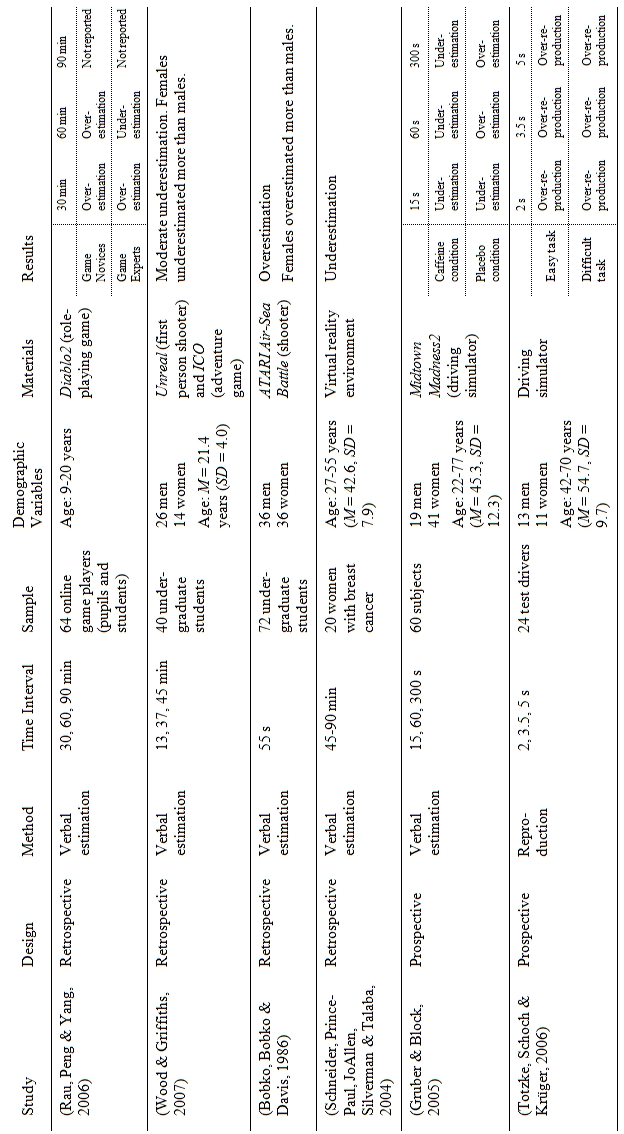
When examining the effects of computer and video games, most studies include the amount of time that participants play their games, in addition to the variables of main interest. Yet, there is little research on time perception itself during or after gaming. This paragraph gives an overview of the few quantitative and qualitative studies that have connected time perception and electronic games. So far, most experimental studies examining the effect of gaming on time perception have used a design in which subjects retrospectively judged the duration spent in the virtual world (see table 1). They yield mixed results and indicate an additional influence of subjects’ gender and game experience on time perception. With regard to the prospective design of the present study, prospective studies show some tendency towards an underestimation of time and an equivalent overreproduction.
In addition to quantitative studies, qualitative studies help to reveal further aspects of time perception in computer gamers. For instance, all participants of a qualitative interview study reported that they lose track of time during a game, and many apply strategies for avoiding time loss, for example setting alarm clocks (Esser & Witting, 1997). An online survey among computer gamers revealed under what conditions subjective time loss occurs (Wood et al., 2007). Game characteristics most associated with time loss were high complexity and a game plot, followed by games providing multi-levels and missions, as did beating high scores and multiplayer interactions. Nearly half of the participants claimed that they experience time loss frequently, one third even every time they play. Their feelings towards time loss reached from relief of boredom and stress to guilt for wasting time.
In summary, the question of how electronic games influence time perception of gamers cannot be settled conclusively. Although players frequently admit losing track of time whilst playing, experimental studies have shown mixed results. The low number of studies in combination with their differences in design, methods, and subjects necessitate further research efforts before a concluding answer to this question can be made.
Table 1: Overview of experiments on time distortion using electronic games.
Purpose of the present study and hypotheses
Besides the unsettled nature of time perception whilst gaming, there is also no clarity about the persistency of potential time distortions beyond a game session. Our study addresses this issue by examining the question whether playing computer games alters time perception after a game session, and if so, in what direction time perception is influenced.
The layout of this study was built on two presumptions. Firstly, on the basis of the attentional-gate model of time (Zakay & Block, 1996) we assume that gamers would experience time losses whilst gaming because attentional resources become reallocated from time processing to the processing of game-relevant tasks. Secondly, with reference to the transfer model of virtual worlds of Fritz (1997), which suggests that players transfer in-game time schemata to post-game situations, we expect that the distorted sense of time will persist in terms of time losses after gaming. Unfortunately Fritz’ model remains rather vague about how such a transfer of time distortion might take place. We assume that the game-favoring allocation of attentional resources continues after a game session since they may not be instantaneously set back to their initial allocation. Such delays in setbacks were reported in an interview study with regard to increased vigilance especially after long gaming periods (Witting, 2007). The author hypothesizes that perceptional schemata activated in the game continue to be active in post-game situations causing the players to perceive real-life situations through the eyes of a gamer.
In contrast to previous studies, time perception of gamers was measured with time production tasks. As a reminder for the following hypotheses: increased time productions reflect a decelerated subjective time flow (i.e. time flies), while decreased time productions correspond to an accelerated subjective time flow (i.e. time drags). Our main hypothesis predicts that computer games cause participants’ subjective time flow to slow down because of the competing processes of time perception and the playing of games and that this game-induced time distortion would continue also after a game session.
Hypothesis 1: Time productions are longer after a game session than before a game session.
Secondly, in accordance with other studies on time perception and attentional processes (Brown, 1997), our second hypothesis predicts that task difficulty would influence performance in time perception tasks. We expect that attentional resources get diverted from the timing task when participants are required to concurrently process nontemporal stimuli causing a slowdown of subjective time flow.
Hypothesis 2: Time productions are longer for temporal tasks that involve cognitive distraction than temporal tasks without distraction.
The third hypothesis predicts an interaction between the measuring time and task difficulty. We assume that the expected increase in time productions after gaming would be more pronounced for timing tasks that involve cognitive distraction than for pure timing tasks. According to the transfer model of virtual worlds (Fritz, 1997), in-game schemata are more easily transferred to the real world if subsequent situations resemble the game in their structural properties. An enriched timing task, which requires a subject to process nontemporal stimuli in parallel should resemble the cognitively demanding situation of gaming closer than an empty timing task, which allows subjects to fully devote their attentional resources to the time judgment.
Hypothesis 3: An increase in time productions after gaming is larger for temporal tasks involving cognitive distraction than for timing tasks without distraction.
Finally, we expect that reports of subjective time loss in former game sessions would be connected to quantifiable time losses after gaming.
Hypothesis 4: The larger subjective time losses in former games are, the longer average time productions would be after gaming.
Materials and Methods
Subjects
The study took place in the natural setting of two officially organized LAN parties1 in Northern Germany between October and December 2007. Two experimenters recruited participants by means of flyers and personal contact. They were offered personalized feedback of their time perception performance after study completion. A total of 48 gamers consented to take part in the experiment. Eight subjects had to be dropped from the analyses due to dropout from the second measuring-time. Thus, the analyses reported herein are based on the 40 subjects (37 males and 3 females) who performed the test completely. Participants ranged in age from 18 to 38 years of age (M = 22.30, SD = 3.94). Close to half of the subjects were employed (17 subjects, 42.5%), eight studied at a university (20%), and six attended school (15%). The remaining test persons included four in practical education (10%), two in military service (5%) and one subject engaged in community service (2.5%). Participants played computer and video games on average for 16.9 hours (SD = 14.3) per week and attended LAN parties between two and 54 times in the previous year (M = 10.4, SD = 13.4), of which three quarters were private LAN parties (M = 8.4, SD = 13.4) rather than official ones (M = 2.0, SD = 1.2). Most subjects planned to play several games in the course of the LAN party. Their last game before the second measuring-time were predominantly shooter games [versions of Counterstrike (N = 14), Battlefield 2 (N = 4), versions of Unreal Tournament (N = 3), Call of Duty (N = 1), Quake3 (N = 1), Crysis (N = 1), Tactical Ops (N = 1)], followed by strategy games [Command & Conquer (N = 4), Warcraft 3 (N = 4), Warhammer (N = 3)], and the role-playing game World of Warcraft (N = 2) and the racing game Flatout 2 (N = 2).
Experimental procedures
In order to reduce noise and distraction from the ongoing LAN party, the experiment was carried out in a calm area of the building. Subjects were informed of the procedure of the experiment and provided written informed consent. The experimenters explained that the study consisted of two measuring-times, the first preferably taking place after a period of recovery from gaming (minimum of two hours), and the second being undertaken subsequent to a game session. A recovery period prior to the first measuring time allowed for a baseline measurement of subjects’ time perception. At both measuring-times, participants completed a questionnaire and performed two time-perception tasks described below. The points of time at which the tests took place differed and were recorded by the experimenters.
The questionnaire included questions about variables with a potential impact on time perception. Among these were aspects of playing electronic games, such as weekly playtime (in hours) and subjective time loss (“I do not realize how quickly time passes whilst gaming.” from “1 = does not apply to me“ to “5 = does apply to me fully”). Subjects were also questioned about their intake of alcohol and caffeine prior to the measurements and about their physical state (tiredness from “1 = wide awake” to “5 = sleepy”) and mental condition (discontentment, “How do you feel?“ from “1 = very good” to “5 = very bad”). Furthermore, participants were asked to give the level of game excitement they experienced in their last game session (from “1 = boring” to “5 = very exciting”).
Due to the prospective design that we used to examine time perception, participants were informed beforehand that they have to pay attention to the passage of time. A stopwatch was used as time-production tool. For all timing tasks, the stopwatch’s display was only visible to the experimenters. The results of the time productions were not reported to the participants in order to prevent a learning effect that could influence the results at the second measuring-time. First, subjects were asked to generate a 10-s interval by pressing a button of the stopwatch, once to start the measurement and then once more when they thought that 10 seconds had passed. The interval was empty, i.e. no activity was undertaken during the interval and the subject could focus completely on keeping track of the passage of time. The second task was to produce an interval of 60 seconds. This time, however, subjects were distracted from the temporal task by writing the alphabet backwards from Z to A onto a sheet of paper. We decided to not use an interval of 10 seconds for the more difficult task because we wanted subjects to get well enough distracted from the timing task. In addition, the timing of a 60-s interval instead of a 10-s interval would preclude subjects from producing the interval by barely counting the number of letters they have written down, e.g. ten letters provided they manage one letter per second. Because of the writing task, the experimenter took over the part of pressing the stopwatch with participants verbally announcing the start and end of the interval.
Statistical Analyses
Time production data were analyzed with the statistical package SPSS (version 13.0). The significance level was set at p ≤ .05. Repeated-measures analyses of variance were performed, using the factors of measuring-time (before and after a game session) and task type (empty 10-s interval and filled 60-s interval). Three outliers of time production values were excluded beforehand. They were detected by use of boxplots and were data that lay more than 1.5 interquartile ranges lower than the first quartile or 1.5 interquartile ranges higher than the third quartile. Since the time intervals differed in absolute length, the effective time productions were converted into standardized production values by dividing the produced time by the respective standard time interval (Block & Zakay, 1997). Correlational and regression analyses examined the relationship between time production and variables potentially connected to time perception.
Results
Accuracy of time perception
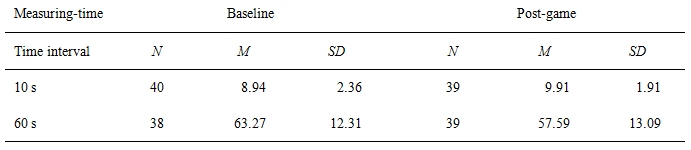
Table 2 displays for each experimental condition the mean time production data before converting. It shows that participants on average underproduced the 10-s interval at the baseline testing. After gaming they still produced shorter intervals than 10 seconds on average, but productions came close to the target interval. As for the 60-s interval, time productions at the baseline were longer than required. After gaming, however, participants underproduced the interval. One-sample t-tests using the standardized ratios of time productions revealed that only the 10-s interval at baseline significantly differed from an accurate timing (M = 0.89, SD = 0.23, t(39) = 3.00, p = .01), i.e. from 1.00.
Table 2: Number of cases, mean time productions, and standard deviations for each experimental condition.
Effect of gaming and task difficulty on time perception
Figure 1 shows the relative scores of time productions for each condition. Values above 1.00 indicate overproductions of time while values below 1.00 reflect underproductions. Time production data were analyzed using a two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance and post hoc paired-sample t-tests.
Neither the main effect of gaming, nor the main effect of task type, were significant (gaming: F(1, 35) = 0.07, p = .80; task type: F(1, 35) = 2.66, p = .11). However, the interaction effect between measuring-time and task type reached significance, F(1, 35) = 17.06, p = .00.
As for the effect of gaming on time perception, only time production ratios of the 10-s interval increased significantly from baseline (M = 0.89, SD = 0.24) to post-game measurement (M = 0.99, SD = 0.19, t(38) = -2.60, p = .01, d = 0.45). In the 60-s interval condition, however, time productions were significantly longer before gaming (M = 1.05, SD = 0.21) than after gaming (M = 0.96, SD = 0.22, t(36) = 2.58, p = .01, d = -0.45).
Regarding the effect of task type on time perception, results showed that the demanding timing task (simultaneously writing the alphabet backwards) gave longer time productions than the pure timing task, but only at the first measuring-time. At baseline testing, the average time production ratio of the filled 60-s interval (M = 1.06, SD = 0.20) was significantly larger than the one of the empty 10-s interval (M = 0.88, SD = 0.23, t(37) = -3.53, p = .00, d = 0.83). After gaming, however, time production ratios of the 60-s interval (M = 0.95, SD = 0.24) fell below ratios of the 10 s interval (M = 0.99, SD = 0.19, t(37) = 0.64, p = .53, d = -.15).
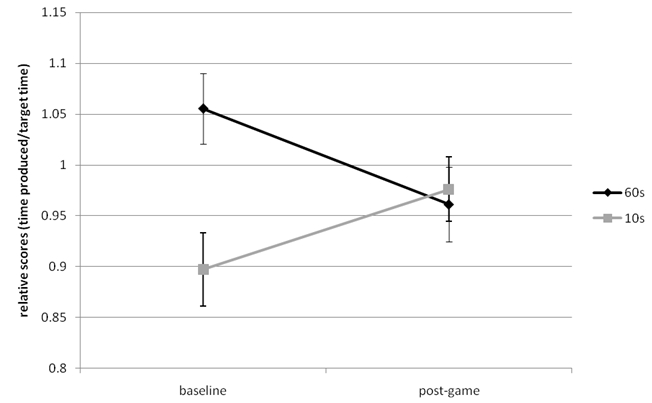
Figure 1: Relative scores of time productions of the 10-s and 60-s interval at baseline and post-game measurement.
The moderating effect of personal variables on time perception
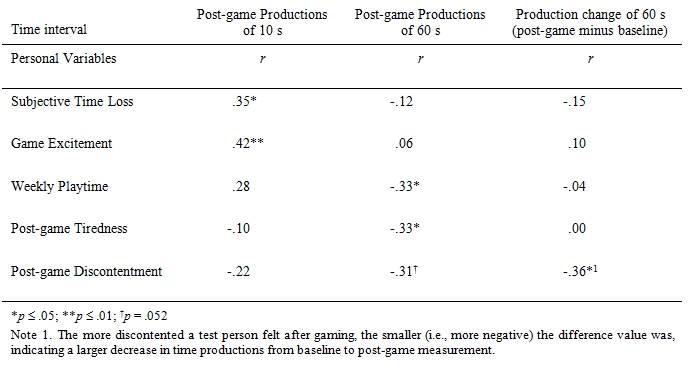
Time productions neither related to participant’s caffeine or alcohol intake prior to the measurements, nor did they relate to the experiment’s time of day. However, other personal variables showed relationships to some of the time productions. At baseline testing, time productions did not significantly correlate with any of the subjects’ personal characteristics. After gaming, however, there were significant correlations with some of the characteristics (see table 3). As for the 10-s interval, the more participants reported that they typically lose time during game sessions, the longer their time productions were. These were also longer the more exciting participants rated their last gaming period prior to measurement. With regard to the 60-s interval, time productions were shorter the longer the reported weekly playtime. Tiredness and discontentment at the post-game measurement also correlated negatively with length of time production. In addition, the less contented the test persons felt after gaming, the larger was their decrease in time productions of that interval from baseline to post-game performance.
Table 3: Pearson correlation coefficients between post-game time productions and personal variables.
The above-described relationships between time productions and personal variables were scrutinized further in multiple regression analyses (see table 4). Results showed that game excitement was the only significant predictor of post-game time productions of the 10-s interval. With regard to the post-game 60-s interval, none of the variables predicted time productions significantly apart from the marginal significance of discontentment after gaming. The predictive value of discontentment increased to significance, however, for the time production change between baseline and post-game measurement for the 60-s interval.
Table 4: Summary of multiple regression analyses (forced entry) of post-game time productions.
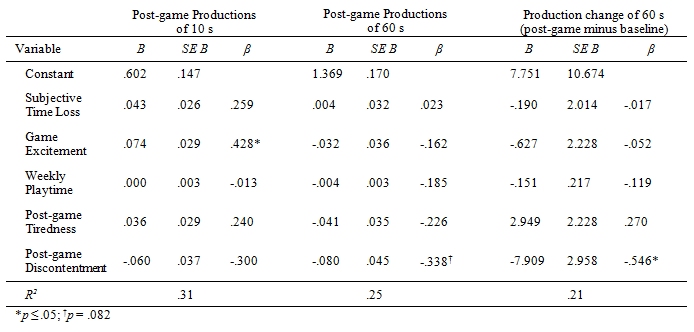
Further analyses that controlled for the effect of personal variables on time productions2 did not yield additional explanatory value in explaining the opposite outcomes of the two timing tasks described above.
Discussion
Previous studies of time perception in electronic games were mainly undertaken in laboratory settings, using verbal estimation tasks. The studies have not confirmed subjective time losses in computer games, a phenomenon often reported by players themselves.
The present study contributes to the research field by examining gamers in the natural setting of a LAN party and by employing the method of time production. The obtained results are mixed and raise further questions into the effect of gaming on time perception. Firstly, except for the 10-s interval at baseline, there were no significant deviations from the requested time interval, indicating that participants had a close to accurate time perception in three out of four conditions. Secondly, the main hypotheses about the effects of gaming and task difficulty on time perception had to be rejected. This was due to an interaction effect that yielded opposite directions of time production changes from baseline to post-game measurement, depending on the respective timing task condition.
As for the effect of gaming on time perception (hypothesis 1), the significant interaction between measuring-time and timing task revealed the predicted increase in time productions after gaming for the 10-s interval. However, it also yielded an unexpected decrease of time productions for the 60-s interval after gaming. With regard to the effect of task difficulty on time perception (hypothesis 2), the interaction showed that relative time productions were, as expected, longer for the filled 60-s interval than for the empty 10-s interval, but only at baseline measurement. However, after gaming, relative time productions of the 60-s interval dropped below those of the 10-s interval. Therefore, we had to reject the extended hypothesis, which stated that game-induced time loss would be more easily transferred to attention-requiring timing tasks compared to easy timing tasks (hypothesis 3). Perhaps, in contrast to our assumption, the demanding timing task did not capture the attentional resources formerly used for game-related tasks. The last hypothesis predicted that subjective time loss in games would relate to objective time loss after gaming (hypothesis 4). This proved to be true for the 10-s interval, for which participants produced longer time intervals the more they reported that they usually lose track of time whilst playing electronic games. However, such a relationship was not found for the 60-s interval.
The results challenge the idea that gaming exerts its influence on time perception uniformly. Most likely, personal and situational variables limit the transfer of game induced time distortion to real-world time perception or even counteract the initial gaming effect. Regression analyses found participants’ discontentment at the second measuring-time to be a significant predictor of post-game timing data, with shorter time productions of the 60-s interval and stronger decreases from baseline to post-game measurement for the 60-s interval the more discontented players felt. These findings imply that discontented participants may have shortened these time productions in order to quickly get over with the second measuring-time. There again, this relationship may also indicate an avoidance response of participants proposed by Angrilli et al. (1997). Their subjects overestimated the duration of highly arousing aversive stimuli they could not escape, which in our study would be associated with shorter time productions.
The above-described relationship only emerged for the 60-s interval, but not for the 10-s interval. However, we cannot determine if subjects’ motivational considerations primarily related to the length of the 60-s interval or to its demand for attentional resources, or even to the combination of both features. The confounding of interval length and task difficulty is a shortcoming of this study, with the empty interval being 10 seconds long and the filled interval being 60 seconds long. In addition, at both measuring times the production of the 60-s interval followed the 10-s interval. This raises the question if the effect of gaming was different in the 60-s interval (e.g. weaker) compared to the 10-s interval and if the production of the 10 s interval exerted any influence on the performance of the 60-s interval.
In accordance with the concept of flow (Csikszentmihalyi, 1990) and the attentional-gate model (Zakay & Block, 1996), post-game time productions of the 10 s interval correlated positively with the level of excitement subjects reported from their last game session. We believe that excitement exerted its influence not primarily through an increase in arousal, which in itself would increase pulse emissions from the internal clock. Rather, excited gamers may have reallocated attentional resources from the processing of time towards the processing of game-related tasks. This reallocation may have caused time losses in the game that were subsequently measured by the timing task.
The finding that time productions were more correct after gaming than before gaming deserves comment. It is tempting to assume that gaming improves timing accuracy. However, this effect may be better explained by the novelty factor at the baseline measurement. In contrast to the post-game measurement, the experimental setting at the baseline is still novel to the subjects and may be regarded as a nontemporal task in itself. We assume that participants drew attentional resources from the timing tasks to the processing of the surroundings and therefore produced time intervals that firstly differed larger from the standard and secondly showed different qualities of time productions (i.e. over- and underproductions). At the post-game measurement, participants were already familiar with the setting and could therefore concentrate better on the timing tasks, resulting in more accurate time productions. Although time perception studies involving distracting nontemporal tasks often show underestimations of time due to a deceleration of subjective time flow, some studies indicate that time judgments also become more inaccurate (both under- and overestimations) because subjects have to judge time on an internal temporal record that is incomplete and unreliable (Brown, 1997, p. 1220). This finding may explain the results of our study in which the novel baseline measurement distracted subjects from timing and led to more inaccurate time productions compared to the familiar post-game measurement. Future studies should use a timing trial before baseline measurement in order to reduce possible biases in time productions due to the effect of novelty on attentional processes.
Admittedly, the reported results need to be interpreted with caution because there was no control group to compare the subjects’ time productions with, which is another weakness of this study. The observed changes in time productions between baseline and post-game measurement cannot exclusively be related to the effect of gaming. These differences in time perception could have also occurred after any other activity or no activity at all. However, in consideration of the experimental setting at a LAN party, the formation of a control group would have meant to keep participants from gaming. This procedure seemed neither feasible nor appropriate for such an event, which is why we refrained from including a control group in the present study. Another methodological concern regards the diversity of games that participants played during the experiment. It is unclear if these games, though predominantly shooters, had different effects on subjects’ time perception, although the results of Wood and Griffiths’ (2007) study indicate similar impacts of shooters and adventure games.
In summary, this study investigated the link between gaming and subsequent time distortion in computer gamers in the natural setting of a LAN party. However, no specific direction of time distortion was found, which may partly be explained by the differing timing tasks employed in this study. Future investigations should aim at examining the effects of gaming on time perception with and without distraction by using timing tasks of same length in a randomized design in order to control for learning effects. They should also control for the potential factors of type of game played, intake of stimulating substances, and time of day when performing timing tasks. In addition to pre- and post-game measurements of time perception, examinations of timing during game sessions could reveal further insight into how gaming influences time perception. Future studies should also include a control group, which could not be realized in the present study, in order to attribute time distortions in gamers more clearly to the effect of computer gaming. Finally, researchers should try to clarify the persistence of time distortions induced by electronic games, which is crucial in determining if gaming changes time perception long enough to have significant effects on safety and performances of gamers in daily life situations.
Acknowledgements
We thank Britta Eglin for her help in data collection.
Appendix
(1) At a LAN (Local Area Network) party people meet in order to play computer games against each other via connecting their computers in a network.
(2) These comprised repeated-measures analyses of covariance of time productions with weekly play time as control and repeated-measures analyses of variance of time production data predicted by tiredness and discontentment at the respective measuring times.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2009 Stefanie Luthman, Thomas Bliesener, Frithjof Staude-Müller
